
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Report Series No. 40A,B,C
WHO/Food Add./67.29
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
ANTIMICROBIALS, ANTIOXIDANTS, EMULSIFIERS,
STABILIZERS, FLOUR-TREATMENT AGENTS, ACIDS AND BASES
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives which met at Rome,
13-20 December, 19651 Geneva, 11-18 October, 19662
1 Ninth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1966 No. 40;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1966, 339
2 Tenth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1967, in press;
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
BENZOIC ACID
Chemical name Benzoic acid; benzenecarboxylic acid; phenyl
carboxylic acid
Empirical formula C7H6O2
Structural formula
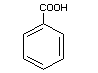 Molecular weight 122.12
Definition Benzoic acid contains not less than 99.5 per
cent. of C7H6O2.
Description Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid. It
may have not more than a faint characteristic
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
POTASSIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Potassium benzoate; potassium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; potassium salt of phenyl
carboxylic, acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2K . 3H2O
Structural formula
Molecular weight 122.12
Definition Benzoic acid contains not less than 99.5 per
cent. of C7H6O2.
Description Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid. It
may have not more than a faint characteristic
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
POTASSIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Potassium benzoate; potassium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; potassium salt of phenyl
carboxylic, acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2K . 3H2O
Structural formula
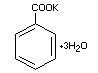 Molecular weight 214.27
Definition Potassium benzoate contains not less than
99.0 per cent. C7H5O2K after drying at 105°
Description White crystalline powder.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
SODIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Sodium benzoate; sodium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; sodium salt of
phenylcarboxylic acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2Na
Structural formula
Molecular weight 214.27
Definition Potassium benzoate contains not less than
99.0 per cent. C7H5O2K after drying at 105°
Description White crystalline powder.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
SODIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Sodium benzoate; sodium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; sodium salt of
phenylcarboxylic acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2Na
Structural formula
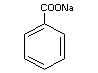 Molecular weight 144.11
Definition Sodium benzoate, after drying for 4 hours at
105°, contains, not less than 99 per cent. of
C7H6O2Na.
Description Sodium benzoate is a white, almost odourless,
crystalline solid.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
The biological data on benzoic acid and sodium benzoate as given
in the Sixth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives (FAO/WHO, 1962) are, relevant for the evaluation of
potassium benzoate. Since the publication of that report the following
relevant additional information has become available.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 3 male and 3 female rats ware fed 0, 2 and 5 per
cent. sodium benzoate in the diet for 28 days. All animals on the 5
per cent. level died during the first 2 weeks showing
hyper-excitability, urinary incontinence and convulsion. Male rats at
the 2 per cent. level showed significant decrease in body-weight. The
food Intake of male and female animals was decreased at the 2 per
cent. level compared with controls (Fanelli & Halliday, 1963).
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that potassium benzoate differs
toxicologically from benzoic acid and sodium benzoate when these are
used as food additives. The estimated acceptable daily intakes of
benzoic acid and its sodium salt for man given in the Sixth Report are
therefore considered applicable to the potassium salt.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
Conditional acceptance 5-10
1 As sum of benzoic acid and potassium and sodium benzoate
(calculated as benzoic acid).
References
Fanelli, G. M. & Halliday, S. L. (1963) Arch. int.
Pharmacodyn.,144, 120
FAO/WHO (1962) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, No. 31;Wld
Hlth Org. techn.Rep. Ser., 228
Molecular weight 144.11
Definition Sodium benzoate, after drying for 4 hours at
105°, contains, not less than 99 per cent. of
C7H6O2Na.
Description Sodium benzoate is a white, almost odourless,
crystalline solid.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
The biological data on benzoic acid and sodium benzoate as given
in the Sixth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives (FAO/WHO, 1962) are, relevant for the evaluation of
potassium benzoate. Since the publication of that report the following
relevant additional information has become available.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 3 male and 3 female rats ware fed 0, 2 and 5 per
cent. sodium benzoate in the diet for 28 days. All animals on the 5
per cent. level died during the first 2 weeks showing
hyper-excitability, urinary incontinence and convulsion. Male rats at
the 2 per cent. level showed significant decrease in body-weight. The
food Intake of male and female animals was decreased at the 2 per
cent. level compared with controls (Fanelli & Halliday, 1963).
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that potassium benzoate differs
toxicologically from benzoic acid and sodium benzoate when these are
used as food additives. The estimated acceptable daily intakes of
benzoic acid and its sodium salt for man given in the Sixth Report are
therefore considered applicable to the potassium salt.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
Conditional acceptance 5-10
1 As sum of benzoic acid and potassium and sodium benzoate
(calculated as benzoic acid).
References
Fanelli, G. M. & Halliday, S. L. (1963) Arch. int.
Pharmacodyn.,144, 120
FAO/WHO (1962) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, No. 31;Wld
Hlth Org. techn.Rep. Ser., 228
See Also:
Toxicological Abbreviations
Benzoic acid (ICSC)
BENZOIC ACID (JECFA Evaluation)
 Molecular weight 122.12
Definition Benzoic acid contains not less than 99.5 per
cent. of C7H6O2.
Description Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid. It
may have not more than a faint characteristic
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
POTASSIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Potassium benzoate; potassium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; potassium salt of phenyl
carboxylic, acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2K . 3H2O
Structural formula
Molecular weight 122.12
Definition Benzoic acid contains not less than 99.5 per
cent. of C7H6O2.
Description Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid. It
may have not more than a faint characteristic
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
POTASSIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Potassium benzoate; potassium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; potassium salt of phenyl
carboxylic, acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2K . 3H2O
Structural formula
 Molecular weight 214.27
Definition Potassium benzoate contains not less than
99.0 per cent. C7H5O2K after drying at 105°
Description White crystalline powder.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
SODIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Sodium benzoate; sodium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; sodium salt of
phenylcarboxylic acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2Na
Structural formula
Molecular weight 214.27
Definition Potassium benzoate contains not less than
99.0 per cent. C7H5O2K after drying at 105°
Description White crystalline powder.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Benzoate)
SODIUM BENZOATE
Chemical Name Sodium benzoate; sodium salt of benzene
carboxylic acid; sodium salt of
phenylcarboxylic acid
Empirical formula C7H5O2Na
Structural formula
 Molecular weight 144.11
Definition Sodium benzoate, after drying for 4 hours at
105°, contains, not less than 99 per cent. of
C7H6O2Na.
Description Sodium benzoate is a white, almost odourless,
crystalline solid.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
The biological data on benzoic acid and sodium benzoate as given
in the Sixth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives (FAO/WHO, 1962) are, relevant for the evaluation of
potassium benzoate. Since the publication of that report the following
relevant additional information has become available.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 3 male and 3 female rats ware fed 0, 2 and 5 per
cent. sodium benzoate in the diet for 28 days. All animals on the 5
per cent. level died during the first 2 weeks showing
hyper-excitability, urinary incontinence and convulsion. Male rats at
the 2 per cent. level showed significant decrease in body-weight. The
food Intake of male and female animals was decreased at the 2 per
cent. level compared with controls (Fanelli & Halliday, 1963).
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that potassium benzoate differs
toxicologically from benzoic acid and sodium benzoate when these are
used as food additives. The estimated acceptable daily intakes of
benzoic acid and its sodium salt for man given in the Sixth Report are
therefore considered applicable to the potassium salt.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
Conditional acceptance 5-10
1 As sum of benzoic acid and potassium and sodium benzoate
(calculated as benzoic acid).
References
Fanelli, G. M. & Halliday, S. L. (1963) Arch. int.
Pharmacodyn.,144, 120
FAO/WHO (1962) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, No. 31;Wld
Hlth Org. techn.Rep. Ser., 228
Molecular weight 144.11
Definition Sodium benzoate, after drying for 4 hours at
105°, contains, not less than 99 per cent. of
C7H6O2Na.
Description Sodium benzoate is a white, almost odourless,
crystalline solid.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
The biological data on benzoic acid and sodium benzoate as given
in the Sixth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives (FAO/WHO, 1962) are, relevant for the evaluation of
potassium benzoate. Since the publication of that report the following
relevant additional information has become available.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 3 male and 3 female rats ware fed 0, 2 and 5 per
cent. sodium benzoate in the diet for 28 days. All animals on the 5
per cent. level died during the first 2 weeks showing
hyper-excitability, urinary incontinence and convulsion. Male rats at
the 2 per cent. level showed significant decrease in body-weight. The
food Intake of male and female animals was decreased at the 2 per
cent. level compared with controls (Fanelli & Halliday, 1963).
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that potassium benzoate differs
toxicologically from benzoic acid and sodium benzoate when these are
used as food additives. The estimated acceptable daily intakes of
benzoic acid and its sodium salt for man given in the Sixth Report are
therefore considered applicable to the potassium salt.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
Conditional acceptance 5-10
1 As sum of benzoic acid and potassium and sodium benzoate
(calculated as benzoic acid).
References
Fanelli, G. M. & Halliday, S. L. (1963) Arch. int.
Pharmacodyn.,144, 120
FAO/WHO (1962) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, No. 31;Wld
Hlth Org. techn.Rep. Ser., 228
