
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Report Series No. 40A,B,C
WHO/Food Add./67.29
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
ANTIMICROBIALS, ANTIOXIDANTS, EMULSIFIERS,
STABILIZERS, FLOUR-TREATMENT AGENTS, ACIDS AND BASES
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives which met at Rome,
13-20 December, 19651 Geneva, 11-18 October, 19662
1 Ninth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1966 No. 40;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1966, 339
2 Tenth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1967, in press;
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
BUTYL p-HYDROXYBENZOATE
Synonym Butylparaben
Chemical names n-butyl-p,hydroxybenzoate; butyl ester
of p-hydroxy benzoic acid
Empirical formula C11H14O3
Structural formula
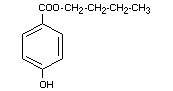 Molecular weight 194.23
Definition Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate contains not
less than 99.0 per cent. C11H14O3.
Description Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate occurs as
colourless micro-crystals or as a white
crystalline powder and may have a slight
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Dogs given 1000 mg/kg body-weight of the butyl ester excreted
only 48.2 per cent. of the dose in the urine within 48 hours.
Metabolic pathways other than hydrolysis and subsequent conjugation
may account for the poor recovery of butyl ester metabolites in
balance experiments (Jones et al., 1956). Dogs fed 1000 mg/kg
body-weight of butyl ester or given 50 mg/kg body-weight i.v. excreted
40.48 per cent. of the ester in the urine as metabolites and 0.5 per
cent. as unchanged ester (Sokol, 1952).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50, References
mg/kg
body-weight
Mouse oral(free acid) 5 000 Sokol, 1952
oral (Na salt) 950 Matthews et al., 1956
i.p. (free acid) 230 appr. Sokol, 1952
i.p.(Na salt) 230 ± 24 Matthews et al., 1956
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female weanling rats were fed
dietary levels of 0, 2 and 8 per cent. of butyl ester for 12 weeks. At
the 8 per cent. level, no males survived the experimental period, the
mortality rate in the females was higher, than that of the controls,
and the rate of weight gain was markedly affected; the animals at this
level also showed depression and decreased motor activity. However,
autopsies with histological examination of animals dying during the
test showed only pneumonia and pulmonary consolidation, without
difference between treated and control animals. Food consumption was
unaffected in all groups and necropsy of all survivors showed no
difference other than the body-weight depression at 8 per cent.
(Matthews et al., 1956).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comment on experimental studies reported
No adequate studies on this substance are available. A toxicological
evaluation is impossible.
REFERENCES
Jones, P. S., Thigpen, D., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson, A. P. (1956)
J. Amer. Pharm. Ass., sci. Ed., 45, 260
Matthews, C., Davidson. J., Bauer, E., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson,
A. P. (1956) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., sci, Ed., 45, 260
Sokol, H. (1952) Drug Stand., 20, 89
Molecular weight 194.23
Definition Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate contains not
less than 99.0 per cent. C11H14O3.
Description Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate occurs as
colourless micro-crystals or as a white
crystalline powder and may have a slight
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Dogs given 1000 mg/kg body-weight of the butyl ester excreted
only 48.2 per cent. of the dose in the urine within 48 hours.
Metabolic pathways other than hydrolysis and subsequent conjugation
may account for the poor recovery of butyl ester metabolites in
balance experiments (Jones et al., 1956). Dogs fed 1000 mg/kg
body-weight of butyl ester or given 50 mg/kg body-weight i.v. excreted
40.48 per cent. of the ester in the urine as metabolites and 0.5 per
cent. as unchanged ester (Sokol, 1952).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50, References
mg/kg
body-weight
Mouse oral(free acid) 5 000 Sokol, 1952
oral (Na salt) 950 Matthews et al., 1956
i.p. (free acid) 230 appr. Sokol, 1952
i.p.(Na salt) 230 ± 24 Matthews et al., 1956
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female weanling rats were fed
dietary levels of 0, 2 and 8 per cent. of butyl ester for 12 weeks. At
the 8 per cent. level, no males survived the experimental period, the
mortality rate in the females was higher, than that of the controls,
and the rate of weight gain was markedly affected; the animals at this
level also showed depression and decreased motor activity. However,
autopsies with histological examination of animals dying during the
test showed only pneumonia and pulmonary consolidation, without
difference between treated and control animals. Food consumption was
unaffected in all groups and necropsy of all survivors showed no
difference other than the body-weight depression at 8 per cent.
(Matthews et al., 1956).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comment on experimental studies reported
No adequate studies on this substance are available. A toxicological
evaluation is impossible.
REFERENCES
Jones, P. S., Thigpen, D., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson, A. P. (1956)
J. Amer. Pharm. Ass., sci. Ed., 45, 260
Matthews, C., Davidson. J., Bauer, E., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson,
A. P. (1956) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., sci, Ed., 45, 260
Sokol, H. (1952) Drug Stand., 20, 89
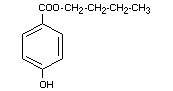 Molecular weight 194.23
Definition Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate contains not
less than 99.0 per cent. C11H14O3.
Description Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate occurs as
colourless micro-crystals or as a white
crystalline powder and may have a slight
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Dogs given 1000 mg/kg body-weight of the butyl ester excreted
only 48.2 per cent. of the dose in the urine within 48 hours.
Metabolic pathways other than hydrolysis and subsequent conjugation
may account for the poor recovery of butyl ester metabolites in
balance experiments (Jones et al., 1956). Dogs fed 1000 mg/kg
body-weight of butyl ester or given 50 mg/kg body-weight i.v. excreted
40.48 per cent. of the ester in the urine as metabolites and 0.5 per
cent. as unchanged ester (Sokol, 1952).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50, References
mg/kg
body-weight
Mouse oral(free acid) 5 000 Sokol, 1952
oral (Na salt) 950 Matthews et al., 1956
i.p. (free acid) 230 appr. Sokol, 1952
i.p.(Na salt) 230 ± 24 Matthews et al., 1956
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female weanling rats were fed
dietary levels of 0, 2 and 8 per cent. of butyl ester for 12 weeks. At
the 8 per cent. level, no males survived the experimental period, the
mortality rate in the females was higher, than that of the controls,
and the rate of weight gain was markedly affected; the animals at this
level also showed depression and decreased motor activity. However,
autopsies with histological examination of animals dying during the
test showed only pneumonia and pulmonary consolidation, without
difference between treated and control animals. Food consumption was
unaffected in all groups and necropsy of all survivors showed no
difference other than the body-weight depression at 8 per cent.
(Matthews et al., 1956).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comment on experimental studies reported
No adequate studies on this substance are available. A toxicological
evaluation is impossible.
REFERENCES
Jones, P. S., Thigpen, D., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson, A. P. (1956)
J. Amer. Pharm. Ass., sci. Ed., 45, 260
Matthews, C., Davidson. J., Bauer, E., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson,
A. P. (1956) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., sci, Ed., 45, 260
Sokol, H. (1952) Drug Stand., 20, 89
Molecular weight 194.23
Definition Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate contains not
less than 99.0 per cent. C11H14O3.
Description Butyl p-hydroxybenzoate occurs as
colourless micro-crystals or as a white
crystalline powder and may have a slight
odour.
Use As an antimicrobial agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Dogs given 1000 mg/kg body-weight of the butyl ester excreted
only 48.2 per cent. of the dose in the urine within 48 hours.
Metabolic pathways other than hydrolysis and subsequent conjugation
may account for the poor recovery of butyl ester metabolites in
balance experiments (Jones et al., 1956). Dogs fed 1000 mg/kg
body-weight of butyl ester or given 50 mg/kg body-weight i.v. excreted
40.48 per cent. of the ester in the urine as metabolites and 0.5 per
cent. as unchanged ester (Sokol, 1952).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50, References
mg/kg
body-weight
Mouse oral(free acid) 5 000 Sokol, 1952
oral (Na salt) 950 Matthews et al., 1956
i.p. (free acid) 230 appr. Sokol, 1952
i.p.(Na salt) 230 ± 24 Matthews et al., 1956
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female weanling rats were fed
dietary levels of 0, 2 and 8 per cent. of butyl ester for 12 weeks. At
the 8 per cent. level, no males survived the experimental period, the
mortality rate in the females was higher, than that of the controls,
and the rate of weight gain was markedly affected; the animals at this
level also showed depression and decreased motor activity. However,
autopsies with histological examination of animals dying during the
test showed only pneumonia and pulmonary consolidation, without
difference between treated and control animals. Food consumption was
unaffected in all groups and necropsy of all survivors showed no
difference other than the body-weight depression at 8 per cent.
(Matthews et al., 1956).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comment on experimental studies reported
No adequate studies on this substance are available. A toxicological
evaluation is impossible.
REFERENCES
Jones, P. S., Thigpen, D., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson, A. P. (1956)
J. Amer. Pharm. Ass., sci. Ed., 45, 260
Matthews, C., Davidson. J., Bauer, E., Morrison, J. L. & Richardson,
A. P. (1956) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., sci, Ed., 45, 260
Sokol, H. (1952) Drug Stand., 20, 89
