
FAO Nutrition Meetings
Resort Series No. 44A
WHO/Food Add./68.33
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SOME
FLAVOURING SUBSTANCES AND
NON-NUTRITIVE SWEETENING AGENTS
Geneva, 21-28 August 1967
The Eleventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food
Additives is published as FAO Nutrition Meetings Report Series,
1967, No. 44; Wld Hlth Org. techn. Rep. Ser., 1968, 383. This
Report contains general considerations, including the principles
adopted for the evaluation, and a summary of the results of the
evaluations of a number of food additives. Additional information,
such as biological data and a toxicological evaluation, considered at
that meeting, is to be found in this document.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1967
ETHYL VANILLIN
Chemical name 3-Ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde
Empirical formula C9H10O3
Strucutral formula
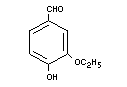 Molecular weight 166.18
Description Fine, white or slightly yellowish
crystals, having a strong vanilla-like
odour and taste; affected by light.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ester is probably metabolized to glucuroethyl vanillin and
ethyl vanillic acid, of which some is conjugated with glucuronic and
sulfuric acids (Williams, 1959).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 750 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rat oral 1590 Sporn, 1960
(continued)
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral >2000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat s.c. 1800 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Guinea-pig i.p. 1140 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rabbit oral 3000 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Dog i.v. 760 (LD) Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Short-term studies
Rat. Doses of 300 mg/kg body-weight were administered to rats
i.g. twice weekly for 14 weeks without any adverse effects. In another
experiment groups of 16 rats were fed 20 mg/kg body-weight/day for 18
weeks without adverse effect, but 64 mg/kg body-weight/day for 10
weeks reduced growth rate and caused myocardial, renal, hepatic, lung,
spleen and stomach injuries (Deichmann & Kitzmuller, 1940). Groups of
5 male rats were fed 0, 2 and 5 per cent. in their diet for 1 year
without any adverse effects (Hagan et al., 1967). Sixteen rats were
given 30 mg weekly for 7 weeks without adverse effect on growth, food
intake or protein utilization (Sporn, 1960).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female rats were fed diets
containing 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 per cent. ethyl vanillin for 2 years
without any adverse effects on growth, organ weights of major organs,
haematology and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Comments
Few direct metabolic studies have been carried out on this ether.
However, the long-term studies in rats permit evaluation. Further
metabolic studies are desirable.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 2 per cent. (= 20 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 1000
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
REFERENCES
Caujolle, F. & Meynier, D. (1954) C.r. hebd. Sean. Acadi. Sci.,
Paris, 238, 2576
Deichmann, W. & Kitzmuller, K. V. (1940) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., 29,
425
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. C., Jenner, P. M., Joes,
W.I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B.
(1967) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M,, Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cork, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet Toxicol ., 2, 327
Sporn, A. (1960) Igiena (Bucharest), 9, 365
Williams, R. T. (1959) Detoxication Mechanisms, Second Edition,
Chapman & Hall, London
Molecular weight 166.18
Description Fine, white or slightly yellowish
crystals, having a strong vanilla-like
odour and taste; affected by light.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ester is probably metabolized to glucuroethyl vanillin and
ethyl vanillic acid, of which some is conjugated with glucuronic and
sulfuric acids (Williams, 1959).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 750 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rat oral 1590 Sporn, 1960
(continued)
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral >2000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat s.c. 1800 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Guinea-pig i.p. 1140 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rabbit oral 3000 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Dog i.v. 760 (LD) Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Short-term studies
Rat. Doses of 300 mg/kg body-weight were administered to rats
i.g. twice weekly for 14 weeks without any adverse effects. In another
experiment groups of 16 rats were fed 20 mg/kg body-weight/day for 18
weeks without adverse effect, but 64 mg/kg body-weight/day for 10
weeks reduced growth rate and caused myocardial, renal, hepatic, lung,
spleen and stomach injuries (Deichmann & Kitzmuller, 1940). Groups of
5 male rats were fed 0, 2 and 5 per cent. in their diet for 1 year
without any adverse effects (Hagan et al., 1967). Sixteen rats were
given 30 mg weekly for 7 weeks without adverse effect on growth, food
intake or protein utilization (Sporn, 1960).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female rats were fed diets
containing 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 per cent. ethyl vanillin for 2 years
without any adverse effects on growth, organ weights of major organs,
haematology and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Comments
Few direct metabolic studies have been carried out on this ether.
However, the long-term studies in rats permit evaluation. Further
metabolic studies are desirable.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 2 per cent. (= 20 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 1000
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
REFERENCES
Caujolle, F. & Meynier, D. (1954) C.r. hebd. Sean. Acadi. Sci.,
Paris, 238, 2576
Deichmann, W. & Kitzmuller, K. V. (1940) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., 29,
425
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. C., Jenner, P. M., Joes,
W.I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B.
(1967) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M,, Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cork, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet Toxicol ., 2, 327
Sporn, A. (1960) Igiena (Bucharest), 9, 365
Williams, R. T. (1959) Detoxication Mechanisms, Second Edition,
Chapman & Hall, London
 Molecular weight 166.18
Description Fine, white or slightly yellowish
crystals, having a strong vanilla-like
odour and taste; affected by light.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ester is probably metabolized to glucuroethyl vanillin and
ethyl vanillic acid, of which some is conjugated with glucuronic and
sulfuric acids (Williams, 1959).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 750 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rat oral 1590 Sporn, 1960
(continued)
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral >2000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat s.c. 1800 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Guinea-pig i.p. 1140 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rabbit oral 3000 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Dog i.v. 760 (LD) Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Short-term studies
Rat. Doses of 300 mg/kg body-weight were administered to rats
i.g. twice weekly for 14 weeks without any adverse effects. In another
experiment groups of 16 rats were fed 20 mg/kg body-weight/day for 18
weeks without adverse effect, but 64 mg/kg body-weight/day for 10
weeks reduced growth rate and caused myocardial, renal, hepatic, lung,
spleen and stomach injuries (Deichmann & Kitzmuller, 1940). Groups of
5 male rats were fed 0, 2 and 5 per cent. in their diet for 1 year
without any adverse effects (Hagan et al., 1967). Sixteen rats were
given 30 mg weekly for 7 weeks without adverse effect on growth, food
intake or protein utilization (Sporn, 1960).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female rats were fed diets
containing 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 per cent. ethyl vanillin for 2 years
without any adverse effects on growth, organ weights of major organs,
haematology and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Comments
Few direct metabolic studies have been carried out on this ether.
However, the long-term studies in rats permit evaluation. Further
metabolic studies are desirable.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 2 per cent. (= 20 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 1000
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
REFERENCES
Caujolle, F. & Meynier, D. (1954) C.r. hebd. Sean. Acadi. Sci.,
Paris, 238, 2576
Deichmann, W. & Kitzmuller, K. V. (1940) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., 29,
425
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. C., Jenner, P. M., Joes,
W.I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B.
(1967) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M,, Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cork, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet Toxicol ., 2, 327
Sporn, A. (1960) Igiena (Bucharest), 9, 365
Williams, R. T. (1959) Detoxication Mechanisms, Second Edition,
Chapman & Hall, London
Molecular weight 166.18
Description Fine, white or slightly yellowish
crystals, having a strong vanilla-like
odour and taste; affected by light.
Biological Data
Biochemical aspects
This ester is probably metabolized to glucuroethyl vanillin and
ethyl vanillic acid, of which some is conjugated with glucuronic and
sulfuric acids (Williams, 1959).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Mouse i.p. 750 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rat oral 1590 Sporn, 1960
(continued)
Animal Route LD50 References
(mg/kg
body-weight)
Rat oral >2000 Jenner et al., 1964
Rat s.c. 1800 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Guinea-pig i.p. 1140 Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Rabbit oral 3000 (LD) Deichmann & Kitzmuller,
1940
Dog i.v. 760 (LD) Caujolle & Meynier, 1954
Short-term studies
Rat. Doses of 300 mg/kg body-weight were administered to rats
i.g. twice weekly for 14 weeks without any adverse effects. In another
experiment groups of 16 rats were fed 20 mg/kg body-weight/day for 18
weeks without adverse effect, but 64 mg/kg body-weight/day for 10
weeks reduced growth rate and caused myocardial, renal, hepatic, lung,
spleen and stomach injuries (Deichmann & Kitzmuller, 1940). Groups of
5 male rats were fed 0, 2 and 5 per cent. in their diet for 1 year
without any adverse effects (Hagan et al., 1967). Sixteen rats were
given 30 mg weekly for 7 weeks without adverse effect on growth, food
intake or protein utilization (Sporn, 1960).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 12 male and 12 female rats were fed diets
containing 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 per cent. ethyl vanillin for 2 years
without any adverse effects on growth, organ weights of major organs,
haematology and histology of major tissues (Hagan et al., 1967).
Comments
Few direct metabolic studies have been carried out on this ether.
However, the long-term studies in rats permit evaluation. Further
metabolic studies are desirable.
EVALUATION
Level causing no toxicological effect
Rat. 2 per cent. (= 20 000 ppm) in the diet, equivalent to 1000
mg/kg body-weight/day.
Estimate of acceptable daily intake for man
mg/kg body-weight
Unconditional acceptance 0-10
REFERENCES
Caujolle, F. & Meynier, D. (1954) C.r. hebd. Sean. Acadi. Sci.,
Paris, 238, 2576
Deichmann, W. & Kitzmuller, K. V. (1940) J. Amer. pharm. Ass., 29,
425
Hagan, E. C., Hansen, W. H., Fitzhugh, O. C., Jenner, P. M., Joes,
W.I., Taylor, J. M., Long, E. L., Nelson, A. A. & Brouwer, J. B.
(1967) Fd Cosmet. Toxicol., 5(2), 141
Jenner, P. M,, Hagan, E.C., Taylor, J. M., Cork, E. L. & Fitzhugh, O.
G. (1964) Fd Cosmet Toxicol ., 2, 327
Sporn, A. (1960) Igiena (Bucharest), 9, 365
Williams, R. T. (1959) Detoxication Mechanisms, Second Edition,
Chapman & Hall, London
