
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Resort Series No. 44A
WHO/Food Add./68.33
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES AND
NON-NUTRITIVE SWEETENING AGENTS
Geneva, 21-28 August 1967
The Eleventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives is published as FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series,
1967, No. 44; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1968, 383. This
Report contains general considerations, including the principles
adopted for the evaluation, and a summary of the results of the
evaluations of a number of food additives. Additional information,
such as biological data and a toxicological evaluation, considered at
that meeting, is to be found in this document.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
EUGENOL
Chemical names 4-Allyl-2-methoxyphenol;
4-Allyl-guaiacol
Empirical formula C10H12O2
Structural formula
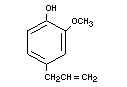 Molecular weight 164.21
Definition Eugenol contains not less than 98 per
cent., by volume, of phenols as
C10H12O2
Description Eugenol is the main constituent of
carnation, cinnamon leaf and clove oils.
It is obtained from clove oil and other
sources. It is a colourless to pale
yellow liquid, having a strongly
aromatic odour of clove, and a pungent,
spicy taste. It darkens and thickens
upon exposure to air.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rats and guinea-pigs given 150 mg/animal orally showed inhibition
of glucosiduronic acid conjugation over 24 hours which was complete in
stomach, almost complete in duodenum and practically absent in liver.
Stomach epithelium was desquamated and punctate haemorrhages were seen
in the pylorus and glandular region. Incubation of slices of stomach,
duodenum or liver with 0.025 eugenol inhibited 75 per cent. of
glucosiduronic acid conjugation, indicating interference with
mucopoly-saccharide formation in tissues with possible gastric ulcer
formation (Hartiala et al., 1966).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse oral 3000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat oral 1930-2680 Sober et al., 1950;
Jenner et al., 1964
s.c. 5000(LD) Binet, 1896
i.p. 800-1000(LD) Binet, 1896
Guinea-pig oral 2130 Jenner et al., 1964
Three male and three female rats given 900 mg/kg intragastrically
daily for 4 days showed gross liver damage (Taylor et al., 1964).
Single intragastric doses of about 500 mg/kg body-weight in the
dog resulted in 2 of the 4 animals to which given. 250 mg/kg body-
weight resulted only in some emesis, and 200 mg/kg was without effect
(Lauber & Hollander, 1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. Twenty male rats were given increasing doses from 1400 to
4000 mg/kg body-weight for 34 days. There was considerable mortality,
slight liver enlargement and adrenal enlargnnent. Histology showed
enlarged liver cells. The forestomach showed severe hyperplasia and
hyperkeratosis of the stratified squamous epithelium with focal
ulceration et al., 1965). In a 12-week feeding study on 15 males and
15 females no adverse effect was noted at 79.3 mg/kg body weight per
day (Oser, 1967). In another study, groups of 10 males and 10 females
were fed diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1.0 per cent. eugenol for 19
weeks without any adverse effect on growth rate, haematology, organ
weights and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is only scanty information available on the metabolism.
High doses are hepatoxic to dogs and rats but the short-term studies
permit evaluation. Metabolic studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 1 per cent. (= 10 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 500
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptble daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-5
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic studies and long-term studies,
including emphasis on the effects on the gastric epithelium and the
liver.
REFERENCES
Binet, P. (1896) Rev.méd. Suisse rom., 15, 449
Hagan, E. C. Jenner, P. M., Jones, W. I., Fitzhugh, O. G., Long, E.
L., Brouwer, J. G. & Webb, W. K. (1965) Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol.,
7, 18
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I, Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Hartiala, K. J. W., Pulkinien, M. & Ball, P. (1966) Nature (Lond.),
210, 739
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L, & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Lauber, F. U. & Hollander, F. (1950) Gastroenterology, 15, 481
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Sober, H. A., Hollander, F. & Sober, E. K. (1950) Proc. Soc. exp.
Biol. Med., 73, 148
Taylor, J. M., Jenner, P. M. & Jones, W. I. (1964) Toxicol. appl.
Pharmacol., 6, 378
Molecular weight 164.21
Definition Eugenol contains not less than 98 per
cent., by volume, of phenols as
C10H12O2
Description Eugenol is the main constituent of
carnation, cinnamon leaf and clove oils.
It is obtained from clove oil and other
sources. It is a colourless to pale
yellow liquid, having a strongly
aromatic odour of clove, and a pungent,
spicy taste. It darkens and thickens
upon exposure to air.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rats and guinea-pigs given 150 mg/animal orally showed inhibition
of glucosiduronic acid conjugation over 24 hours which was complete in
stomach, almost complete in duodenum and practically absent in liver.
Stomach epithelium was desquamated and punctate haemorrhages were seen
in the pylorus and glandular region. Incubation of slices of stomach,
duodenum or liver with 0.025 eugenol inhibited 75 per cent. of
glucosiduronic acid conjugation, indicating interference with
mucopoly-saccharide formation in tissues with possible gastric ulcer
formation (Hartiala et al., 1966).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse oral 3000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat oral 1930-2680 Sober et al., 1950;
Jenner et al., 1964
s.c. 5000(LD) Binet, 1896
i.p. 800-1000(LD) Binet, 1896
Guinea-pig oral 2130 Jenner et al., 1964
Three male and three female rats given 900 mg/kg intragastrically
daily for 4 days showed gross liver damage (Taylor et al., 1964).
Single intragastric doses of about 500 mg/kg body-weight in the
dog resulted in 2 of the 4 animals to which given. 250 mg/kg body-
weight resulted only in some emesis, and 200 mg/kg was without effect
(Lauber & Hollander, 1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. Twenty male rats were given increasing doses from 1400 to
4000 mg/kg body-weight for 34 days. There was considerable mortality,
slight liver enlargement and adrenal enlargnnent. Histology showed
enlarged liver cells. The forestomach showed severe hyperplasia and
hyperkeratosis of the stratified squamous epithelium with focal
ulceration et al., 1965). In a 12-week feeding study on 15 males and
15 females no adverse effect was noted at 79.3 mg/kg body weight per
day (Oser, 1967). In another study, groups of 10 males and 10 females
were fed diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1.0 per cent. eugenol for 19
weeks without any adverse effect on growth rate, haematology, organ
weights and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is only scanty information available on the metabolism.
High doses are hepatoxic to dogs and rats but the short-term studies
permit evaluation. Metabolic studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 1 per cent. (= 10 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 500
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptble daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-5
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic studies and long-term studies,
including emphasis on the effects on the gastric epithelium and the
liver.
REFERENCES
Binet, P. (1896) Rev.méd. Suisse rom., 15, 449
Hagan, E. C. Jenner, P. M., Jones, W. I., Fitzhugh, O. G., Long, E.
L., Brouwer, J. G. & Webb, W. K. (1965) Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol.,
7, 18
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I, Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Hartiala, K. J. W., Pulkinien, M. & Ball, P. (1966) Nature (Lond.),
210, 739
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L, & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Lauber, F. U. & Hollander, F. (1950) Gastroenterology, 15, 481
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Sober, H. A., Hollander, F. & Sober, E. K. (1950) Proc. Soc. exp.
Biol. Med., 73, 148
Taylor, J. M., Jenner, P. M. & Jones, W. I. (1964) Toxicol. appl.
Pharmacol., 6, 378
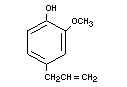 Molecular weight 164.21
Definition Eugenol contains not less than 98 per
cent., by volume, of phenols as
C10H12O2
Description Eugenol is the main constituent of
carnation, cinnamon leaf and clove oils.
It is obtained from clove oil and other
sources. It is a colourless to pale
yellow liquid, having a strongly
aromatic odour of clove, and a pungent,
spicy taste. It darkens and thickens
upon exposure to air.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rats and guinea-pigs given 150 mg/animal orally showed inhibition
of glucosiduronic acid conjugation over 24 hours which was complete in
stomach, almost complete in duodenum and practically absent in liver.
Stomach epithelium was desquamated and punctate haemorrhages were seen
in the pylorus and glandular region. Incubation of slices of stomach,
duodenum or liver with 0.025 eugenol inhibited 75 per cent. of
glucosiduronic acid conjugation, indicating interference with
mucopoly-saccharide formation in tissues with possible gastric ulcer
formation (Hartiala et al., 1966).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse oral 3000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat oral 1930-2680 Sober et al., 1950;
Jenner et al., 1964
s.c. 5000(LD) Binet, 1896
i.p. 800-1000(LD) Binet, 1896
Guinea-pig oral 2130 Jenner et al., 1964
Three male and three female rats given 900 mg/kg intragastrically
daily for 4 days showed gross liver damage (Taylor et al., 1964).
Single intragastric doses of about 500 mg/kg body-weight in the
dog resulted in 2 of the 4 animals to which given. 250 mg/kg body-
weight resulted only in some emesis, and 200 mg/kg was without effect
(Lauber & Hollander, 1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. Twenty male rats were given increasing doses from 1400 to
4000 mg/kg body-weight for 34 days. There was considerable mortality,
slight liver enlargement and adrenal enlargnnent. Histology showed
enlarged liver cells. The forestomach showed severe hyperplasia and
hyperkeratosis of the stratified squamous epithelium with focal
ulceration et al., 1965). In a 12-week feeding study on 15 males and
15 females no adverse effect was noted at 79.3 mg/kg body weight per
day (Oser, 1967). In another study, groups of 10 males and 10 females
were fed diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1.0 per cent. eugenol for 19
weeks without any adverse effect on growth rate, haematology, organ
weights and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is only scanty information available on the metabolism.
High doses are hepatoxic to dogs and rats but the short-term studies
permit evaluation. Metabolic studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 1 per cent. (= 10 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 500
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptble daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-5
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic studies and long-term studies,
including emphasis on the effects on the gastric epithelium and the
liver.
REFERENCES
Binet, P. (1896) Rev.méd. Suisse rom., 15, 449
Hagan, E. C. Jenner, P. M., Jones, W. I., Fitzhugh, O. G., Long, E.
L., Brouwer, J. G. & Webb, W. K. (1965) Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol.,
7, 18
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I, Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Hartiala, K. J. W., Pulkinien, M. & Ball, P. (1966) Nature (Lond.),
210, 739
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L, & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Lauber, F. U. & Hollander, F. (1950) Gastroenterology, 15, 481
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Sober, H. A., Hollander, F. & Sober, E. K. (1950) Proc. Soc. exp.
Biol. Med., 73, 148
Taylor, J. M., Jenner, P. M. & Jones, W. I. (1964) Toxicol. appl.
Pharmacol., 6, 378
Molecular weight 164.21
Definition Eugenol contains not less than 98 per
cent., by volume, of phenols as
C10H12O2
Description Eugenol is the main constituent of
carnation, cinnamon leaf and clove oils.
It is obtained from clove oil and other
sources. It is a colourless to pale
yellow liquid, having a strongly
aromatic odour of clove, and a pungent,
spicy taste. It darkens and thickens
upon exposure to air.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rats and guinea-pigs given 150 mg/animal orally showed inhibition
of glucosiduronic acid conjugation over 24 hours which was complete in
stomach, almost complete in duodenum and practically absent in liver.
Stomach epithelium was desquamated and punctate haemorrhages were seen
in the pylorus and glandular region. Incubation of slices of stomach,
duodenum or liver with 0.025 eugenol inhibited 75 per cent. of
glucosiduronic acid conjugation, indicating interference with
mucopoly-saccharide formation in tissues with possible gastric ulcer
formation (Hartiala et al., 1966).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse oral 3000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat oral 1930-2680 Sober et al., 1950;
Jenner et al., 1964
s.c. 5000(LD) Binet, 1896
i.p. 800-1000(LD) Binet, 1896
Guinea-pig oral 2130 Jenner et al., 1964
Three male and three female rats given 900 mg/kg intragastrically
daily for 4 days showed gross liver damage (Taylor et al., 1964).
Single intragastric doses of about 500 mg/kg body-weight in the
dog resulted in 2 of the 4 animals to which given. 250 mg/kg body-
weight resulted only in some emesis, and 200 mg/kg was without effect
(Lauber & Hollander, 1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. Twenty male rats were given increasing doses from 1400 to
4000 mg/kg body-weight for 34 days. There was considerable mortality,
slight liver enlargement and adrenal enlargnnent. Histology showed
enlarged liver cells. The forestomach showed severe hyperplasia and
hyperkeratosis of the stratified squamous epithelium with focal
ulceration et al., 1965). In a 12-week feeding study on 15 males and
15 females no adverse effect was noted at 79.3 mg/kg body weight per
day (Oser, 1967). In another study, groups of 10 males and 10 females
were fed diets containing 0, 0.1 and 1.0 per cent. eugenol for 19
weeks without any adverse effect on growth rate, haematology, organ
weights and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is only scanty information available on the metabolism.
High doses are hepatoxic to dogs and rats but the short-term studies
permit evaluation. Metabolic studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 1 per cent. (= 10 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 500
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptble daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-5
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic studies and long-term studies,
including emphasis on the effects on the gastric epithelium and the
liver.
REFERENCES
Binet, P. (1896) Rev.méd. Suisse rom., 15, 449
Hagan, E. C. Jenner, P. M., Jones, W. I., Fitzhugh, O. G., Long, E.
L., Brouwer, J. G. & Webb, W. K. (1965) Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol.,
7, 18
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I, Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Hartiala, K. J. W., Pulkinien, M. & Ball, P. (1966) Nature (Lond.),
210, 739
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L, & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Lauber, F. U. & Hollander, F. (1950) Gastroenterology, 15, 481
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Sober, H. A., Hollander, F. & Sober, E. K. (1950) Proc. Soc. exp.
Biol. Med., 73, 148
Taylor, J. M., Jenner, P. M. & Jones, W. I. (1964) Toxicol. appl.
Pharmacol., 6, 378
