
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Report Series No. 40A,B,C
WHO/Food Add./67.29
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
ANTIMICROBIALS, ANTIOXIDANTS, EMULSIFIERS,
STABILIZERS, FLOUR-TREATMENT AGENTS, ACIDS AND BASES
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives which met at Rome,
13-20 December, 19651 Geneva, 11-18 October, 19662
1 Ninth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1966 No. 40;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1966, 339
2 Tenth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1967, in press;
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
PROPIONIC ACID
Chemical names Propionic acid; Propanoic acid
Empirical formula C3H6O2
Structural formula CH3CH2COOH
Molecular weight 74.08
Definition Propionic, acid is a liquid with a
slightly pungent odour.
Use As mould inhibitor
Biological Data
(See Sodium Propionate)
CALCIUM PROPIONATE
Chemical names Calcium propionate; Calcium propanoate
Empirical formula C6H10O4Ca
Structural formula
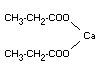 Molecular weight 186.23
Definition Calcium propionate, after drying at
110°, contains not less than 99 per
cent. of C6H10O4Ca.
Description Calcium propionate is a white
crystalline solid with not more than a
faint odour of propionic acid.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Propionate)
SODIUM PROPIONATE
Chemical names Sodium propionate; Sodium propanoate.
Empirical formula C3H5O2Na
Structural formula CH3-CH2-COONa
Molecular weight 96.06
Definition Sodium propionate, after drying at 110°
contains not less than 99 per cent. of
C3H5O2Na
Description Sodium propionate is a white or
colourless, crystalline, hygroscopic
solid with not more than a faint
characteristic odour.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological data
Biological data on propionates are given in the Sixth Report of
the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, FAO Nutrition
Meetings Report Series No. 31; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser.,
228.
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that propionic acid differs
toxicologically from its calcium and sodium salts. The estimated
acceptable daily intakes of these salts for man given in the Sixth
Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives are
therefore considered applicable to the acid.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
Conditional acceptance 10-20
1 As the sum of propionic acid and calcium and sodium propionate
(calculated as propionic acid).
Molecular weight 186.23
Definition Calcium propionate, after drying at
110°, contains not less than 99 per
cent. of C6H10O4Ca.
Description Calcium propionate is a white
crystalline solid with not more than a
faint odour of propionic acid.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Propionate)
SODIUM PROPIONATE
Chemical names Sodium propionate; Sodium propanoate.
Empirical formula C3H5O2Na
Structural formula CH3-CH2-COONa
Molecular weight 96.06
Definition Sodium propionate, after drying at 110°
contains not less than 99 per cent. of
C3H5O2Na
Description Sodium propionate is a white or
colourless, crystalline, hygroscopic
solid with not more than a faint
characteristic odour.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological data
Biological data on propionates are given in the Sixth Report of
the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, FAO Nutrition
Meetings Report Series No. 31; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser.,
228.
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that propionic acid differs
toxicologically from its calcium and sodium salts. The estimated
acceptable daily intakes of these salts for man given in the Sixth
Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives are
therefore considered applicable to the acid.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
Conditional acceptance 10-20
1 As the sum of propionic acid and calcium and sodium propionate
(calculated as propionic acid).
See Also:
Toxicological Abbreviations
Propionic acid (ICSC)
PROPIONIC ACID (JECFA Evaluation)
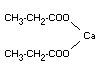 Molecular weight 186.23
Definition Calcium propionate, after drying at
110°, contains not less than 99 per
cent. of C6H10O4Ca.
Description Calcium propionate is a white
crystalline solid with not more than a
faint odour of propionic acid.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Propionate)
SODIUM PROPIONATE
Chemical names Sodium propionate; Sodium propanoate.
Empirical formula C3H5O2Na
Structural formula CH3-CH2-COONa
Molecular weight 96.06
Definition Sodium propionate, after drying at 110°
contains not less than 99 per cent. of
C3H5O2Na
Description Sodium propionate is a white or
colourless, crystalline, hygroscopic
solid with not more than a faint
characteristic odour.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological data
Biological data on propionates are given in the Sixth Report of
the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, FAO Nutrition
Meetings Report Series No. 31; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser.,
228.
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that propionic acid differs
toxicologically from its calcium and sodium salts. The estimated
acceptable daily intakes of these salts for man given in the Sixth
Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives are
therefore considered applicable to the acid.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
Conditional acceptance 10-20
1 As the sum of propionic acid and calcium and sodium propionate
(calculated as propionic acid).
Molecular weight 186.23
Definition Calcium propionate, after drying at
110°, contains not less than 99 per
cent. of C6H10O4Ca.
Description Calcium propionate is a white
crystalline solid with not more than a
faint odour of propionic acid.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological Data
(See Sodium Propionate)
SODIUM PROPIONATE
Chemical names Sodium propionate; Sodium propanoate.
Empirical formula C3H5O2Na
Structural formula CH3-CH2-COONa
Molecular weight 96.06
Definition Sodium propionate, after drying at 110°
contains not less than 99 per cent. of
C3H5O2Na
Description Sodium propionate is a white or
colourless, crystalline, hygroscopic
solid with not more than a faint
characteristic odour.
Use As mould inhibitor.
Biological data
Biological data on propionates are given in the Sixth Report of
the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, FAO Nutrition
Meetings Report Series No. 31; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser.,
228.
Evaluation
There is no reason to believe that propionic acid differs
toxicologically from its calcium and sodium salts. The estimated
acceptable daily intakes of these salts for man given in the Sixth
Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives are
therefore considered applicable to the acid.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
Conditional acceptance 10-20
1 As the sum of propionic acid and calcium and sodium propionate
(calculated as propionic acid).
