
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Resort Series No. 44A
WHO/Food Add./68.33
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES AND
NON-NUTRITIVE SWEETENING AGENTS
Geneva, 21-28 August 1967
The Eleventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives is published as FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series,
1967, No. 44; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1968, 383. This
Report contains general considerations, including the principles
adopted for the evaluation, and a summary of the results of the
evaluations of a number of food additives. Additional information,
such as biological data and a toxicological evaluation, considered at
that meeting, is to be found in this document.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
alpha-IONONE
Chemical name alpha-Ionone
Empirical formula C13H20O
Structural formula
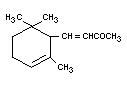 Molecular weight 192.30
Definition alpha-Ionone contains not less than 95 per
cent. of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A colourless to pale yellow liquid having a
woody-violet odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ketone is metabolized in the dog to 5-hydroxy-alpha-ionone
(Prelog et al., 1951).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day study on groups of 15 males and 15 females
given either 0 or 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day, no adverse effects were
observed (Oser et al.,1965). Another study on groups of 10 males and
10 females used a mixture of 65 per cent. alpha- and 40 per cent.
ß-ionone at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet for 17 weeks. A
dose-dependent moderate swelling of liver parenchyma was noted which
occurred to a very slight degree at the lowest level. No other adverse
effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is some biochemical information available and this together
with the short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic
studies and long-term studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 230 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 327
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Prelog, V., Wursch, J. & Meier, H. L. (1951) Helv. Chim. Acta, 34,
859
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Schobesch, D., Manu, V., Panaitescu, E. L Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
Molecular weight 192.30
Definition alpha-Ionone contains not less than 95 per
cent. of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A colourless to pale yellow liquid having a
woody-violet odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ketone is metabolized in the dog to 5-hydroxy-alpha-ionone
(Prelog et al., 1951).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day study on groups of 15 males and 15 females
given either 0 or 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day, no adverse effects were
observed (Oser et al.,1965). Another study on groups of 10 males and
10 females used a mixture of 65 per cent. alpha- and 40 per cent.
ß-ionone at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet for 17 weeks. A
dose-dependent moderate swelling of liver parenchyma was noted which
occurred to a very slight degree at the lowest level. No other adverse
effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is some biochemical information available and this together
with the short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic
studies and long-term studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 230 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 327
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Prelog, V., Wursch, J. & Meier, H. L. (1951) Helv. Chim. Acta, 34,
859
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Schobesch, D., Manu, V., Panaitescu, E. L Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
 Molecular weight 192.30
Definition alpha-Ionone contains not less than 95 per
cent. of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A colourless to pale yellow liquid having a
woody-violet odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ketone is metabolized in the dog to 5-hydroxy-alpha-ionone
(Prelog et al., 1951).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day study on groups of 15 males and 15 females
given either 0 or 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day, no adverse effects were
observed (Oser et al.,1965). Another study on groups of 10 males and
10 females used a mixture of 65 per cent. alpha- and 40 per cent.
ß-ionone at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet for 17 weeks. A
dose-dependent moderate swelling of liver parenchyma was noted which
occurred to a very slight degree at the lowest level. No other adverse
effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is some biochemical information available and this together
with the short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic
studies and long-term studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 230 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 327
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Prelog, V., Wursch, J. & Meier, H. L. (1951) Helv. Chim. Acta, 34,
859
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Schobesch, D., Manu, V., Panaitescu, E. L Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
Molecular weight 192.30
Definition alpha-Ionone contains not less than 95 per
cent. of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A colourless to pale yellow liquid having a
woody-violet odour.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ketone is metabolized in the dog to 5-hydroxy-alpha-ionone
(Prelog et al., 1951).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day study on groups of 15 males and 15 females
given either 0 or 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day, no adverse effects were
observed (Oser et al.,1965). Another study on groups of 10 males and
10 females used a mixture of 65 per cent. alpha- and 40 per cent.
ß-ionone at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet for 17 weeks. A
dose-dependent moderate swelling of liver parenchyma was noted which
occurred to a very slight degree at the lowest level. No other adverse
effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
There is some biochemical information available and this together
with the short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic
studies and long-term studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 11.5 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 230 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 327
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Prelog, V., Wursch, J. & Meier, H. L. (1951) Helv. Chim. Acta, 34,
859
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Schobesch, D., Manu, V., Panaitescu, E. L Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
