
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Resort Series No. 44A
WHO/Food Add./68.33
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES AND
NON-NUTRITIVE SWEETENING AGENTS
Geneva, 21-28 August 1967
The Eleventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives is published as FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series,
1967, No. 44; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1968, 383. This
Report contains general considerations, including the principles
adopted for the evaluation, and a summary of the results of the
evaluations of a number of food additives. Additional information,
such as biological data and a toxicological evaluation, considered at
that meeting, is to be found in this document.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
BENZYL ACETATE
Chemical name Benzyl ethanoate
Empirical formula C9H10O2
Structural formula
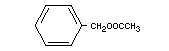 Molecular weight 150.18
Definition Benzyl acetate contains not less than 97 per
cent. C9H10O2.
Description A colourless liquid having a characteristic
floral odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This compound is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract,
through the lungs and through the intact skin. It is hydrolyzed in man
to benzyl alcohol and acetate; the benzyl radical is oxidized to
benzoic acid and excreted as hippuric acid while the acetate fraction
follows normal metabolic pathways (Snapper et al., 1925).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 2490-3690 Jenner et al., 1967;
von Oettingen, 1960
Rabbit oral 2640 von Oettingen, 1960
Oral or parenteral administration to rabbits or dogs caused CNS
paralysis and diuresis.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed a mixture of
aromatic esters, including 15.8 mg/kg body-weight/day of benzyl
acetate, for 12 weeks. No adverse effects were noted (Oser, 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
Although the animal data are confined to acute and short-term
studies, the known metabolic fate of this ester provides a basis for
evaluation. The acceptable daily intake is expressed in terms of the
final metabolite, benzoic acid.
EVALUATION
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
REFERENCES
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. 1964 Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
von Oettingen, W. F. (1960) A.M.A. Arch. Ind. Health, 21, 28
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Snapper, I., Grunbaum, A. & Sturkop, S. (1925) Biochem. Z., 155,
163
1 Calculated as total benzoic, acid from all food additive sources.
Molecular weight 150.18
Definition Benzyl acetate contains not less than 97 per
cent. C9H10O2.
Description A colourless liquid having a characteristic
floral odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This compound is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract,
through the lungs and through the intact skin. It is hydrolyzed in man
to benzyl alcohol and acetate; the benzyl radical is oxidized to
benzoic acid and excreted as hippuric acid while the acetate fraction
follows normal metabolic pathways (Snapper et al., 1925).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 2490-3690 Jenner et al., 1967;
von Oettingen, 1960
Rabbit oral 2640 von Oettingen, 1960
Oral or parenteral administration to rabbits or dogs caused CNS
paralysis and diuresis.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed a mixture of
aromatic esters, including 15.8 mg/kg body-weight/day of benzyl
acetate, for 12 weeks. No adverse effects were noted (Oser, 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
Although the animal data are confined to acute and short-term
studies, the known metabolic fate of this ester provides a basis for
evaluation. The acceptable daily intake is expressed in terms of the
final metabolite, benzoic acid.
EVALUATION
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
REFERENCES
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. 1964 Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
von Oettingen, W. F. (1960) A.M.A. Arch. Ind. Health, 21, 28
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Snapper, I., Grunbaum, A. & Sturkop, S. (1925) Biochem. Z., 155,
163
1 Calculated as total benzoic, acid from all food additive sources.
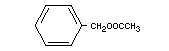 Molecular weight 150.18
Definition Benzyl acetate contains not less than 97 per
cent. C9H10O2.
Description A colourless liquid having a characteristic
floral odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This compound is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract,
through the lungs and through the intact skin. It is hydrolyzed in man
to benzyl alcohol and acetate; the benzyl radical is oxidized to
benzoic acid and excreted as hippuric acid while the acetate fraction
follows normal metabolic pathways (Snapper et al., 1925).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 2490-3690 Jenner et al., 1967;
von Oettingen, 1960
Rabbit oral 2640 von Oettingen, 1960
Oral or parenteral administration to rabbits or dogs caused CNS
paralysis and diuresis.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed a mixture of
aromatic esters, including 15.8 mg/kg body-weight/day of benzyl
acetate, for 12 weeks. No adverse effects were noted (Oser, 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
Although the animal data are confined to acute and short-term
studies, the known metabolic fate of this ester provides a basis for
evaluation. The acceptable daily intake is expressed in terms of the
final metabolite, benzoic acid.
EVALUATION
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
REFERENCES
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. 1964 Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
von Oettingen, W. F. (1960) A.M.A. Arch. Ind. Health, 21, 28
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Snapper, I., Grunbaum, A. & Sturkop, S. (1925) Biochem. Z., 155,
163
1 Calculated as total benzoic, acid from all food additive sources.
Molecular weight 150.18
Definition Benzyl acetate contains not less than 97 per
cent. C9H10O2.
Description A colourless liquid having a characteristic
floral odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This compound is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract,
through the lungs and through the intact skin. It is hydrolyzed in man
to benzyl alcohol and acetate; the benzyl radical is oxidized to
benzoic acid and excreted as hippuric acid while the acetate fraction
follows normal metabolic pathways (Snapper et al., 1925).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 2490-3690 Jenner et al., 1967;
von Oettingen, 1960
Rabbit oral 2640 von Oettingen, 1960
Oral or parenteral administration to rabbits or dogs caused CNS
paralysis and diuresis.
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed a mixture of
aromatic esters, including 15.8 mg/kg body-weight/day of benzyl
acetate, for 12 weeks. No adverse effects were noted (Oser, 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
Although the animal data are confined to acute and short-term
studies, the known metabolic fate of this ester provides a basis for
evaluation. The acceptable daily intake is expressed in terms of the
final metabolite, benzoic acid.
EVALUATION
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight1
Unconditional acceptance 0-5
REFERENCES
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. 1964 Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
von Oettingen, W. F. (1960) A.M.A. Arch. Ind. Health, 21, 28
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Snapper, I., Grunbaum, A. & Sturkop, S. (1925) Biochem. Z., 155,
163
1 Calculated as total benzoic, acid from all food additive sources.
