
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Report Series No. 40A,B,C
WHO/Food Add./67.29
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
ANTIMICROBIALS, ANTIOXIDANTS, EMULSIFIERS,
STABILIZERS, FLOUR-TREATMENT AGENTS, ACIDS AND BASES
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives which met at Rome,
13-20 December, 19651 Geneva, 11-18 October, 19662
1 Ninth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1966 No. 40;
Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1966, 339
2 Tenth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives, FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series, 1967, in press;
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
GLUCONO-DELTA-LACTONE (GLUCONIC ACID)
Synonym Deltagluconolactone
Chemical name Glucono-delta-lactone; D-gluconic acid
delta-lactone
Empirical formula C6H10O6
Structural formula
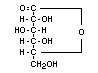 Molecular weight 178.14
Description A fine, white, nearly odourless,
crystalline powder with a sweet taste
and an acid after-taste.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Glucono-delta-lactone, in an aqueous medium, readily forms an
equilibrium mixture of the lactone and gluconic acid. These are
intermediates in the oxidation of glucose through the pentose
phosphate cycle, which, while not the main pathway of glucose
metabolism, is well recognized.
When three men were given 10 g (167 mg/kg) of
glucono-delta-lactone orally as a 10 per cent. solution, the amounts
recovered in the urine in 7 hours represented 7.7-15 per cent. of the
dose. No pathological urine constituents were noted. When 5 g (84
mg/kg) was given orally none was recovered in the urine. The largest
dose given to man was 30 g (500 mg/kg) (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Acute toxicity
Animal Compound Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rabbit Sodium gluconate i.v. 7 630 Gajatto, 1939
The administration for 3-6 days of large oral doses (5-10 g/day)
of gluconic acid to five normal humans did not produce any renal
changes, as by the absence of blood, protein, casts and sugar in the
urine (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed gluconic
acid (as glucono-delta-lactone) for 26 weeks at levels of 0 and 10 000
ppm in the diet without ill effects or demonstrable changes in the
main organs on microscopic examination (Harper & Gaunt, 1962).
Long-term studies
No data are available.
Evaluation
Consideration of glucono-delta-lactone and gluconic acid is based
mainly on the metabolic evidence that these compounds are
intermediates in a normal pathway of glucose metabolism in mammalian
species. There is also considerable experience with the comparatively
low toxicity of gluconate to man and animals.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-15
Conditional acceptance 15-50
REFERENCES
Chenoweth, M. B., Civin, H., Salzman, C., Cohn, M. & Gold, H. (1941)
J. Lab. Clin. Med., 26, 1574
Gajatto, S. (1939) Arch. Farmacol. 68, 1
Harper, K. H. & Gaunt, I. F. (1962) Unpublished report of Huntingdon
Research Centre
Molecular weight 178.14
Description A fine, white, nearly odourless,
crystalline powder with a sweet taste
and an acid after-taste.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Glucono-delta-lactone, in an aqueous medium, readily forms an
equilibrium mixture of the lactone and gluconic acid. These are
intermediates in the oxidation of glucose through the pentose
phosphate cycle, which, while not the main pathway of glucose
metabolism, is well recognized.
When three men were given 10 g (167 mg/kg) of
glucono-delta-lactone orally as a 10 per cent. solution, the amounts
recovered in the urine in 7 hours represented 7.7-15 per cent. of the
dose. No pathological urine constituents were noted. When 5 g (84
mg/kg) was given orally none was recovered in the urine. The largest
dose given to man was 30 g (500 mg/kg) (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Acute toxicity
Animal Compound Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rabbit Sodium gluconate i.v. 7 630 Gajatto, 1939
The administration for 3-6 days of large oral doses (5-10 g/day)
of gluconic acid to five normal humans did not produce any renal
changes, as by the absence of blood, protein, casts and sugar in the
urine (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed gluconic
acid (as glucono-delta-lactone) for 26 weeks at levels of 0 and 10 000
ppm in the diet without ill effects or demonstrable changes in the
main organs on microscopic examination (Harper & Gaunt, 1962).
Long-term studies
No data are available.
Evaluation
Consideration of glucono-delta-lactone and gluconic acid is based
mainly on the metabolic evidence that these compounds are
intermediates in a normal pathway of glucose metabolism in mammalian
species. There is also considerable experience with the comparatively
low toxicity of gluconate to man and animals.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-15
Conditional acceptance 15-50
REFERENCES
Chenoweth, M. B., Civin, H., Salzman, C., Cohn, M. & Gold, H. (1941)
J. Lab. Clin. Med., 26, 1574
Gajatto, S. (1939) Arch. Farmacol. 68, 1
Harper, K. H. & Gaunt, I. F. (1962) Unpublished report of Huntingdon
Research Centre
 Molecular weight 178.14
Description A fine, white, nearly odourless,
crystalline powder with a sweet taste
and an acid after-taste.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Glucono-delta-lactone, in an aqueous medium, readily forms an
equilibrium mixture of the lactone and gluconic acid. These are
intermediates in the oxidation of glucose through the pentose
phosphate cycle, which, while not the main pathway of glucose
metabolism, is well recognized.
When three men were given 10 g (167 mg/kg) of
glucono-delta-lactone orally as a 10 per cent. solution, the amounts
recovered in the urine in 7 hours represented 7.7-15 per cent. of the
dose. No pathological urine constituents were noted. When 5 g (84
mg/kg) was given orally none was recovered in the urine. The largest
dose given to man was 30 g (500 mg/kg) (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Acute toxicity
Animal Compound Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rabbit Sodium gluconate i.v. 7 630 Gajatto, 1939
The administration for 3-6 days of large oral doses (5-10 g/day)
of gluconic acid to five normal humans did not produce any renal
changes, as by the absence of blood, protein, casts and sugar in the
urine (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed gluconic
acid (as glucono-delta-lactone) for 26 weeks at levels of 0 and 10 000
ppm in the diet without ill effects or demonstrable changes in the
main organs on microscopic examination (Harper & Gaunt, 1962).
Long-term studies
No data are available.
Evaluation
Consideration of glucono-delta-lactone and gluconic acid is based
mainly on the metabolic evidence that these compounds are
intermediates in a normal pathway of glucose metabolism in mammalian
species. There is also considerable experience with the comparatively
low toxicity of gluconate to man and animals.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-15
Conditional acceptance 15-50
REFERENCES
Chenoweth, M. B., Civin, H., Salzman, C., Cohn, M. & Gold, H. (1941)
J. Lab. Clin. Med., 26, 1574
Gajatto, S. (1939) Arch. Farmacol. 68, 1
Harper, K. H. & Gaunt, I. F. (1962) Unpublished report of Huntingdon
Research Centre
Molecular weight 178.14
Description A fine, white, nearly odourless,
crystalline powder with a sweet taste
and an acid after-taste.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Glucono-delta-lactone, in an aqueous medium, readily forms an
equilibrium mixture of the lactone and gluconic acid. These are
intermediates in the oxidation of glucose through the pentose
phosphate cycle, which, while not the main pathway of glucose
metabolism, is well recognized.
When three men were given 10 g (167 mg/kg) of
glucono-delta-lactone orally as a 10 per cent. solution, the amounts
recovered in the urine in 7 hours represented 7.7-15 per cent. of the
dose. No pathological urine constituents were noted. When 5 g (84
mg/kg) was given orally none was recovered in the urine. The largest
dose given to man was 30 g (500 mg/kg) (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Acute toxicity
Animal Compound Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rabbit Sodium gluconate i.v. 7 630 Gajatto, 1939
The administration for 3-6 days of large oral doses (5-10 g/day)
of gluconic acid to five normal humans did not produce any renal
changes, as by the absence of blood, protein, casts and sugar in the
urine (Chenoweth et al., 1941).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed gluconic
acid (as glucono-delta-lactone) for 26 weeks at levels of 0 and 10 000
ppm in the diet without ill effects or demonstrable changes in the
main organs on microscopic examination (Harper & Gaunt, 1962).
Long-term studies
No data are available.
Evaluation
Consideration of glucono-delta-lactone and gluconic acid is based
mainly on the metabolic evidence that these compounds are
intermediates in a normal pathway of glucose metabolism in mammalian
species. There is also considerable experience with the comparatively
low toxicity of gluconate to man and animals.
Estimate of acceptable daily intakes for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-15
Conditional acceptance 15-50
REFERENCES
Chenoweth, M. B., Civin, H., Salzman, C., Cohn, M. & Gold, H. (1941)
J. Lab. Clin. Med., 26, 1574
Gajatto, S. (1939) Arch. Farmacol. 68, 1
Harper, K. H. & Gaunt, I. F. (1962) Unpublished report of Huntingdon
Research Centre
