
FAO Meeting Report No. PL/1965/10/1
WHO/Food Add./27.65
EVALUATION OF THE TOXICITY OF PESTICIDE RESIDUES IN FOOD
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint Meeting of the FAO Committee on Pesticides in Agriculture and
the WHO Expert Committee on Pesticide Residues, which met in Rome,
15-22 March 19651
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1965
1 Report of the second joint meeting of the FAO Committee on
Pesticides in Agriculture and the WHO Expert Committee on Pesticide
Residues, FAO Meeting Report No. PL/1965/10; WHO/Food Add./26.65
ZINEB
Chemical name
Zinc ethylene-1,2-bisdithiocarbamate
Empirical formula
C4H6N2S4Zn
Structural formula
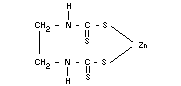 BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
The capacity of the human gut to absorb zineb is not known,
though in the rat 11-17% is taken up after ingestion. It is believed
that thiocarbamates may act as inhibitors of certain -SH enzymes in
the body.
A person suffering from hypocatalasaemia developed
sulfhaemoglobinaemia, haemolytic anaemia and Heinz body formation
after contact with zineb (Pinkhas et al., 1963).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral >5200 Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 40 weanling rats, 20 females and 20 males, were
given diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb
for up to 30 days. Thyroid enlargement was seen at all dose levels,
but, unequivocal histopathological changes were observed only at 10
000 ppm (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Dog. Three groups each of 3 dogs were fed for one year diets
containing 20, 2000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb. All the animals survived
and no persistent change in growth rate was seen in any of the groups;
there were no histopathological changes in the tissues, except in the
thyroid gland, and haematological findings were normal. At 10 000 ppm
thyroid hyperplasia was found (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1963; Kampmeier
& Haag, 1954).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups, each of 10 young male and 10 young female rats,
were fed diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of
zineb for 2 years. At the two highest dose levels there was an
apparent increase in mortality rate among the females and at 10 000
ppm there was a tendency towards diminished growth in both sexes.
Haematological studies were all normal. A goitrogenic effect was seen
at all dose levels. Kidney damage was seen in 6 animals at the 10 000
ppm dose level, and in one animal in each of the groups receiving
1000, 2500, and 5000 ppm, but not in any of those given 500 ppm. The
tumour incidence was not significantly greater among any of the
treated animals than it was in the controls (Blackwell-Smith et al.,
1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Comments on the experimental studies reported
For zineb, as for most of the dithiocarbamates, short- and
long-term studies in animals have been reported, but for all of them
biochemical data are inadequate.
EVALUATION
The chemical nature of the residues of the dithiocarbamates in
or on the plant has not been ascertained. The compounds themselves
have effects on the thyroid, nervous system and blood in animals. In
the absence of information about their mode of action an acceptable
intake for man cannot be estimated.
Further work required
Determination and evaluation of the toxicity of the plant
residues. Extension of the long-term studies, including reproduction
studies, which should concern at least two species, with special
attention to neurological changes, goitrogenicity and occurrence of
anaemia.
REFERENCES
Blackwell-Smith, R., jr, Finnegan, J. K., Larson, P. S., Sahyoun,
P. F., Dreyfuss, M. L. & Haag, H. B. (1953) J. Phamacol. exp.
Ther., 109, 159
Kampmeier, C. & Haag, H. B. (1954) Agricult. Chemicals, April, 49
Pinkhas, J., Djaldetti, M., Joshua, H., Reswick, C. & de Vries, A.
(1963) Blood, 21, 484
BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
The capacity of the human gut to absorb zineb is not known,
though in the rat 11-17% is taken up after ingestion. It is believed
that thiocarbamates may act as inhibitors of certain -SH enzymes in
the body.
A person suffering from hypocatalasaemia developed
sulfhaemoglobinaemia, haemolytic anaemia and Heinz body formation
after contact with zineb (Pinkhas et al., 1963).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral >5200 Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 40 weanling rats, 20 females and 20 males, were
given diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb
for up to 30 days. Thyroid enlargement was seen at all dose levels,
but, unequivocal histopathological changes were observed only at 10
000 ppm (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Dog. Three groups each of 3 dogs were fed for one year diets
containing 20, 2000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb. All the animals survived
and no persistent change in growth rate was seen in any of the groups;
there were no histopathological changes in the tissues, except in the
thyroid gland, and haematological findings were normal. At 10 000 ppm
thyroid hyperplasia was found (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1963; Kampmeier
& Haag, 1954).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups, each of 10 young male and 10 young female rats,
were fed diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of
zineb for 2 years. At the two highest dose levels there was an
apparent increase in mortality rate among the females and at 10 000
ppm there was a tendency towards diminished growth in both sexes.
Haematological studies were all normal. A goitrogenic effect was seen
at all dose levels. Kidney damage was seen in 6 animals at the 10 000
ppm dose level, and in one animal in each of the groups receiving
1000, 2500, and 5000 ppm, but not in any of those given 500 ppm. The
tumour incidence was not significantly greater among any of the
treated animals than it was in the controls (Blackwell-Smith et al.,
1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Comments on the experimental studies reported
For zineb, as for most of the dithiocarbamates, short- and
long-term studies in animals have been reported, but for all of them
biochemical data are inadequate.
EVALUATION
The chemical nature of the residues of the dithiocarbamates in
or on the plant has not been ascertained. The compounds themselves
have effects on the thyroid, nervous system and blood in animals. In
the absence of information about their mode of action an acceptable
intake for man cannot be estimated.
Further work required
Determination and evaluation of the toxicity of the plant
residues. Extension of the long-term studies, including reproduction
studies, which should concern at least two species, with special
attention to neurological changes, goitrogenicity and occurrence of
anaemia.
REFERENCES
Blackwell-Smith, R., jr, Finnegan, J. K., Larson, P. S., Sahyoun,
P. F., Dreyfuss, M. L. & Haag, H. B. (1953) J. Phamacol. exp.
Ther., 109, 159
Kampmeier, C. & Haag, H. B. (1954) Agricult. Chemicals, April, 49
Pinkhas, J., Djaldetti, M., Joshua, H., Reswick, C. & de Vries, A.
(1963) Blood, 21, 484
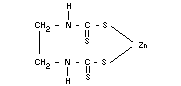 BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
The capacity of the human gut to absorb zineb is not known,
though in the rat 11-17% is taken up after ingestion. It is believed
that thiocarbamates may act as inhibitors of certain -SH enzymes in
the body.
A person suffering from hypocatalasaemia developed
sulfhaemoglobinaemia, haemolytic anaemia and Heinz body formation
after contact with zineb (Pinkhas et al., 1963).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral >5200 Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 40 weanling rats, 20 females and 20 males, were
given diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb
for up to 30 days. Thyroid enlargement was seen at all dose levels,
but, unequivocal histopathological changes were observed only at 10
000 ppm (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Dog. Three groups each of 3 dogs were fed for one year diets
containing 20, 2000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb. All the animals survived
and no persistent change in growth rate was seen in any of the groups;
there were no histopathological changes in the tissues, except in the
thyroid gland, and haematological findings were normal. At 10 000 ppm
thyroid hyperplasia was found (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1963; Kampmeier
& Haag, 1954).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups, each of 10 young male and 10 young female rats,
were fed diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of
zineb for 2 years. At the two highest dose levels there was an
apparent increase in mortality rate among the females and at 10 000
ppm there was a tendency towards diminished growth in both sexes.
Haematological studies were all normal. A goitrogenic effect was seen
at all dose levels. Kidney damage was seen in 6 animals at the 10 000
ppm dose level, and in one animal in each of the groups receiving
1000, 2500, and 5000 ppm, but not in any of those given 500 ppm. The
tumour incidence was not significantly greater among any of the
treated animals than it was in the controls (Blackwell-Smith et al.,
1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Comments on the experimental studies reported
For zineb, as for most of the dithiocarbamates, short- and
long-term studies in animals have been reported, but for all of them
biochemical data are inadequate.
EVALUATION
The chemical nature of the residues of the dithiocarbamates in
or on the plant has not been ascertained. The compounds themselves
have effects on the thyroid, nervous system and blood in animals. In
the absence of information about their mode of action an acceptable
intake for man cannot be estimated.
Further work required
Determination and evaluation of the toxicity of the plant
residues. Extension of the long-term studies, including reproduction
studies, which should concern at least two species, with special
attention to neurological changes, goitrogenicity and occurrence of
anaemia.
REFERENCES
Blackwell-Smith, R., jr, Finnegan, J. K., Larson, P. S., Sahyoun,
P. F., Dreyfuss, M. L. & Haag, H. B. (1953) J. Phamacol. exp.
Ther., 109, 159
Kampmeier, C. & Haag, H. B. (1954) Agricult. Chemicals, April, 49
Pinkhas, J., Djaldetti, M., Joshua, H., Reswick, C. & de Vries, A.
(1963) Blood, 21, 484
BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
The capacity of the human gut to absorb zineb is not known,
though in the rat 11-17% is taken up after ingestion. It is believed
that thiocarbamates may act as inhibitors of certain -SH enzymes in
the body.
A person suffering from hypocatalasaemia developed
sulfhaemoglobinaemia, haemolytic anaemia and Heinz body formation
after contact with zineb (Pinkhas et al., 1963).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral >5200 Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953
Short-term studies
Rat. Groups of 40 weanling rats, 20 females and 20 males, were
given diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb
for up to 30 days. Thyroid enlargement was seen at all dose levels,
but, unequivocal histopathological changes were observed only at 10
000 ppm (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Dog. Three groups each of 3 dogs were fed for one year diets
containing 20, 2000 and 10 000 ppm of zineb. All the animals survived
and no persistent change in growth rate was seen in any of the groups;
there were no histopathological changes in the tissues, except in the
thyroid gland, and haematological findings were normal. At 10 000 ppm
thyroid hyperplasia was found (Blackwell-Smith et al., 1963; Kampmeier
& Haag, 1954).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups, each of 10 young male and 10 young female rats,
were fed diets containing 500, 1000, 2500, 5000 and 10 000 ppm of
zineb for 2 years. At the two highest dose levels there was an
apparent increase in mortality rate among the females and at 10 000
ppm there was a tendency towards diminished growth in both sexes.
Haematological studies were all normal. A goitrogenic effect was seen
at all dose levels. Kidney damage was seen in 6 animals at the 10 000
ppm dose level, and in one animal in each of the groups receiving
1000, 2500, and 5000 ppm, but not in any of those given 500 ppm. The
tumour incidence was not significantly greater among any of the
treated animals than it was in the controls (Blackwell-Smith et al.,
1953; Kampmeier & Haag, 1954).
Comments on the experimental studies reported
For zineb, as for most of the dithiocarbamates, short- and
long-term studies in animals have been reported, but for all of them
biochemical data are inadequate.
EVALUATION
The chemical nature of the residues of the dithiocarbamates in
or on the plant has not been ascertained. The compounds themselves
have effects on the thyroid, nervous system and blood in animals. In
the absence of information about their mode of action an acceptable
intake for man cannot be estimated.
Further work required
Determination and evaluation of the toxicity of the plant
residues. Extension of the long-term studies, including reproduction
studies, which should concern at least two species, with special
attention to neurological changes, goitrogenicity and occurrence of
anaemia.
REFERENCES
Blackwell-Smith, R., jr, Finnegan, J. K., Larson, P. S., Sahyoun,
P. F., Dreyfuss, M. L. & Haag, H. B. (1953) J. Phamacol. exp.
Ther., 109, 159
Kampmeier, C. & Haag, H. B. (1954) Agricult. Chemicals, April, 49
Pinkhas, J., Djaldetti, M., Joshua, H., Reswick, C. & de Vries, A.
(1963) Blood, 21, 484
