
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Report Series No. 40A,B,C
WHO/Food Add./67.29
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
ANTIMICROBIALS, ANTIOXIDANTS, EMULSIFIERS,
STABILIZERS, FLOUR-TREATMENT AGENTS, ACIDS AND BASES
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives which met at Rome,
13-20 December, 19651 Geneva, 11-18 October, 19662
1 Ninth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1966 No. 40;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1966, 339
2 Tenth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1967, in press;
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
SODIUM CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE
Synonyms Sodium cellulose glycolate; Na-CMC; CMC
Chemical name Sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of
cellulose.
Chemical formula
[C6H7O2(OH) x (OCH2COONa)y]n
where x = 2.00-2.40
y = 1.00-0.60
x + y = 3.00
Structural formula
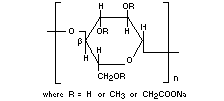 Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Monosubstituted structural unit: 242.16
Macromolecules: from about 21 000
(n about 100)
up to 500 000 (n about 2000)
Definition Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is the
sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of
cellulose, where the substitution degree
ranges from 0.20 to 1.00. After drying
at 110° to constant weight it contains
not less than 99.5 per cent. of sodium
carboxymethylcellulose.
Description Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is a white
or a slightly yellowish, almost
odourless and tasteless hygroscopic
powder, consisting of very fine
particles, fine granules, or fine
fibres.
Uses Thickener, binder, emulsifier,
stabilizer and colloidal suspending
agent in salad dressing, fruit pie
fillings, baked goods, dietetic foods
and many others.
Biological Data
This additive was evaluated by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee
on Food Additives in its Seventh Report (FAO/WHO, 1964). Since its
publication some new experimental work has been carried out on these
compounds. This and other work not included in the Seventh Report is
presented and discussed in this monograph.
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 male and 50 female mice were maintained for
up to 100 weeks on ad lib. diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent.
of sodium carboxymethylcellulose. There was no apparent difference in
mortality and tumour incidence between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were maintained for
up to 2 years on ad lib. diets, containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent. of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose. No difference in mortality and tumour
incidence was apparent between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Comments
The additional information supports the previous evaluation of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Mouse. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance: Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCE
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished reports submitted to
WHO.
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives
Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Monosubstituted structural unit: 242.16
Macromolecules: from about 21 000
(n about 100)
up to 500 000 (n about 2000)
Definition Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is the
sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of
cellulose, where the substitution degree
ranges from 0.20 to 1.00. After drying
at 110° to constant weight it contains
not less than 99.5 per cent. of sodium
carboxymethylcellulose.
Description Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is a white
or a slightly yellowish, almost
odourless and tasteless hygroscopic
powder, consisting of very fine
particles, fine granules, or fine
fibres.
Uses Thickener, binder, emulsifier,
stabilizer and colloidal suspending
agent in salad dressing, fruit pie
fillings, baked goods, dietetic foods
and many others.
Biological Data
This additive was evaluated by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee
on Food Additives in its Seventh Report (FAO/WHO, 1964). Since its
publication some new experimental work has been carried out on these
compounds. This and other work not included in the Seventh Report is
presented and discussed in this monograph.
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 male and 50 female mice were maintained for
up to 100 weeks on ad lib. diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent.
of sodium carboxymethylcellulose. There was no apparent difference in
mortality and tumour incidence between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were maintained for
up to 2 years on ad lib. diets, containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent. of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose. No difference in mortality and tumour
incidence was apparent between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Comments
The additional information supports the previous evaluation of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Mouse. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance: Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCE
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished reports submitted to
WHO.
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives
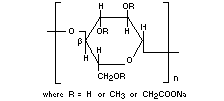 Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Monosubstituted structural unit: 242.16
Macromolecules: from about 21 000
(n about 100)
up to 500 000 (n about 2000)
Definition Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is the
sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of
cellulose, where the substitution degree
ranges from 0.20 to 1.00. After drying
at 110° to constant weight it contains
not less than 99.5 per cent. of sodium
carboxymethylcellulose.
Description Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is a white
or a slightly yellowish, almost
odourless and tasteless hygroscopic
powder, consisting of very fine
particles, fine granules, or fine
fibres.
Uses Thickener, binder, emulsifier,
stabilizer and colloidal suspending
agent in salad dressing, fruit pie
fillings, baked goods, dietetic foods
and many others.
Biological Data
This additive was evaluated by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee
on Food Additives in its Seventh Report (FAO/WHO, 1964). Since its
publication some new experimental work has been carried out on these
compounds. This and other work not included in the Seventh Report is
presented and discussed in this monograph.
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 male and 50 female mice were maintained for
up to 100 weeks on ad lib. diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent.
of sodium carboxymethylcellulose. There was no apparent difference in
mortality and tumour incidence between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were maintained for
up to 2 years on ad lib. diets, containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent. of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose. No difference in mortality and tumour
incidence was apparent between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Comments
The additional information supports the previous evaluation of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Mouse. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance: Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCE
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished reports submitted to
WHO.
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives
Molecular weight Unsubstituted structural unit: 162.14
Monosubstituted structural unit: 242.16
Macromolecules: from about 21 000
(n about 100)
up to 500 000 (n about 2000)
Definition Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is the
sodium salt of a carboxymethyl ether of
cellulose, where the substitution degree
ranges from 0.20 to 1.00. After drying
at 110° to constant weight it contains
not less than 99.5 per cent. of sodium
carboxymethylcellulose.
Description Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is a white
or a slightly yellowish, almost
odourless and tasteless hygroscopic
powder, consisting of very fine
particles, fine granules, or fine
fibres.
Uses Thickener, binder, emulsifier,
stabilizer and colloidal suspending
agent in salad dressing, fruit pie
fillings, baked goods, dietetic foods
and many others.
Biological Data
This additive was evaluated by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee
on Food Additives in its Seventh Report (FAO/WHO, 1964). Since its
publication some new experimental work has been carried out on these
compounds. This and other work not included in the Seventh Report is
presented and discussed in this monograph.
Long-term studies
Mouse. Groups of 50 male and 50 female mice were maintained for
up to 100 weeks on ad lib. diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent.
of sodium carboxymethylcellulose. There was no apparent difference in
mortality and tumour incidence between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Rat. Groups of 50 male and 50 female rats were maintained for
up to 2 years on ad lib. diets, containing 0, 0.1 and 1 per cent. of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose. No difference in mortality and tumour
incidence was apparent between the groups (Imperial Chemical
Industries, 1966).
Comments
The additional information supports the previous evaluation of
sodium carboxymethylcellulose.
Evaluation
Level causing no toxicological effect
Mouse. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Rat. 10 000 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 500 mg/kg
body-weight/day
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-301
Conditional acceptance: Higher levels may be used for
dietetic or calorie control purposes
REFERENCE
Imperial Chemical Industries (1966) Unpublished reports submitted to
WHO.
1 As sum of total cellulose derivatives
