
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Report Series No. 40A,B,C
WHO/Food Add./67.29
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
ANTIMICROBIALS, ANTIOXIDANTS, EMULSIFIERS,
STABILIZERS, FLOUR-TREATMENT AGENTS, ACIDS AND BASES
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives which met at Rome,
13-20 December, 19651 Geneva, 11-18 October, 19662
1 Ninth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1966 No. 40;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1966, 339
2 Tenth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1967, in press;
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
METHYLETHYLCELLULOSE
Synonym MEC
Chemical name Methyl ethyl ethers of cellulose
Molecular formula
[C6H7O2(OH) x (OCH3)y(OC2H5)z]n
Structural formula
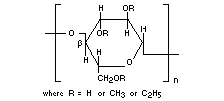 Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 0.77 : 181
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 1.2 : 190
Low polymers (n about 200) : 40 000
High polymers (data to be supplied by
the manufacturer)
Definition Methylethylcellulose contains between
3.5 and 6.5 per cent. of methoxyl groups
and 14.5 and 19.0 per cent. ethoxyl
groups. Alkoxyl content expressed as
methoxyl is 13.2 to 19.6 per cent.
Description Methylethylcellulose is hygroscopic,
slightly yellowish, odourless and
tasteless fibre or powder.
Uses As thickening agent, stabilizer and
foaming agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
A variety of water soluble cellulose derivatives, collectively
known as cellulose ethers, have been used for many years in food
technology. Some members, i.e. methyl cellulose and sodium
carboxymethylcellulose, have been evaluated previously (FAO/WHO,
1964). Methylethylcellulose is similarly regarded as metabolically
inert and is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals
and man.
After feeding a single dose of 0.6 g of methylethylcellulose in
the diet of rats some 90 per cent. of the dose was recovered from the
faeces by the end of the fourth day. Nearly all alkoxyl groups
remained attached to the cellulose chain during passage through the
gut (Gage, 1962).
Acute toxicity
No data are available but from short-term tests It can be
inferred that 3 g daily in the diet had no effect in rats (Imperial
Chemical Industries, 1966).
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 males and 50 female mice ware fed 0, 0.1
and 1 per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was
slightly reduced in both sexes at the 1 per cent. level in the latter
part of the test period. There was no difference between the groups in
survival, tumour incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic
appearance of internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were fed 0, 0.1 and 1
per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was reduced
in males at the 1 per cent. level in the latter part of the test
period. There was no difference between the groups in survival, tumour
incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic appearance of
internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Comments
In view of the metabolic inertness and non-absorbability of this
compound, evaluation is based on data provided for other members in
addition to those referable to methylethylcellulose alone.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance : Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCES
FAO/WHO (1964) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 281
Gage, J. C. (1962) Unpublished report to WHO
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished report to WHO
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives.
Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 0.77 : 181
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 1.2 : 190
Low polymers (n about 200) : 40 000
High polymers (data to be supplied by
the manufacturer)
Definition Methylethylcellulose contains between
3.5 and 6.5 per cent. of methoxyl groups
and 14.5 and 19.0 per cent. ethoxyl
groups. Alkoxyl content expressed as
methoxyl is 13.2 to 19.6 per cent.
Description Methylethylcellulose is hygroscopic,
slightly yellowish, odourless and
tasteless fibre or powder.
Uses As thickening agent, stabilizer and
foaming agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
A variety of water soluble cellulose derivatives, collectively
known as cellulose ethers, have been used for many years in food
technology. Some members, i.e. methyl cellulose and sodium
carboxymethylcellulose, have been evaluated previously (FAO/WHO,
1964). Methylethylcellulose is similarly regarded as metabolically
inert and is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals
and man.
After feeding a single dose of 0.6 g of methylethylcellulose in
the diet of rats some 90 per cent. of the dose was recovered from the
faeces by the end of the fourth day. Nearly all alkoxyl groups
remained attached to the cellulose chain during passage through the
gut (Gage, 1962).
Acute toxicity
No data are available but from short-term tests It can be
inferred that 3 g daily in the diet had no effect in rats (Imperial
Chemical Industries, 1966).
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 males and 50 female mice ware fed 0, 0.1
and 1 per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was
slightly reduced in both sexes at the 1 per cent. level in the latter
part of the test period. There was no difference between the groups in
survival, tumour incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic
appearance of internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were fed 0, 0.1 and 1
per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was reduced
in males at the 1 per cent. level in the latter part of the test
period. There was no difference between the groups in survival, tumour
incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic appearance of
internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Comments
In view of the metabolic inertness and non-absorbability of this
compound, evaluation is based on data provided for other members in
addition to those referable to methylethylcellulose alone.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance : Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCES
FAO/WHO (1964) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 281
Gage, J. C. (1962) Unpublished report to WHO
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished report to WHO
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives.
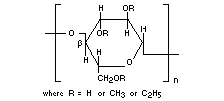 Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 0.77 : 181
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 1.2 : 190
Low polymers (n about 200) : 40 000
High polymers (data to be supplied by
the manufacturer)
Definition Methylethylcellulose contains between
3.5 and 6.5 per cent. of methoxyl groups
and 14.5 and 19.0 per cent. ethoxyl
groups. Alkoxyl content expressed as
methoxyl is 13.2 to 19.6 per cent.
Description Methylethylcellulose is hygroscopic,
slightly yellowish, odourless and
tasteless fibre or powder.
Uses As thickening agent, stabilizer and
foaming agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
A variety of water soluble cellulose derivatives, collectively
known as cellulose ethers, have been used for many years in food
technology. Some members, i.e. methyl cellulose and sodium
carboxymethylcellulose, have been evaluated previously (FAO/WHO,
1964). Methylethylcellulose is similarly regarded as metabolically
inert and is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals
and man.
After feeding a single dose of 0.6 g of methylethylcellulose in
the diet of rats some 90 per cent. of the dose was recovered from the
faeces by the end of the fourth day. Nearly all alkoxyl groups
remained attached to the cellulose chain during passage through the
gut (Gage, 1962).
Acute toxicity
No data are available but from short-term tests It can be
inferred that 3 g daily in the diet had no effect in rats (Imperial
Chemical Industries, 1966).
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 males and 50 female mice ware fed 0, 0.1
and 1 per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was
slightly reduced in both sexes at the 1 per cent. level in the latter
part of the test period. There was no difference between the groups in
survival, tumour incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic
appearance of internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were fed 0, 0.1 and 1
per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was reduced
in males at the 1 per cent. level in the latter part of the test
period. There was no difference between the groups in survival, tumour
incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic appearance of
internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Comments
In view of the metabolic inertness and non-absorbability of this
compound, evaluation is based on data provided for other members in
addition to those referable to methylethylcellulose alone.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance : Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCES
FAO/WHO (1964) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 281
Gage, J. C. (1962) Unpublished report to WHO
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished report to WHO
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives.
Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 0.77 : 181
Structural unit with a total degree of
substitution of 1.2 : 190
Low polymers (n about 200) : 40 000
High polymers (data to be supplied by
the manufacturer)
Definition Methylethylcellulose contains between
3.5 and 6.5 per cent. of methoxyl groups
and 14.5 and 19.0 per cent. ethoxyl
groups. Alkoxyl content expressed as
methoxyl is 13.2 to 19.6 per cent.
Description Methylethylcellulose is hygroscopic,
slightly yellowish, odourless and
tasteless fibre or powder.
Uses As thickening agent, stabilizer and
foaming agent.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
A variety of water soluble cellulose derivatives, collectively
known as cellulose ethers, have been used for many years in food
technology. Some members, i.e. methyl cellulose and sodium
carboxymethylcellulose, have been evaluated previously (FAO/WHO,
1964). Methylethylcellulose is similarly regarded as metabolically
inert and is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals
and man.
After feeding a single dose of 0.6 g of methylethylcellulose in
the diet of rats some 90 per cent. of the dose was recovered from the
faeces by the end of the fourth day. Nearly all alkoxyl groups
remained attached to the cellulose chain during passage through the
gut (Gage, 1962).
Acute toxicity
No data are available but from short-term tests It can be
inferred that 3 g daily in the diet had no effect in rats (Imperial
Chemical Industries, 1966).
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 males and 50 female mice ware fed 0, 0.1
and 1 per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was
slightly reduced in both sexes at the 1 per cent. level in the latter
part of the test period. There was no difference between the groups in
survival, tumour incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic
appearance of internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were fed 0, 0.1 and 1
per cent. of methylethylcellulose for 2 years. Body-weight was reduced
in males at the 1 per cent. level in the latter part of the test
period. There was no difference between the groups in survival, tumour
incidence, blood picture and gross and microscopic appearance of
internal organs (Imperial Chemical Industries, 1966).
Comments
In view of the metabolic inertness and non-absorbability of this
compound, evaluation is based on data provided for other members in
addition to those referable to methylethylcellulose alone.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance : Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCES
FAO/WHO (1964) FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series No. 35;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 281
Gage, J. C. (1962) Unpublished report to WHO
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished report to WHO
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives.
