
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Resort Series No. 44A
WHO/Food Add./68.33
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES AND
NON-NUTRITIVE SWEETENING AGENTS
Geneva, 21-28 August 1967
The Eleventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives is published as FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series,
1967, No. 44; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1968, 383. This
Report contains general considerations, including the principles
adopted for the evaluation, and a summary of the results of the
evaluations of a number of food additives. Additional information,
such as biological data and a toxicological evaluation, considered at
that meeting, is to be found in this document.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
▀-IONONE
Chemical name ▀-Ionone
Empirical formula C13H20O
Structural formula
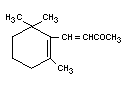 Molecular weight 192.30
Definition ▀-Ionone contains not less than 95 per cent.
of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A slightly yellow liquid having a more
fruity and woody odour than alpha-ionone.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rabbits were fed 5 g of ▀-ionone per animal daily for 2-3 weeks.
In addition to 4 per cent. benzoic acid and 1.4 per cent. of
m-hydroxybenzoic acid, 42 per cent. of the total dose was recovered
as mostly neutral metabolites from the urine. 35-40 per cent. of the
neutral metabolites, i.e. ▀-ionol, dihydro-▀-ional, hydroxy-▀-ionol,
dihydroxy-▀-ionol and hydroxy-▀-ionone, retained the ionone
trimethylcyclohexene ring (Bielig & Hayasida, 1940). More recent
studies identified 4-oxo-▀-ionone, 4-hydroxy-▀-ionol and probably
4-oxo-▀-ionol (Prelog & Meier, 1950).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day feeding study on 15 males and 15 females, no
adverse effects were reported at a level of 228 ppm in the diet (Oser,
1967). In another 90-day study, groups of 15 males and 15 females were
fed 0 or 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day without adverse effect (Oser et
al., 1965). A 17-week study on groups of 10 male and 10 female rats
used a mixture of 60 per cent. alpha-ionone and 40 per cent. ▀-ionone
at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet. A dose-related swelling
of the liver parenchyma was noted, but was only very slight at the
lowest level. No other adverse effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
The biochemical information available together with the
short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic and long-term
studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 246 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Bielig, H.-J. & Hayasida, A. (1940) Z. physiol. Chem., 266, 99
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A., Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Prelog, V. & Meier, H. L. (1950) Helv. chim. Acta, 33, 1276
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Sch÷besch, O., Marin, V., Panaitescu, E. & Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
Molecular weight 192.30
Definition ▀-Ionone contains not less than 95 per cent.
of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A slightly yellow liquid having a more
fruity and woody odour than alpha-ionone.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rabbits were fed 5 g of ▀-ionone per animal daily for 2-3 weeks.
In addition to 4 per cent. benzoic acid and 1.4 per cent. of
m-hydroxybenzoic acid, 42 per cent. of the total dose was recovered
as mostly neutral metabolites from the urine. 35-40 per cent. of the
neutral metabolites, i.e. ▀-ionol, dihydro-▀-ional, hydroxy-▀-ionol,
dihydroxy-▀-ionol and hydroxy-▀-ionone, retained the ionone
trimethylcyclohexene ring (Bielig & Hayasida, 1940). More recent
studies identified 4-oxo-▀-ionone, 4-hydroxy-▀-ionol and probably
4-oxo-▀-ionol (Prelog & Meier, 1950).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day feeding study on 15 males and 15 females, no
adverse effects were reported at a level of 228 ppm in the diet (Oser,
1967). In another 90-day study, groups of 15 males and 15 females were
fed 0 or 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day without adverse effect (Oser et
al., 1965). A 17-week study on groups of 10 male and 10 female rats
used a mixture of 60 per cent. alpha-ionone and 40 per cent. ▀-ionone
at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet. A dose-related swelling
of the liver parenchyma was noted, but was only very slight at the
lowest level. No other adverse effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
The biochemical information available together with the
short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic and long-term
studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 246 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Bielig, H.-J. & Hayasida, A. (1940) Z. physiol. Chem., 266, 99
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A., Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Prelog, V. & Meier, H. L. (1950) Helv. chim. Acta, 33, 1276
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Sch÷besch, O., Marin, V., Panaitescu, E. & Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
 Molecular weight 192.30
Definition ▀-Ionone contains not less than 95 per cent.
of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A slightly yellow liquid having a more
fruity and woody odour than alpha-ionone.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rabbits were fed 5 g of ▀-ionone per animal daily for 2-3 weeks.
In addition to 4 per cent. benzoic acid and 1.4 per cent. of
m-hydroxybenzoic acid, 42 per cent. of the total dose was recovered
as mostly neutral metabolites from the urine. 35-40 per cent. of the
neutral metabolites, i.e. ▀-ionol, dihydro-▀-ional, hydroxy-▀-ionol,
dihydroxy-▀-ionol and hydroxy-▀-ionone, retained the ionone
trimethylcyclohexene ring (Bielig & Hayasida, 1940). More recent
studies identified 4-oxo-▀-ionone, 4-hydroxy-▀-ionol and probably
4-oxo-▀-ionol (Prelog & Meier, 1950).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day feeding study on 15 males and 15 females, no
adverse effects were reported at a level of 228 ppm in the diet (Oser,
1967). In another 90-day study, groups of 15 males and 15 females were
fed 0 or 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day without adverse effect (Oser et
al., 1965). A 17-week study on groups of 10 male and 10 female rats
used a mixture of 60 per cent. alpha-ionone and 40 per cent. ▀-ionone
at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet. A dose-related swelling
of the liver parenchyma was noted, but was only very slight at the
lowest level. No other adverse effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
The biochemical information available together with the
short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic and long-term
studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 246 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Bielig, H.-J. & Hayasida, A. (1940) Z. physiol. Chem., 266, 99
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A., Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Prelog, V. & Meier, H. L. (1950) Helv. chim. Acta, 33, 1276
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Sch÷besch, O., Marin, V., Panaitescu, E. & Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
Molecular weight 192.30
Definition ▀-Ionone contains not less than 95 per cent.
of ketones expressed as C13H20O.
Description A slightly yellow liquid having a more
fruity and woody odour than alpha-ionone.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
Rabbits were fed 5 g of ▀-ionone per animal daily for 2-3 weeks.
In addition to 4 per cent. benzoic acid and 1.4 per cent. of
m-hydroxybenzoic acid, 42 per cent. of the total dose was recovered
as mostly neutral metabolites from the urine. 35-40 per cent. of the
neutral metabolites, i.e. ▀-ionol, dihydro-▀-ional, hydroxy-▀-ionol,
dihydroxy-▀-ionol and hydroxy-▀-ionone, retained the ionone
trimethylcyclohexene ring (Bielig & Hayasida, 1940). More recent
studies identified 4-oxo-▀-ionone, 4-hydroxy-▀-ionol and probably
4-oxo-▀-ionol (Prelog & Meier, 1950).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 2277 Sporn et al., 1963
Rat oral 4590 Jenner et al., 1964
Feeding 13-115 mg daily to rats for 5-9 days has been reported to
cause fatty infiltration of liver parenchymal cells (Shillinger,
1950).
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 90-day feeding study on 15 males and 15 females, no
adverse effects were reported at a level of 228 ppm in the diet (Oser,
1967). In another 90-day study, groups of 15 males and 15 females were
fed 0 or 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day without adverse effect (Oser et
al., 1965). A 17-week study on groups of 10 male and 10 female rats
used a mixture of 60 per cent. alpha-ionone and 40 per cent. ▀-ionone
at 0, 0.1, 0.25 and 1.0 per cent. of the diet. A dose-related swelling
of the liver parenchyma was noted, but was only very slight at the
lowest level. No other adverse effects were seen (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
None available.
Comments
The biochemical information available together with the
short-term studies allows assessment. Further metabolic and long-term
studies are needed.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 12.3 mg/kg body-weight/day equivalent to 246 ppm in the
diet.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Conditional acceptance 0-0.1
Further work required
Biochemical and metabolic as well as long-term studies, with
special emphasis on effects on the liver.
REFERENCES
Bielig, H.-J. & Hayasida, A. (1940) Z. physiol. Chem., 266, 99
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A., Brouwer, J. B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L., Carson, S. & Oser, M. (1965) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 3,
563
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Prelog, V. & Meier, H. L. (1950) Helv. chim. Acta, 33, 1276
Shillinger, J. I. (1950) Gig. i. San., 3, 37
Sporn, A., Sch÷besch, O., Marin, V., Panaitescu, E. & Runcanu, L.
(1963) Igiena, 12, 437
