
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Resort Series No. 44A
WHO/Food Add./68.33
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES AND
NON-NUTRITIVE SWEETENING AGENTS
Geneva, 21-28 August 1967
The Eleventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives is published as FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series,
1967, No. 44; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1968, 383. This
Report contains general considerations, including the principles
adopted for the evaluation, and a summary of the results of the
evaluations of a number of food additives. Additional information,
such as biological data and a toxicological evaluation, considered at
that meeting, is to be found in this document.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
ETHYL METHYLPHENYLGLYCIDATE
Synonyms Aldehyde C-16; strawberry aldehyde
Chemical name Ethyl methylphenylglycidate
Empirical Formula C12H14O3
Structural formula
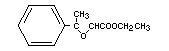 Molecular weight 206.24
Definition Ethyl methylphenylglycidate contains not less
than 98 per cent. C12H14O3.
Description Ethyl methylphenylglycidate is usually
prepared by the reaction of acetophenone and
the ethyl ester of monochloroacetic acid in
the presence of an alkaline condensing agent.
It is a colourless to pale yellow liquid with
a strong fruity odour suggestive of
strawberries.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
In vito experiments using simulated gastric juice showed over
80 per cent. cleavage of the epoxy-linkage after 1 hour; with
intestinal fluid some 70 per cent. of the epoxy-linkage was destroyed
in 3 hours. Ester hydrolysis occurred to only a minor degree (Oser,
1967).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 5470 Jenner et al., 1964
Guinea-pig oral 4050 Jenner et al., 1964
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 12-week study on 15 males and 15 females using mixed
esters no adverse effect was noted at a level of 21 mg/kg/day (Oser,
1967). In another study lasting for 16 weeks, groups of 5 male and 5
female rats were fed 0 and 1 per cent. of ester iIn their diet. Growth
retardation, particularly of males was observed, as well as testicular
atrophy (Hagan et al., 1967).
In a 1-year study on 5 male and 5 female rats the ester was fed
at 0 and 0.25 per cent. in the diet without producing any adverse
effects on body-weight gain, organ weights and histology of major
organs (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed diets
containing various proportions of ester for 2 years. At the 0.5 per
cent. level paralysis of hind-quarters was observed as well as
demyelinating degenerative changes in the sciatic nerve (Baer &
Griepentrog, 1967).
Comments
The biochemical studies suggest little hydrolysis of the ester
but substantial though not complete destruction of the epoxy-linkage.
A no-effect level has only been established in a short-term study
lasting for one year, while the long-term study has produced evidence
of a possible cumulative demyelination effect. Further metabolic
studies and adequate long-term studies are essential.
EVALUATION
Level causing no significant toxicological effect
Rat. C.25 per cent. (= 2500 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 125
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Temporary acceptance 0-0.6
Further work required
Within four years, biochemical and metabolic studies and adequate
long-term studies with special emphasis on neurological effects, the
effect on bone marrow and testicular tissue.
REFERENCES
Baer, F. & Griepentrog, F. (1967) Med. Ehrnährung, 8, 244
Hagan, E. C., Hausen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J.B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L., & Fitzhugh,
O. C. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Molecular weight 206.24
Definition Ethyl methylphenylglycidate contains not less
than 98 per cent. C12H14O3.
Description Ethyl methylphenylglycidate is usually
prepared by the reaction of acetophenone and
the ethyl ester of monochloroacetic acid in
the presence of an alkaline condensing agent.
It is a colourless to pale yellow liquid with
a strong fruity odour suggestive of
strawberries.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
In vito experiments using simulated gastric juice showed over
80 per cent. cleavage of the epoxy-linkage after 1 hour; with
intestinal fluid some 70 per cent. of the epoxy-linkage was destroyed
in 3 hours. Ester hydrolysis occurred to only a minor degree (Oser,
1967).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 5470 Jenner et al., 1964
Guinea-pig oral 4050 Jenner et al., 1964
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 12-week study on 15 males and 15 females using mixed
esters no adverse effect was noted at a level of 21 mg/kg/day (Oser,
1967). In another study lasting for 16 weeks, groups of 5 male and 5
female rats were fed 0 and 1 per cent. of ester iIn their diet. Growth
retardation, particularly of males was observed, as well as testicular
atrophy (Hagan et al., 1967).
In a 1-year study on 5 male and 5 female rats the ester was fed
at 0 and 0.25 per cent. in the diet without producing any adverse
effects on body-weight gain, organ weights and histology of major
organs (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed diets
containing various proportions of ester for 2 years. At the 0.5 per
cent. level paralysis of hind-quarters was observed as well as
demyelinating degenerative changes in the sciatic nerve (Baer &
Griepentrog, 1967).
Comments
The biochemical studies suggest little hydrolysis of the ester
but substantial though not complete destruction of the epoxy-linkage.
A no-effect level has only been established in a short-term study
lasting for one year, while the long-term study has produced evidence
of a possible cumulative demyelination effect. Further metabolic
studies and adequate long-term studies are essential.
EVALUATION
Level causing no significant toxicological effect
Rat. C.25 per cent. (= 2500 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 125
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Temporary acceptance 0-0.6
Further work required
Within four years, biochemical and metabolic studies and adequate
long-term studies with special emphasis on neurological effects, the
effect on bone marrow and testicular tissue.
REFERENCES
Baer, F. & Griepentrog, F. (1967) Med. Ehrnährung, 8, 244
Hagan, E. C., Hausen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J.B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L., & Fitzhugh,
O. C. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
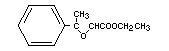 Molecular weight 206.24
Definition Ethyl methylphenylglycidate contains not less
than 98 per cent. C12H14O3.
Description Ethyl methylphenylglycidate is usually
prepared by the reaction of acetophenone and
the ethyl ester of monochloroacetic acid in
the presence of an alkaline condensing agent.
It is a colourless to pale yellow liquid with
a strong fruity odour suggestive of
strawberries.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
In vito experiments using simulated gastric juice showed over
80 per cent. cleavage of the epoxy-linkage after 1 hour; with
intestinal fluid some 70 per cent. of the epoxy-linkage was destroyed
in 3 hours. Ester hydrolysis occurred to only a minor degree (Oser,
1967).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 5470 Jenner et al., 1964
Guinea-pig oral 4050 Jenner et al., 1964
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 12-week study on 15 males and 15 females using mixed
esters no adverse effect was noted at a level of 21 mg/kg/day (Oser,
1967). In another study lasting for 16 weeks, groups of 5 male and 5
female rats were fed 0 and 1 per cent. of ester iIn their diet. Growth
retardation, particularly of males was observed, as well as testicular
atrophy (Hagan et al., 1967).
In a 1-year study on 5 male and 5 female rats the ester was fed
at 0 and 0.25 per cent. in the diet without producing any adverse
effects on body-weight gain, organ weights and histology of major
organs (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed diets
containing various proportions of ester for 2 years. At the 0.5 per
cent. level paralysis of hind-quarters was observed as well as
demyelinating degenerative changes in the sciatic nerve (Baer &
Griepentrog, 1967).
Comments
The biochemical studies suggest little hydrolysis of the ester
but substantial though not complete destruction of the epoxy-linkage.
A no-effect level has only been established in a short-term study
lasting for one year, while the long-term study has produced evidence
of a possible cumulative demyelination effect. Further metabolic
studies and adequate long-term studies are essential.
EVALUATION
Level causing no significant toxicological effect
Rat. C.25 per cent. (= 2500 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 125
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Temporary acceptance 0-0.6
Further work required
Within four years, biochemical and metabolic studies and adequate
long-term studies with special emphasis on neurological effects, the
effect on bone marrow and testicular tissue.
REFERENCES
Baer, F. & Griepentrog, F. (1967) Med. Ehrnährung, 8, 244
Hagan, E. C., Hausen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J.B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L., & Fitzhugh,
O. C. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
Molecular weight 206.24
Definition Ethyl methylphenylglycidate contains not less
than 98 per cent. C12H14O3.
Description Ethyl methylphenylglycidate is usually
prepared by the reaction of acetophenone and
the ethyl ester of monochloroacetic acid in
the presence of an alkaline condensing agent.
It is a colourless to pale yellow liquid with
a strong fruity odour suggestive of
strawberries.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
In vito experiments using simulated gastric juice showed over
80 per cent. cleavage of the epoxy-linkage after 1 hour; with
intestinal fluid some 70 per cent. of the epoxy-linkage was destroyed
in 3 hours. Ester hydrolysis occurred to only a minor degree (Oser,
1967).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral 5470 Jenner et al., 1964
Guinea-pig oral 4050 Jenner et al., 1964
Short-term studies
Rat. In a 12-week study on 15 males and 15 females using mixed
esters no adverse effect was noted at a level of 21 mg/kg/day (Oser,
1967). In another study lasting for 16 weeks, groups of 5 male and 5
female rats were fed 0 and 1 per cent. of ester iIn their diet. Growth
retardation, particularly of males was observed, as well as testicular
atrophy (Hagan et al., 1967).
In a 1-year study on 5 male and 5 female rats the ester was fed
at 0 and 0.25 per cent. in the diet without producing any adverse
effects on body-weight gain, organ weights and histology of major
organs (Hagan et al., 1967).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 20 male and 20 female rats were fed diets
containing various proportions of ester for 2 years. At the 0.5 per
cent. level paralysis of hind-quarters was observed as well as
demyelinating degenerative changes in the sciatic nerve (Baer &
Griepentrog, 1967).
Comments
The biochemical studies suggest little hydrolysis of the ester
but substantial though not complete destruction of the epoxy-linkage.
A no-effect level has only been established in a short-term study
lasting for one year, while the long-term study has produced evidence
of a possible cumulative demyelination effect. Further metabolic
studies and adequate long-term studies are essential.
EVALUATION
Level causing no significant toxicological effect
Rat. C.25 per cent. (= 2500 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 125
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Temporary acceptance 0-0.6
Further work required
Within four years, biochemical and metabolic studies and adequate
long-term studies with special emphasis on neurological effects, the
effect on bone marrow and testicular tissue.
REFERENCES
Baer, F. & Griepentrog, F. (1967) Med. Ehrnährung, 8, 244
Hagan, E. C., Hausen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. G., Jenner, P. M., Jones, W.
I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J.B. (1967)
Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M., Hagan, E. C., Taylor, J. M., Cook, E. L., & Fitzhugh,
O. C. (1964) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 2, 327
Oser, B. L. (1967) Unpublished report
