
FAO/PL:1967/M/11/1
WHO/Food Add./68.30
1967 EVALUATIONS OF SOME PESTICIDE RESIDUES IN FOOD
THE MONOGRAPHS
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint Meeting of the FAO Working Party of Experts and the WHO Expert
Committee on Pesticide Residues, which met in Rome, 4 - 11 December,
1967. (FAO/WHO, 1968)
FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION
Rome, 1968
MANCOZEB
IDENTITY
Chemical name
Zinc ion coordination product with manganese
ethylene-1,2-bisdithiocarbamate polymer.
Empirical formula
(C4H6N2S4Mn)a . (C4H4N2S4Zn)y
Structural formula
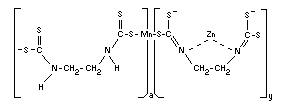 The polymer contains 1.6 per cent zinc, i.e., 6 per cent of the units
are in the form of the coordination complex.
Other relevant chemical properties
The addition of zinc chloride to a suspension of maneb yields a
product mancozeb, superior to maneb. Mancozeb is essentially inert to
oxidation by atmospheric oxidation, in contract with maneb. It is also
essentially non-phytotoxic in contrast with maneb, zineb or mixtures
of these which are harmful to a number of plants.
The standard formulation is an 80 per cent wettable powder containing
Mn++ 16 per cent and Zn++ 2 per cent.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Biochemical aspects
For information see In animals.
Acute toxicity
LD50
Animal Route (mg/kg b.w.) Reference
Rat Oral 8000 Larson, 1965
Special studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed 0, 100, 300 and 1000
ppm of the active product for three months, in a study comparing the
thyroid effect of this compound with that of propylthiouracil in
similar groups of rats at 300 ppm for three months or 1333 ppm for 5
weeks. Oxygen consumption studies were conducted during the third
month, and at the end of the study 131-I-uptake was determined for
each animal, following which the thyroid gland was examined
microscopically. At 1000 ppm, terminal body weights were adversely
affected and PBI was depressed in the females; thyroid weight ratios
were elevated and the metabolic rate was lowered in the males; and one
animal of each sex showed significant thyroid hyperplasia, 131I-uptake
was not affected. At 100 and 300 ppm, PBI was significantly increased
in both sexes, but thyroid weights and histology and metabolic rates
were unaffected. In the groups fed propylthiouracil, weight gain
depression, increased thyroid weight ratios, lowered 131I-uptakes,
lowered metabolic rates and severe thyroid hyperplasia were seen in
both sexes. Propylthiouracil did not affect PBI (Larson, 1965).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 10 males and 10 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 75 and
100 ppm for 13 weeks. No effect of the compound was found on
body-weight gain, survival, food consumption, peripheral blood
picture, urinary constituents and weights and histologic appearance of
major organs. (Larson, 1965).
In a three-generation reproduction study, mating groups of 20 males
and 20 females were maintained on diets containing 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the compound. Two litters were produced per generation and
filial generations were composed of second-litter animals. Parental
generation animals were followed for 90 weeks (reported under
"Long-term studies"); the first litters from each generation were
given gross post-mortem examination after weaning, as were all
breeding generations after weaning their second litters. The second
litters of the second filial generation were given thorough
histopathologic examinations at weaning age. At 1000 ppm, lowered
fertility was seen in the first and second filial generations, without
effect on gestation, lactation, viability of offspring or weaning
weights. Uninterpretable, significant variations (both relative
increases and decreases) in thyroid weight ratios were found in 8 of
20 group means at 100 and 1000 ppm. Histological examination of the
F3b animals disclosed no thyroid hyperplasia at any level, nor any
other significant organ pathology, (Larson, 1965).
Dog. Groups of 4 males and 4 females were fed 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the active product for 2 years. PBI and 131I-uptake were
determined at 6, 12 and 24 months: the only deviations from control
values were seen at 24 months, in lower 131I-uptakes at 48 and 72
hours in the 100 ppm group, and at 72 hours in the 1000 ppm group. No
adverse effect was seen on behaviour, survival, rate of weight gain,
food consumption, blood picture, urine, clinical indices of hepatic
and renal function, organ weight ratios and the gross and histologic
appearance of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 males and 25 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 100 and
1000 ppm for 90 weeks. The only significant effect of the compound was
hyperplasia of the thyroid acinar epithelium in some of the animals in
the 1000 ppm group. This effect was not seen at lover levels, and no
effect at any level was found on survival, body-weight gain, food
consumption, blood picture, urine, metabolic rate (determined at 30
weeks and one year for controls and 1000 ppm animals and for all
groups at 21 months), organ weight ratios and microscopic appearance
of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Comments
In the long-term study in the rat a level of 100 ppm was without
toxicological effect. In the two-year feeding study in the dog, a
lower 131I-uptake was observed in the 100 ppm group and the 1000 ppm
group at 24 months, but not at 6 and 12 months. This type of study has
not been conducted on any of the other dithiocarbamates. No other
effects were observed in this study.
More information is needed on the chemical nature of the residues in
or on the plant. While these data are being obtained, a temporary ADI
is proposed.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 100 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 5 mg/kg body-weight per day.
Estimate of temporary acceptable daily intake for man
0 - 0.025 mg/kg body-weight (alone or in combination with other
ethylene bisdithiocarbamates).
This value is based on experiments carried out with mancozeb and does
not take account of chemical alterations after application.
Further work required
Studies of the compound in plants to determine the chemical nature of
the residues, followed by appropriate toxicological studies.
Results of the above work should be made available not later than 30
June 1971 after which a re-evaluation of this compound will be made.
The re-evaluation may be made at an earlier meeting should relevant
information become available.
EVALUATION FOR TOLERANCES
USE PATTERN
Pre-harvest treatments
Mancozeb was introduced in 1961 as a material superior to maneb or a
mixture of maneb and zineb in the protection of certain agricultural
crops from plant pathogenic fungi.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Using good agricultural practice of an appropriate spray
concentration, number of applications and time interval before harvest
the residue values indicated in Table I were found.
FATE OF RESIDUES
In plants
The following have been identified as intermediate degradation
products of mancozeb applied to plants : ethylene bis-isothiocyanate,
ethylene thiourea, Jaffe's base [N-2(2-imidazolyl)-ethylene thiourea],
ethylene urea, 2-imidazoline, N-formyl ethylenediamine,
ethylenediamine, elemental sulfur and sulfate ion. A preliminary
measurement of ethylene thiourea from sugar beet tops after 17 days
using a high level of mancozeb indicated a level of 2 per cent.
In animals
An experiment with C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet for seven
days at 20 mg per rat per day (approx. 1000 ppm) indicated that the
metabolism follows pathways similar to its degradation on plants. The
distribution of carbon-14 made 24 hours after the final feeding of
C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet was as follows : feces 70.90
per cent, urine 15.5 per cent, cage washings 3.98 per cent and
carcasses 1.45 per cent, total 91.83 per cent. Of the activity in the
feces 47 ± 4 per cent was estimated as mancozeb from the hot
acid-CS2-evolved assay, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 7.5 per
cent, ethylenethiourea 6.0 per cent and ethylene urea 2.0 per cent,
total identified 62 per cent.
TABLE I
Crops Time Interval Treatment per Applications Residue (ppm)
(days) acre (lb/acre) (Number) Mean Range
Almonds, hull 16 9 1 0.07 0.06-0.08
" , meat 55.1 43.0 -78.5
Apples 56 4 8 1.5 1.2 -1.8
Cranberries 55 6 4 0.99 0.85-1.12
Plums and prunes 12 6 3 1.33 1.11-1.51
Barley 26 2 3 1.41 0.52-2.38
Cotton (seed) 26 3 2 0.21 0.12-0.40
Peanuts, nuts 21 2 6 0.04 0.01-0.09
" , hay 54.0 43 - 64
Sugar beets, roots 61 2 3 0.09 Nil -0.14
" " , silage 0.288
Carrots 15 2 15 0.26 0.08-0.49
Celery 5 2 10 1.01 0.38-1.88
Cucumber 7 2 5 0.38 0.21-0.52
Lettuce and endive 14 2 8 0.10 0.025-0.19
Melons 7 3 8 0.85 0.05-1.86
Tomatoes 7 3 8 0.58 0.51-0.79
The C14-components of the urine identified were as follows : ethylene
thiourea 28 per cent, N-acetyl ethylediamine 19 per cent, ethylene
urea 12 per cent, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 5.5 per cent,
ethylenediamine 1.5 per cent, being 70 per cent of the total activity
(Rohm and Haas, 1967).
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The method of residue determination is the same for the other
dithiocarbamate fungicides based on the determination of carbon
disulfide released on acid treatment (Gordon, Schuckert and Bornak,
1967) and is non-specific for mancozeb.
NATIONAL TOLERANCES
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
United States
of America 65 peanut vine hay, sugar beet tops
28 raisins
25 straw of barley, oats, rye and wheat
20 bran of barley, oats, rye and wheat
15 bananas (2 ppm in pulp)
10 apples, celery, crab apples, fennel,
pears, quinces, papayas
7 cranberries, cucumbers, grapes, summer
squash, tomatoes (0 in pulp), edible
melons (0 in pulp)
5 grains of barley, oats, rye and wheat
2 carrots and sugar beets
1 flour of barley, oats, rye and wheat
0.5 corn, cottonseed, kidney, liver,
peanuts
Canada 1 sugar beets
(continued)
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
Canada 2 apples, cucumbers, melons, squash
tomatoes.
Federal Republic 3 leaf vegetables, fruit vegetables,
of Germany pulses, fruit including grapes.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TOLERANCES
In light of the non-specificity of the available analytical method, it
is not possible to make recommendations for tolerances of mancozeb per
se at this time.
FURTHER WORK
Further work required before recommendations for tolerances can be
made
Development of an analytical method specific for mancozeb or, failing
this, data indicating that a combined tolerance for all
dithiocarbamate fungicides would be acceptable.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Larson, P.S. (1965) Unpublished report submitted by Rohm and Haas
Company.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Gordon, C,F,, Schuckert, R.J., Bornak, W.E. (1967) Improved method for
the determination of ethylenebisdithiocarbamate residues in plants,
fruits and vegetables. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 50 : 1102-1108.
Rohm and Haas. (1967) Unpublished data submitted to FAO.
The polymer contains 1.6 per cent zinc, i.e., 6 per cent of the units
are in the form of the coordination complex.
Other relevant chemical properties
The addition of zinc chloride to a suspension of maneb yields a
product mancozeb, superior to maneb. Mancozeb is essentially inert to
oxidation by atmospheric oxidation, in contract with maneb. It is also
essentially non-phytotoxic in contrast with maneb, zineb or mixtures
of these which are harmful to a number of plants.
The standard formulation is an 80 per cent wettable powder containing
Mn++ 16 per cent and Zn++ 2 per cent.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Biochemical aspects
For information see In animals.
Acute toxicity
LD50
Animal Route (mg/kg b.w.) Reference
Rat Oral 8000 Larson, 1965
Special studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed 0, 100, 300 and 1000
ppm of the active product for three months, in a study comparing the
thyroid effect of this compound with that of propylthiouracil in
similar groups of rats at 300 ppm for three months or 1333 ppm for 5
weeks. Oxygen consumption studies were conducted during the third
month, and at the end of the study 131-I-uptake was determined for
each animal, following which the thyroid gland was examined
microscopically. At 1000 ppm, terminal body weights were adversely
affected and PBI was depressed in the females; thyroid weight ratios
were elevated and the metabolic rate was lowered in the males; and one
animal of each sex showed significant thyroid hyperplasia, 131I-uptake
was not affected. At 100 and 300 ppm, PBI was significantly increased
in both sexes, but thyroid weights and histology and metabolic rates
were unaffected. In the groups fed propylthiouracil, weight gain
depression, increased thyroid weight ratios, lowered 131I-uptakes,
lowered metabolic rates and severe thyroid hyperplasia were seen in
both sexes. Propylthiouracil did not affect PBI (Larson, 1965).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 10 males and 10 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 75 and
100 ppm for 13 weeks. No effect of the compound was found on
body-weight gain, survival, food consumption, peripheral blood
picture, urinary constituents and weights and histologic appearance of
major organs. (Larson, 1965).
In a three-generation reproduction study, mating groups of 20 males
and 20 females were maintained on diets containing 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the compound. Two litters were produced per generation and
filial generations were composed of second-litter animals. Parental
generation animals were followed for 90 weeks (reported under
"Long-term studies"); the first litters from each generation were
given gross post-mortem examination after weaning, as were all
breeding generations after weaning their second litters. The second
litters of the second filial generation were given thorough
histopathologic examinations at weaning age. At 1000 ppm, lowered
fertility was seen in the first and second filial generations, without
effect on gestation, lactation, viability of offspring or weaning
weights. Uninterpretable, significant variations (both relative
increases and decreases) in thyroid weight ratios were found in 8 of
20 group means at 100 and 1000 ppm. Histological examination of the
F3b animals disclosed no thyroid hyperplasia at any level, nor any
other significant organ pathology, (Larson, 1965).
Dog. Groups of 4 males and 4 females were fed 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the active product for 2 years. PBI and 131I-uptake were
determined at 6, 12 and 24 months: the only deviations from control
values were seen at 24 months, in lower 131I-uptakes at 48 and 72
hours in the 100 ppm group, and at 72 hours in the 1000 ppm group. No
adverse effect was seen on behaviour, survival, rate of weight gain,
food consumption, blood picture, urine, clinical indices of hepatic
and renal function, organ weight ratios and the gross and histologic
appearance of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 males and 25 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 100 and
1000 ppm for 90 weeks. The only significant effect of the compound was
hyperplasia of the thyroid acinar epithelium in some of the animals in
the 1000 ppm group. This effect was not seen at lover levels, and no
effect at any level was found on survival, body-weight gain, food
consumption, blood picture, urine, metabolic rate (determined at 30
weeks and one year for controls and 1000 ppm animals and for all
groups at 21 months), organ weight ratios and microscopic appearance
of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Comments
In the long-term study in the rat a level of 100 ppm was without
toxicological effect. In the two-year feeding study in the dog, a
lower 131I-uptake was observed in the 100 ppm group and the 1000 ppm
group at 24 months, but not at 6 and 12 months. This type of study has
not been conducted on any of the other dithiocarbamates. No other
effects were observed in this study.
More information is needed on the chemical nature of the residues in
or on the plant. While these data are being obtained, a temporary ADI
is proposed.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 100 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 5 mg/kg body-weight per day.
Estimate of temporary acceptable daily intake for man
0 - 0.025 mg/kg body-weight (alone or in combination with other
ethylene bisdithiocarbamates).
This value is based on experiments carried out with mancozeb and does
not take account of chemical alterations after application.
Further work required
Studies of the compound in plants to determine the chemical nature of
the residues, followed by appropriate toxicological studies.
Results of the above work should be made available not later than 30
June 1971 after which a re-evaluation of this compound will be made.
The re-evaluation may be made at an earlier meeting should relevant
information become available.
EVALUATION FOR TOLERANCES
USE PATTERN
Pre-harvest treatments
Mancozeb was introduced in 1961 as a material superior to maneb or a
mixture of maneb and zineb in the protection of certain agricultural
crops from plant pathogenic fungi.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Using good agricultural practice of an appropriate spray
concentration, number of applications and time interval before harvest
the residue values indicated in Table I were found.
FATE OF RESIDUES
In plants
The following have been identified as intermediate degradation
products of mancozeb applied to plants : ethylene bis-isothiocyanate,
ethylene thiourea, Jaffe's base [N-2(2-imidazolyl)-ethylene thiourea],
ethylene urea, 2-imidazoline, N-formyl ethylenediamine,
ethylenediamine, elemental sulfur and sulfate ion. A preliminary
measurement of ethylene thiourea from sugar beet tops after 17 days
using a high level of mancozeb indicated a level of 2 per cent.
In animals
An experiment with C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet for seven
days at 20 mg per rat per day (approx. 1000 ppm) indicated that the
metabolism follows pathways similar to its degradation on plants. The
distribution of carbon-14 made 24 hours after the final feeding of
C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet was as follows : feces 70.90
per cent, urine 15.5 per cent, cage washings 3.98 per cent and
carcasses 1.45 per cent, total 91.83 per cent. Of the activity in the
feces 47 ± 4 per cent was estimated as mancozeb from the hot
acid-CS2-evolved assay, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 7.5 per
cent, ethylenethiourea 6.0 per cent and ethylene urea 2.0 per cent,
total identified 62 per cent.
TABLE I
Crops Time Interval Treatment per Applications Residue (ppm)
(days) acre (lb/acre) (Number) Mean Range
Almonds, hull 16 9 1 0.07 0.06-0.08
" , meat 55.1 43.0 -78.5
Apples 56 4 8 1.5 1.2 -1.8
Cranberries 55 6 4 0.99 0.85-1.12
Plums and prunes 12 6 3 1.33 1.11-1.51
Barley 26 2 3 1.41 0.52-2.38
Cotton (seed) 26 3 2 0.21 0.12-0.40
Peanuts, nuts 21 2 6 0.04 0.01-0.09
" , hay 54.0 43 - 64
Sugar beets, roots 61 2 3 0.09 Nil -0.14
" " , silage 0.288
Carrots 15 2 15 0.26 0.08-0.49
Celery 5 2 10 1.01 0.38-1.88
Cucumber 7 2 5 0.38 0.21-0.52
Lettuce and endive 14 2 8 0.10 0.025-0.19
Melons 7 3 8 0.85 0.05-1.86
Tomatoes 7 3 8 0.58 0.51-0.79
The C14-components of the urine identified were as follows : ethylene
thiourea 28 per cent, N-acetyl ethylediamine 19 per cent, ethylene
urea 12 per cent, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 5.5 per cent,
ethylenediamine 1.5 per cent, being 70 per cent of the total activity
(Rohm and Haas, 1967).
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The method of residue determination is the same for the other
dithiocarbamate fungicides based on the determination of carbon
disulfide released on acid treatment (Gordon, Schuckert and Bornak,
1967) and is non-specific for mancozeb.
NATIONAL TOLERANCES
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
United States
of America 65 peanut vine hay, sugar beet tops
28 raisins
25 straw of barley, oats, rye and wheat
20 bran of barley, oats, rye and wheat
15 bananas (2 ppm in pulp)
10 apples, celery, crab apples, fennel,
pears, quinces, papayas
7 cranberries, cucumbers, grapes, summer
squash, tomatoes (0 in pulp), edible
melons (0 in pulp)
5 grains of barley, oats, rye and wheat
2 carrots and sugar beets
1 flour of barley, oats, rye and wheat
0.5 corn, cottonseed, kidney, liver,
peanuts
Canada 1 sugar beets
(continued)
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
Canada 2 apples, cucumbers, melons, squash
tomatoes.
Federal Republic 3 leaf vegetables, fruit vegetables,
of Germany pulses, fruit including grapes.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TOLERANCES
In light of the non-specificity of the available analytical method, it
is not possible to make recommendations for tolerances of mancozeb per
se at this time.
FURTHER WORK
Further work required before recommendations for tolerances can be
made
Development of an analytical method specific for mancozeb or, failing
this, data indicating that a combined tolerance for all
dithiocarbamate fungicides would be acceptable.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Larson, P.S. (1965) Unpublished report submitted by Rohm and Haas
Company.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Gordon, C,F,, Schuckert, R.J., Bornak, W.E. (1967) Improved method for
the determination of ethylenebisdithiocarbamate residues in plants,
fruits and vegetables. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 50 : 1102-1108.
Rohm and Haas. (1967) Unpublished data submitted to FAO.
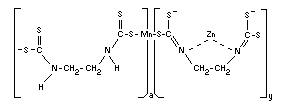 The polymer contains 1.6 per cent zinc, i.e., 6 per cent of the units
are in the form of the coordination complex.
Other relevant chemical properties
The addition of zinc chloride to a suspension of maneb yields a
product mancozeb, superior to maneb. Mancozeb is essentially inert to
oxidation by atmospheric oxidation, in contract with maneb. It is also
essentially non-phytotoxic in contrast with maneb, zineb or mixtures
of these which are harmful to a number of plants.
The standard formulation is an 80 per cent wettable powder containing
Mn++ 16 per cent and Zn++ 2 per cent.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Biochemical aspects
For information see In animals.
Acute toxicity
LD50
Animal Route (mg/kg b.w.) Reference
Rat Oral 8000 Larson, 1965
Special studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed 0, 100, 300 and 1000
ppm of the active product for three months, in a study comparing the
thyroid effect of this compound with that of propylthiouracil in
similar groups of rats at 300 ppm for three months or 1333 ppm for 5
weeks. Oxygen consumption studies were conducted during the third
month, and at the end of the study 131-I-uptake was determined for
each animal, following which the thyroid gland was examined
microscopically. At 1000 ppm, terminal body weights were adversely
affected and PBI was depressed in the females; thyroid weight ratios
were elevated and the metabolic rate was lowered in the males; and one
animal of each sex showed significant thyroid hyperplasia, 131I-uptake
was not affected. At 100 and 300 ppm, PBI was significantly increased
in both sexes, but thyroid weights and histology and metabolic rates
were unaffected. In the groups fed propylthiouracil, weight gain
depression, increased thyroid weight ratios, lowered 131I-uptakes,
lowered metabolic rates and severe thyroid hyperplasia were seen in
both sexes. Propylthiouracil did not affect PBI (Larson, 1965).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 10 males and 10 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 75 and
100 ppm for 13 weeks. No effect of the compound was found on
body-weight gain, survival, food consumption, peripheral blood
picture, urinary constituents and weights and histologic appearance of
major organs. (Larson, 1965).
In a three-generation reproduction study, mating groups of 20 males
and 20 females were maintained on diets containing 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the compound. Two litters were produced per generation and
filial generations were composed of second-litter animals. Parental
generation animals were followed for 90 weeks (reported under
"Long-term studies"); the first litters from each generation were
given gross post-mortem examination after weaning, as were all
breeding generations after weaning their second litters. The second
litters of the second filial generation were given thorough
histopathologic examinations at weaning age. At 1000 ppm, lowered
fertility was seen in the first and second filial generations, without
effect on gestation, lactation, viability of offspring or weaning
weights. Uninterpretable, significant variations (both relative
increases and decreases) in thyroid weight ratios were found in 8 of
20 group means at 100 and 1000 ppm. Histological examination of the
F3b animals disclosed no thyroid hyperplasia at any level, nor any
other significant organ pathology, (Larson, 1965).
Dog. Groups of 4 males and 4 females were fed 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the active product for 2 years. PBI and 131I-uptake were
determined at 6, 12 and 24 months: the only deviations from control
values were seen at 24 months, in lower 131I-uptakes at 48 and 72
hours in the 100 ppm group, and at 72 hours in the 1000 ppm group. No
adverse effect was seen on behaviour, survival, rate of weight gain,
food consumption, blood picture, urine, clinical indices of hepatic
and renal function, organ weight ratios and the gross and histologic
appearance of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 males and 25 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 100 and
1000 ppm for 90 weeks. The only significant effect of the compound was
hyperplasia of the thyroid acinar epithelium in some of the animals in
the 1000 ppm group. This effect was not seen at lover levels, and no
effect at any level was found on survival, body-weight gain, food
consumption, blood picture, urine, metabolic rate (determined at 30
weeks and one year for controls and 1000 ppm animals and for all
groups at 21 months), organ weight ratios and microscopic appearance
of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Comments
In the long-term study in the rat a level of 100 ppm was without
toxicological effect. In the two-year feeding study in the dog, a
lower 131I-uptake was observed in the 100 ppm group and the 1000 ppm
group at 24 months, but not at 6 and 12 months. This type of study has
not been conducted on any of the other dithiocarbamates. No other
effects were observed in this study.
More information is needed on the chemical nature of the residues in
or on the plant. While these data are being obtained, a temporary ADI
is proposed.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 100 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 5 mg/kg body-weight per day.
Estimate of temporary acceptable daily intake for man
0 - 0.025 mg/kg body-weight (alone or in combination with other
ethylene bisdithiocarbamates).
This value is based on experiments carried out with mancozeb and does
not take account of chemical alterations after application.
Further work required
Studies of the compound in plants to determine the chemical nature of
the residues, followed by appropriate toxicological studies.
Results of the above work should be made available not later than 30
June 1971 after which a re-evaluation of this compound will be made.
The re-evaluation may be made at an earlier meeting should relevant
information become available.
EVALUATION FOR TOLERANCES
USE PATTERN
Pre-harvest treatments
Mancozeb was introduced in 1961 as a material superior to maneb or a
mixture of maneb and zineb in the protection of certain agricultural
crops from plant pathogenic fungi.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Using good agricultural practice of an appropriate spray
concentration, number of applications and time interval before harvest
the residue values indicated in Table I were found.
FATE OF RESIDUES
In plants
The following have been identified as intermediate degradation
products of mancozeb applied to plants : ethylene bis-isothiocyanate,
ethylene thiourea, Jaffe's base [N-2(2-imidazolyl)-ethylene thiourea],
ethylene urea, 2-imidazoline, N-formyl ethylenediamine,
ethylenediamine, elemental sulfur and sulfate ion. A preliminary
measurement of ethylene thiourea from sugar beet tops after 17 days
using a high level of mancozeb indicated a level of 2 per cent.
In animals
An experiment with C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet for seven
days at 20 mg per rat per day (approx. 1000 ppm) indicated that the
metabolism follows pathways similar to its degradation on plants. The
distribution of carbon-14 made 24 hours after the final feeding of
C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet was as follows : feces 70.90
per cent, urine 15.5 per cent, cage washings 3.98 per cent and
carcasses 1.45 per cent, total 91.83 per cent. Of the activity in the
feces 47 ± 4 per cent was estimated as mancozeb from the hot
acid-CS2-evolved assay, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 7.5 per
cent, ethylenethiourea 6.0 per cent and ethylene urea 2.0 per cent,
total identified 62 per cent.
TABLE I
Crops Time Interval Treatment per Applications Residue (ppm)
(days) acre (lb/acre) (Number) Mean Range
Almonds, hull 16 9 1 0.07 0.06-0.08
" , meat 55.1 43.0 -78.5
Apples 56 4 8 1.5 1.2 -1.8
Cranberries 55 6 4 0.99 0.85-1.12
Plums and prunes 12 6 3 1.33 1.11-1.51
Barley 26 2 3 1.41 0.52-2.38
Cotton (seed) 26 3 2 0.21 0.12-0.40
Peanuts, nuts 21 2 6 0.04 0.01-0.09
" , hay 54.0 43 - 64
Sugar beets, roots 61 2 3 0.09 Nil -0.14
" " , silage 0.288
Carrots 15 2 15 0.26 0.08-0.49
Celery 5 2 10 1.01 0.38-1.88
Cucumber 7 2 5 0.38 0.21-0.52
Lettuce and endive 14 2 8 0.10 0.025-0.19
Melons 7 3 8 0.85 0.05-1.86
Tomatoes 7 3 8 0.58 0.51-0.79
The C14-components of the urine identified were as follows : ethylene
thiourea 28 per cent, N-acetyl ethylediamine 19 per cent, ethylene
urea 12 per cent, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 5.5 per cent,
ethylenediamine 1.5 per cent, being 70 per cent of the total activity
(Rohm and Haas, 1967).
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The method of residue determination is the same for the other
dithiocarbamate fungicides based on the determination of carbon
disulfide released on acid treatment (Gordon, Schuckert and Bornak,
1967) and is non-specific for mancozeb.
NATIONAL TOLERANCES
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
United States
of America 65 peanut vine hay, sugar beet tops
28 raisins
25 straw of barley, oats, rye and wheat
20 bran of barley, oats, rye and wheat
15 bananas (2 ppm in pulp)
10 apples, celery, crab apples, fennel,
pears, quinces, papayas
7 cranberries, cucumbers, grapes, summer
squash, tomatoes (0 in pulp), edible
melons (0 in pulp)
5 grains of barley, oats, rye and wheat
2 carrots and sugar beets
1 flour of barley, oats, rye and wheat
0.5 corn, cottonseed, kidney, liver,
peanuts
Canada 1 sugar beets
(continued)
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
Canada 2 apples, cucumbers, melons, squash
tomatoes.
Federal Republic 3 leaf vegetables, fruit vegetables,
of Germany pulses, fruit including grapes.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TOLERANCES
In light of the non-specificity of the available analytical method, it
is not possible to make recommendations for tolerances of mancozeb per
se at this time.
FURTHER WORK
Further work required before recommendations for tolerances can be
made
Development of an analytical method specific for mancozeb or, failing
this, data indicating that a combined tolerance for all
dithiocarbamate fungicides would be acceptable.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Larson, P.S. (1965) Unpublished report submitted by Rohm and Haas
Company.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Gordon, C,F,, Schuckert, R.J., Bornak, W.E. (1967) Improved method for
the determination of ethylenebisdithiocarbamate residues in plants,
fruits and vegetables. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 50 : 1102-1108.
Rohm and Haas. (1967) Unpublished data submitted to FAO.
The polymer contains 1.6 per cent zinc, i.e., 6 per cent of the units
are in the form of the coordination complex.
Other relevant chemical properties
The addition of zinc chloride to a suspension of maneb yields a
product mancozeb, superior to maneb. Mancozeb is essentially inert to
oxidation by atmospheric oxidation, in contract with maneb. It is also
essentially non-phytotoxic in contrast with maneb, zineb or mixtures
of these which are harmful to a number of plants.
The standard formulation is an 80 per cent wettable powder containing
Mn++ 16 per cent and Zn++ 2 per cent.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Biochemical aspects
For information see In animals.
Acute toxicity
LD50
Animal Route (mg/kg b.w.) Reference
Rat Oral 8000 Larson, 1965
Special studies
Rat. Groups of 15 males and 15 females were fed 0, 100, 300 and 1000
ppm of the active product for three months, in a study comparing the
thyroid effect of this compound with that of propylthiouracil in
similar groups of rats at 300 ppm for three months or 1333 ppm for 5
weeks. Oxygen consumption studies were conducted during the third
month, and at the end of the study 131-I-uptake was determined for
each animal, following which the thyroid gland was examined
microscopically. At 1000 ppm, terminal body weights were adversely
affected and PBI was depressed in the females; thyroid weight ratios
were elevated and the metabolic rate was lowered in the males; and one
animal of each sex showed significant thyroid hyperplasia, 131I-uptake
was not affected. At 100 and 300 ppm, PBI was significantly increased
in both sexes, but thyroid weights and histology and metabolic rates
were unaffected. In the groups fed propylthiouracil, weight gain
depression, increased thyroid weight ratios, lowered 131I-uptakes,
lowered metabolic rates and severe thyroid hyperplasia were seen in
both sexes. Propylthiouracil did not affect PBI (Larson, 1965).
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 10 males and 10 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 75 and
100 ppm for 13 weeks. No effect of the compound was found on
body-weight gain, survival, food consumption, peripheral blood
picture, urinary constituents and weights and histologic appearance of
major organs. (Larson, 1965).
In a three-generation reproduction study, mating groups of 20 males
and 20 females were maintained on diets containing 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the compound. Two litters were produced per generation and
filial generations were composed of second-litter animals. Parental
generation animals were followed for 90 weeks (reported under
"Long-term studies"); the first litters from each generation were
given gross post-mortem examination after weaning, as were all
breeding generations after weaning their second litters. The second
litters of the second filial generation were given thorough
histopathologic examinations at weaning age. At 1000 ppm, lowered
fertility was seen in the first and second filial generations, without
effect on gestation, lactation, viability of offspring or weaning
weights. Uninterpretable, significant variations (both relative
increases and decreases) in thyroid weight ratios were found in 8 of
20 group means at 100 and 1000 ppm. Histological examination of the
F3b animals disclosed no thyroid hyperplasia at any level, nor any
other significant organ pathology, (Larson, 1965).
Dog. Groups of 4 males and 4 females were fed 0, 25, 100 and 1000
ppm of the active product for 2 years. PBI and 131I-uptake were
determined at 6, 12 and 24 months: the only deviations from control
values were seen at 24 months, in lower 131I-uptakes at 48 and 72
hours in the 100 ppm group, and at 72 hours in the 1000 ppm group. No
adverse effect was seen on behaviour, survival, rate of weight gain,
food consumption, blood picture, urine, clinical indices of hepatic
and renal function, organ weight ratios and the gross and histologic
appearance of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 males and 25 females were fed 0, 25, 50, 100 and
1000 ppm for 90 weeks. The only significant effect of the compound was
hyperplasia of the thyroid acinar epithelium in some of the animals in
the 1000 ppm group. This effect was not seen at lover levels, and no
effect at any level was found on survival, body-weight gain, food
consumption, blood picture, urine, metabolic rate (determined at 30
weeks and one year for controls and 1000 ppm animals and for all
groups at 21 months), organ weight ratios and microscopic appearance
of major organs. (Larson, 1965).
Comments
In the long-term study in the rat a level of 100 ppm was without
toxicological effect. In the two-year feeding study in the dog, a
lower 131I-uptake was observed in the 100 ppm group and the 1000 ppm
group at 24 months, but not at 6 and 12 months. This type of study has
not been conducted on any of the other dithiocarbamates. No other
effects were observed in this study.
More information is needed on the chemical nature of the residues in
or on the plant. While these data are being obtained, a temporary ADI
is proposed.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 100 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 5 mg/kg body-weight per day.
Estimate of temporary acceptable daily intake for man
0 - 0.025 mg/kg body-weight (alone or in combination with other
ethylene bisdithiocarbamates).
This value is based on experiments carried out with mancozeb and does
not take account of chemical alterations after application.
Further work required
Studies of the compound in plants to determine the chemical nature of
the residues, followed by appropriate toxicological studies.
Results of the above work should be made available not later than 30
June 1971 after which a re-evaluation of this compound will be made.
The re-evaluation may be made at an earlier meeting should relevant
information become available.
EVALUATION FOR TOLERANCES
USE PATTERN
Pre-harvest treatments
Mancozeb was introduced in 1961 as a material superior to maneb or a
mixture of maneb and zineb in the protection of certain agricultural
crops from plant pathogenic fungi.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Using good agricultural practice of an appropriate spray
concentration, number of applications and time interval before harvest
the residue values indicated in Table I were found.
FATE OF RESIDUES
In plants
The following have been identified as intermediate degradation
products of mancozeb applied to plants : ethylene bis-isothiocyanate,
ethylene thiourea, Jaffe's base [N-2(2-imidazolyl)-ethylene thiourea],
ethylene urea, 2-imidazoline, N-formyl ethylenediamine,
ethylenediamine, elemental sulfur and sulfate ion. A preliminary
measurement of ethylene thiourea from sugar beet tops after 17 days
using a high level of mancozeb indicated a level of 2 per cent.
In animals
An experiment with C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet for seven
days at 20 mg per rat per day (approx. 1000 ppm) indicated that the
metabolism follows pathways similar to its degradation on plants. The
distribution of carbon-14 made 24 hours after the final feeding of
C14 labelled mancozeb in the rat diet was as follows : feces 70.90
per cent, urine 15.5 per cent, cage washings 3.98 per cent and
carcasses 1.45 per cent, total 91.83 per cent. Of the activity in the
feces 47 ± 4 per cent was estimated as mancozeb from the hot
acid-CS2-evolved assay, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 7.5 per
cent, ethylenethiourea 6.0 per cent and ethylene urea 2.0 per cent,
total identified 62 per cent.
TABLE I
Crops Time Interval Treatment per Applications Residue (ppm)
(days) acre (lb/acre) (Number) Mean Range
Almonds, hull 16 9 1 0.07 0.06-0.08
" , meat 55.1 43.0 -78.5
Apples 56 4 8 1.5 1.2 -1.8
Cranberries 55 6 4 0.99 0.85-1.12
Plums and prunes 12 6 3 1.33 1.11-1.51
Barley 26 2 3 1.41 0.52-2.38
Cotton (seed) 26 3 2 0.21 0.12-0.40
Peanuts, nuts 21 2 6 0.04 0.01-0.09
" , hay 54.0 43 - 64
Sugar beets, roots 61 2 3 0.09 Nil -0.14
" " , silage 0.288
Carrots 15 2 15 0.26 0.08-0.49
Celery 5 2 10 1.01 0.38-1.88
Cucumber 7 2 5 0.38 0.21-0.52
Lettuce and endive 14 2 8 0.10 0.025-0.19
Melons 7 3 8 0.85 0.05-1.86
Tomatoes 7 3 8 0.58 0.51-0.79
The C14-components of the urine identified were as follows : ethylene
thiourea 28 per cent, N-acetyl ethylediamine 19 per cent, ethylene
urea 12 per cent, ethylene bisisothiocyanate sulfide 5.5 per cent,
ethylenediamine 1.5 per cent, being 70 per cent of the total activity
(Rohm and Haas, 1967).
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The method of residue determination is the same for the other
dithiocarbamate fungicides based on the determination of carbon
disulfide released on acid treatment (Gordon, Schuckert and Bornak,
1967) and is non-specific for mancozeb.
NATIONAL TOLERANCES
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
United States
of America 65 peanut vine hay, sugar beet tops
28 raisins
25 straw of barley, oats, rye and wheat
20 bran of barley, oats, rye and wheat
15 bananas (2 ppm in pulp)
10 apples, celery, crab apples, fennel,
pears, quinces, papayas
7 cranberries, cucumbers, grapes, summer
squash, tomatoes (0 in pulp), edible
melons (0 in pulp)
5 grains of barley, oats, rye and wheat
2 carrots and sugar beets
1 flour of barley, oats, rye and wheat
0.5 corn, cottonseed, kidney, liver,
peanuts
Canada 1 sugar beets
(continued)
Country Tolerance, ppm Crop
Canada 2 apples, cucumbers, melons, squash
tomatoes.
Federal Republic 3 leaf vegetables, fruit vegetables,
of Germany pulses, fruit including grapes.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TOLERANCES
In light of the non-specificity of the available analytical method, it
is not possible to make recommendations for tolerances of mancozeb per
se at this time.
FURTHER WORK
Further work required before recommendations for tolerances can be
made
Development of an analytical method specific for mancozeb or, failing
this, data indicating that a combined tolerance for all
dithiocarbamate fungicides would be acceptable.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Larson, P.S. (1965) Unpublished report submitted by Rohm and Haas
Company.
REFERENCES PERTINENT TO EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKES
Gordon, C,F,, Schuckert, R.J., Bornak, W.E. (1967) Improved method for
the determination of ethylenebisdithiocarbamate residues in plants,
fruits and vegetables. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 50 : 1102-1108.
Rohm and Haas. (1967) Unpublished data submitted to FAO.
