
PESTICIDE RESIDUES IN FOOD - 1979
Sponsored jointly by FAO and WHO
EVALUATIONS 1979
Joint meeting of the
FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide Residues
in Food and the Environment
and the
WHO Expert Group on Pesticide Residues
Geneva, 3-12 December 1979
THIOMETON
Explanation
Thiometon was previously evaluated in 1969, 1973 and 1976. In 1973 a
temporary ADI and some temporary MRLs were proposed. Further
information from (1) a long-term chronic toxicity study; (2)
metabolism studies in plants and animals; (3) supervised trials, was
required. In 1976 some further information on metabolism in plants
and animals, and some further data from supervised trials were
considered. In the absence of a long-term chronic toxicity study, the
temporary ADI was extended to 1979. Further information on the level
and fate of residues in livestock feed containing residues was also
listed as desirable.
At the present meeting reports of additional toxicological studies and
of supervised trials on some 30 commodities, apparently intended to
confirm temporary MRLs previously recommended and to support a few
additional figures, were considered.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE
BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
About 15 mg/kg body weight of radioactive thiometon, labelled in the
OCH3-groups, was administered orally to rats. Most of the activity
was excreted in urine (83% after 24 hours, 91% after 96 hours). In
the faeces, 5.5% was excreted, and 4% remained in the carcass after 96
hours. In the blood, the maximum level (6.1 µg equivalents/ml) was
reached after three hours.
In bile-canulated rats, 4 percent of the dose was excreted in the bile
and about 76% in urine after 72 hours. In another experiment where
the expired air was measured, about 5% was excreted as 14CO2, about
90% in urine, and about 4% in faeces. Absorption, distribution and
elimination in the rat occurred rapidly (Tanner, et al., 1978).
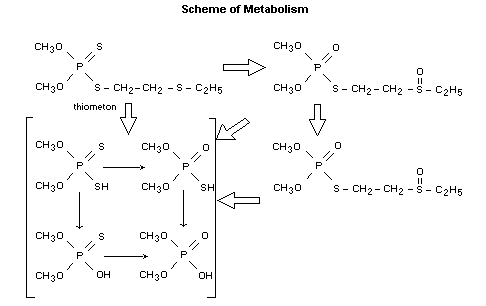
Biotransformation
In the urine, no unchanged thiometon was found. TLC analyses of 0-24
hours urine samples revealed the presence of three major radioactive
components two of which were characterized as O-thiometon sulfoxide
(26 percent of the dose) and O-thiometon sulfone (5 percent). The
main metabolite (52%) was a very polar compound which was
characterized as O,O-dimethylphosphoric acid. From the excretion of
small amounts of the radioactivity in expired air, it was concluded
that O-demethylation took place, but only to a limited extent (Tanner,
et al., 1978).
 TOXICOLOGICAL STUDIES
Special Study on Reproduction
In a standard 3-generation, 2 litter/generation reproduction study,
groups of 30 female and 30 male animals were fed diets containing 0,
1, 2.5 and 6.25 ppm thiometon. From the F1b, F2b, and F3b
generations, five pregnant females per group were killed for
teratological investigation. From 10 animals per sex in each dosage
group of the F3b generation, about 30 organs or tissues were studied
histopathologically.
In the 6.25 ppm group, the lactation index was lower in the F1b, F3b
and F3c litters, the viability index in the F2b and F3b litters, and
pup weight in the F2a and P3b litters. The number of stillborns was
somewhat higher in the F3a. There was no influence on the fertility
or the gestation indices, and no histopathological or teratogenic
abnormalities were found. It was concluded that 6.25 ppm had a
marginal effect on reproduction (Carpy and Klotzsche, 1978).
Short-term studies
Dog
Groups of 4 male and 4 female animals were fed for two years on diets
containing 0, 6, 12 or 48 ppm thiometon. Treatment of the test
animals did not affect general condition, behaviour, mortality,
ophthalmoscopic findings and organ weights. Growth, food consumption,
hematology, clinical chemistry, and urinalysis showed occasionally
abnormal values, but there was no dose-response relationship. The
main effect was noted as cholinesterase inhibition. At 48 ppm, a
statistically significant cholinesterase inhibition in plasma and RBC
was found in males and females at all times (after 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 13,
20 and 26 weeks and thereafter each 3 months). At 12 ppm, only the
male animals showed a significant cholinesterase inhibition in RBC.
Plasma cholinesterase in the 12 ppm group was slightly inhibited in
males and females, especially toward the end of the experiment. Brain
cholinesterase activity was reduced slightly at 48 ppm.
Histopathologically no dose-related effects were found. The dosage
level of 6 ppm was considered to be the no-effect level (Hamburger,
et al., 1978).
Long-Term Studies
Rat
Groups of 50 male and 50 female animals were fed for two years on
diets containing 0, 1, 2.5, 6.25, or 300 ppm thiometon. During the
first six weeks of the study, the diets contained 0, 0.2, 1,2 or 20
ppm, respectively. After 60 weeks, five rats of each sex per dose
group (with the exception of the 300 ppm group) were sacrificed.
Soon after increasing the dosage level to 300 ppm, the animals lost
weight and showed signs of acute poisoning (11 males and 14 females
died). Thereafter, mortality did not differ from other dosage groups.
At 300 ppm, the body weight remained low during the study. In this
group, a decreased food consumption and water intake was observed and
a number of hematological and clinical chemical parameters were
affected. In females, hemoglobin, MCV, and MCH were generally lower
during the study. Glucose, protein, and cholesterol levels were also
decreased while urea in blood was increased. The activities of SGPT
and alkaline phosphatase were increased. Cholinesterase activity in
plasma, RBC, brain and liver was strongly inhibited with 300 ppm. At
6.5 ppm, lower values for cholinesterase in plasma and RBC were
observed on some occasions. In the brain, a slight inhibition of
cholinesterase was noted in females. At 2.5 ppm, RBC cholinesterase
activity was reduced in both sexes on most occasions. This reduction
was always less than 20% and of marginal significance. The urine had
a higher specific gravity at 300 ppm, but the volume produced in 24
hours was low. In the urine, red and white blood cells and amorphous
uric acid crystals were found more frequently in this group during the
last half year of the experiment. At the conclusion of the study, the
relative weight of spleen was decreased, while weights of adrenals,
lungs, brain pituitary and gonads were increased at 300 ppm in both
sexes. The relative weight of the liver was decreased in males only.
Histopathologically, the number of tumors at 300 ppm was decreased,
especially the mammary tumors. Thiometon was not carcinogenic and did
not induce any specific lesions in any organ at any dose level. A
no-effect level in this study is 2.5 ppm (Hamburger, et al., 1978).
COMMENTS
In 1973, a temporary acceptable daily intake of 0.005 mg/kg body
weight was established. The long-term study in rats, required by the
1977 Meeting and additional studies on metabolism in animals, a 2-year
study in dogs, and a 3-generation study in rats were reviewed.
Thiometon is almost completely absorbed in the rat and is excreted
rapidly, mainly in the urine.
In a 2-year dog study, a no-effect level was found to be 6 ppm in the
diet. In the long-term rat study, a no-effect level of 2.5 ppm was
observed. In both studies, the no-effect level was based on
cholinesterase inhibition. In a 3-generation reproduction study, it
was found that thiometon was not teratogenic and that 6.25 ppm in the
diet had a marginal effect on reproduction.
After evaluation of the available toxicological information, an ADI
was allocated.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing No Toxicological Effect
Rat: 2.5 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.12 mg/kg body weight
Dog: 6 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.15 mg/kg body weight
ESTIMATE OF ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE FOR MAN
0 - 0.003 mg/kg body weight
RESIDUES IN FOOD AND THEIR EVALUATION
USE PATTERNS
No additional information was received.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Reports of additional supervised trials on 19 crops in five countries
were available (Sandoz, 1979). Most of the residue trials were
carried out in India, while some other were carried out in Italy,
Australia, France and Switzerland. Of the crops studies the data
relative to 12 did not indicate a need for a change in any of the
previously recommended MRLs.
Of the remaining crops, the information supported additional MRLs for
mustard seed, rape seed and eggplant (See Recommendations). These
recommendations are based partly on similarities with other crops. No
information was available on "normal" or registered use patterns in
the countries where the trials were conducted. However, the
pre-harvest interval on these crops was not a factor in that residues
at no time exceeded the MRL level in the similar crops. On certain
other crops, substantial waiting periods would be required before
residues declined to MRL levels.
Table 1 contains a summary of the residues found in the supervised
trials for various crops. The residue values as reported by the
analyst are apparently the simple arithmetic sum of ppm thiometon
sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone which were determined separately.
In comparing these values to the recommended MRLs it should be noted
that the MRLs are based on measurement of the thiometon sulfone but
expressed as thiometon and excluding the P=O analogues.
Table 1. Thiometon residues in crops from supervised trials (formulated
product Ekatin 25 EC used in each trial)
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Cabbage 0.375 kg/ha 3 n.d. - 0.06 India
(1) 5 n.d
20 n.d.
Cauliflower 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.13-0.25 India
(1) 5 n.d - 0.03
10 n.d.
20 n.d.
Eggplant 0.375% 2 0.08 - 0.11 India
(1) 6 trace - 0.05
11 n.d.
20 n.d.
Okra 0.375% 3 trace - n.d. India
(1) 10 n.d. - 0.02
20 n.d.
0.375% 3 0.02 - 0.04 India
(1) 5 n.d.
20 n.d.
Tomatoes 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.08 India
(1) 10 n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.03 India
(1) 5 n.d.
Peach 0.03% 7 0.26 - 0.38 Italy
1 14 0.08 - 0.1
21 n.d. - 0.02
35 n.d.
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Grape 0.03% 13 0.8 Italy
(1) 28 0.2
40 0.11 - 0.16
63 0.08
Potatoes 0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
Sugarbeet 0.025% 0 Root: 0.22 - 0.12 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 4.95
28 Root: n.d.
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. - 0.05 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 0.23 - 0.7
28 Root. n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 1.4 - 2.6
28 Root: n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
Lucerne 98 g/ha 3 1.15 Australia
(1) 7 n.d.
14 n.d. - 0.02
24 n.d. - 0.02
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Lucerne 147 g/ha 7 trace - 0.02 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
220 g/ha 7 n.d. - 0.03 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
294 g/ha 7 0.09 Australia
(1) 14 0.03
24 0.09
Lupine 0.025% 7 0.24 Australia
(1) 28 0.03
0.05% 7 0.52 Australia
(1) 28 0.1
Rape 0.025% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
0.05% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
Wheat 243 g/ha 43 n.d. France
(1)
150 43 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 43 n.d.
(1)
240 66 n.d. France
(1)
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Wheat 150 66 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 66 n.d.
(1)
Rice 0.4375 kg/ha 41 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.4375 kg/ha 22 grain n.d.
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 43 grain n.d. India
(1) straw n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain (0.04 - 0.07)
(1) straw 0.02
Mustard 0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d.
(2)
Sorghum 0.375 kg/ha 31 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain n.d.
(1)
Groundnuts 0.375 kg/ha 56 n.d. India
(1)
n.d. = not detectable
"Thiometon residues" comprise thiometon, its sulfoxide and their
corresponding P=O analogues.
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The analytical method employed included a permangate oxidation
procedure which converts thiometon and thiometon sulfoxide to
thiometon sulfone along with P=O thiometon which is also measured as
the sulfone. It is probably the basic method evaluated by the 1976
Meeting (FAO/WHO, 1977) except for minor modifications, (e.g. in
certain trials acetone was identified as the extracting solvent rather
than acetonitrile). The limit of detection was 0.02 to 0.04 mg/kg for
each component depending on substrate. Residue values were reported
separately for thiometon sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone.
The residue components of thiometon are identical or similar to
several other pesticides including disulfoton, demeton-methyl, demeton
and phorate. These compounds would probably interfere with the
determination of thiometon. The method therefore has limited value as
a regulatory one.
APPRAISAL
A series of reports on additional supervised residue trials from five
countries tended to confirm previously recommended temporary MRLs for
twelve commodities, and permitted recommendation for three additional
MRLs.
RECOMMENDATIONS
An ADI having now been allocated, the temporary MRLs recommended by
the 1973 and 1976 Meetings can be converted to maximum residue limits.
The existing temporary MRL for chives was previously inserted by error
and should be deleted. In addition, maximum residue limits are
recommended for three new commodities listed below. The limits refer
to the sum of thiometon, thiometon sulfoxide, and thiometon sulfone
determined as thiometon sulfone and expressed as thiometon.
Commodity Maximum residue limit, mg/kg
Mustard seed 0.05*
Rape seed 0.05*
Eggplants 0.5
(* At or about limit of determination)
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION (in addition to items
previously listed)
Desirable
Further information on approved use patterns.
REFERENCES
Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - 3-Generation Study in Rats (including
Teratogenicity). (1978) Unpublished Data submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Hamburger, F., Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - Thiometon 2-year Feeding
Study in Dogs. (1978) Unpublished report submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Thiometon 2-year Feeding Study in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Tanner, P., Meier, J. and Schreier, E. - Thiometon. Pharmacokinetic
Studies with 14C-thiometon in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
TOXICOLOGICAL STUDIES
Special Study on Reproduction
In a standard 3-generation, 2 litter/generation reproduction study,
groups of 30 female and 30 male animals were fed diets containing 0,
1, 2.5 and 6.25 ppm thiometon. From the F1b, F2b, and F3b
generations, five pregnant females per group were killed for
teratological investigation. From 10 animals per sex in each dosage
group of the F3b generation, about 30 organs or tissues were studied
histopathologically.
In the 6.25 ppm group, the lactation index was lower in the F1b, F3b
and F3c litters, the viability index in the F2b and F3b litters, and
pup weight in the F2a and P3b litters. The number of stillborns was
somewhat higher in the F3a. There was no influence on the fertility
or the gestation indices, and no histopathological or teratogenic
abnormalities were found. It was concluded that 6.25 ppm had a
marginal effect on reproduction (Carpy and Klotzsche, 1978).
Short-term studies
Dog
Groups of 4 male and 4 female animals were fed for two years on diets
containing 0, 6, 12 or 48 ppm thiometon. Treatment of the test
animals did not affect general condition, behaviour, mortality,
ophthalmoscopic findings and organ weights. Growth, food consumption,
hematology, clinical chemistry, and urinalysis showed occasionally
abnormal values, but there was no dose-response relationship. The
main effect was noted as cholinesterase inhibition. At 48 ppm, a
statistically significant cholinesterase inhibition in plasma and RBC
was found in males and females at all times (after 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 13,
20 and 26 weeks and thereafter each 3 months). At 12 ppm, only the
male animals showed a significant cholinesterase inhibition in RBC.
Plasma cholinesterase in the 12 ppm group was slightly inhibited in
males and females, especially toward the end of the experiment. Brain
cholinesterase activity was reduced slightly at 48 ppm.
Histopathologically no dose-related effects were found. The dosage
level of 6 ppm was considered to be the no-effect level (Hamburger,
et al., 1978).
Long-Term Studies
Rat
Groups of 50 male and 50 female animals were fed for two years on
diets containing 0, 1, 2.5, 6.25, or 300 ppm thiometon. During the
first six weeks of the study, the diets contained 0, 0.2, 1,2 or 20
ppm, respectively. After 60 weeks, five rats of each sex per dose
group (with the exception of the 300 ppm group) were sacrificed.
Soon after increasing the dosage level to 300 ppm, the animals lost
weight and showed signs of acute poisoning (11 males and 14 females
died). Thereafter, mortality did not differ from other dosage groups.
At 300 ppm, the body weight remained low during the study. In this
group, a decreased food consumption and water intake was observed and
a number of hematological and clinical chemical parameters were
affected. In females, hemoglobin, MCV, and MCH were generally lower
during the study. Glucose, protein, and cholesterol levels were also
decreased while urea in blood was increased. The activities of SGPT
and alkaline phosphatase were increased. Cholinesterase activity in
plasma, RBC, brain and liver was strongly inhibited with 300 ppm. At
6.5 ppm, lower values for cholinesterase in plasma and RBC were
observed on some occasions. In the brain, a slight inhibition of
cholinesterase was noted in females. At 2.5 ppm, RBC cholinesterase
activity was reduced in both sexes on most occasions. This reduction
was always less than 20% and of marginal significance. The urine had
a higher specific gravity at 300 ppm, but the volume produced in 24
hours was low. In the urine, red and white blood cells and amorphous
uric acid crystals were found more frequently in this group during the
last half year of the experiment. At the conclusion of the study, the
relative weight of spleen was decreased, while weights of adrenals,
lungs, brain pituitary and gonads were increased at 300 ppm in both
sexes. The relative weight of the liver was decreased in males only.
Histopathologically, the number of tumors at 300 ppm was decreased,
especially the mammary tumors. Thiometon was not carcinogenic and did
not induce any specific lesions in any organ at any dose level. A
no-effect level in this study is 2.5 ppm (Hamburger, et al., 1978).
COMMENTS
In 1973, a temporary acceptable daily intake of 0.005 mg/kg body
weight was established. The long-term study in rats, required by the
1977 Meeting and additional studies on metabolism in animals, a 2-year
study in dogs, and a 3-generation study in rats were reviewed.
Thiometon is almost completely absorbed in the rat and is excreted
rapidly, mainly in the urine.
In a 2-year dog study, a no-effect level was found to be 6 ppm in the
diet. In the long-term rat study, a no-effect level of 2.5 ppm was
observed. In both studies, the no-effect level was based on
cholinesterase inhibition. In a 3-generation reproduction study, it
was found that thiometon was not teratogenic and that 6.25 ppm in the
diet had a marginal effect on reproduction.
After evaluation of the available toxicological information, an ADI
was allocated.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing No Toxicological Effect
Rat: 2.5 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.12 mg/kg body weight
Dog: 6 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.15 mg/kg body weight
ESTIMATE OF ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE FOR MAN
0 - 0.003 mg/kg body weight
RESIDUES IN FOOD AND THEIR EVALUATION
USE PATTERNS
No additional information was received.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Reports of additional supervised trials on 19 crops in five countries
were available (Sandoz, 1979). Most of the residue trials were
carried out in India, while some other were carried out in Italy,
Australia, France and Switzerland. Of the crops studies the data
relative to 12 did not indicate a need for a change in any of the
previously recommended MRLs.
Of the remaining crops, the information supported additional MRLs for
mustard seed, rape seed and eggplant (See Recommendations). These
recommendations are based partly on similarities with other crops. No
information was available on "normal" or registered use patterns in
the countries where the trials were conducted. However, the
pre-harvest interval on these crops was not a factor in that residues
at no time exceeded the MRL level in the similar crops. On certain
other crops, substantial waiting periods would be required before
residues declined to MRL levels.
Table 1 contains a summary of the residues found in the supervised
trials for various crops. The residue values as reported by the
analyst are apparently the simple arithmetic sum of ppm thiometon
sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone which were determined separately.
In comparing these values to the recommended MRLs it should be noted
that the MRLs are based on measurement of the thiometon sulfone but
expressed as thiometon and excluding the P=O analogues.
Table 1. Thiometon residues in crops from supervised trials (formulated
product Ekatin 25 EC used in each trial)
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Cabbage 0.375 kg/ha 3 n.d. - 0.06 India
(1) 5 n.d
20 n.d.
Cauliflower 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.13-0.25 India
(1) 5 n.d - 0.03
10 n.d.
20 n.d.
Eggplant 0.375% 2 0.08 - 0.11 India
(1) 6 trace - 0.05
11 n.d.
20 n.d.
Okra 0.375% 3 trace - n.d. India
(1) 10 n.d. - 0.02
20 n.d.
0.375% 3 0.02 - 0.04 India
(1) 5 n.d.
20 n.d.
Tomatoes 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.08 India
(1) 10 n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.03 India
(1) 5 n.d.
Peach 0.03% 7 0.26 - 0.38 Italy
1 14 0.08 - 0.1
21 n.d. - 0.02
35 n.d.
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Grape 0.03% 13 0.8 Italy
(1) 28 0.2
40 0.11 - 0.16
63 0.08
Potatoes 0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
Sugarbeet 0.025% 0 Root: 0.22 - 0.12 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 4.95
28 Root: n.d.
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. - 0.05 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 0.23 - 0.7
28 Root. n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 1.4 - 2.6
28 Root: n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
Lucerne 98 g/ha 3 1.15 Australia
(1) 7 n.d.
14 n.d. - 0.02
24 n.d. - 0.02
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Lucerne 147 g/ha 7 trace - 0.02 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
220 g/ha 7 n.d. - 0.03 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
294 g/ha 7 0.09 Australia
(1) 14 0.03
24 0.09
Lupine 0.025% 7 0.24 Australia
(1) 28 0.03
0.05% 7 0.52 Australia
(1) 28 0.1
Rape 0.025% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
0.05% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
Wheat 243 g/ha 43 n.d. France
(1)
150 43 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 43 n.d.
(1)
240 66 n.d. France
(1)
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Wheat 150 66 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 66 n.d.
(1)
Rice 0.4375 kg/ha 41 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.4375 kg/ha 22 grain n.d.
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 43 grain n.d. India
(1) straw n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain (0.04 - 0.07)
(1) straw 0.02
Mustard 0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d.
(2)
Sorghum 0.375 kg/ha 31 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain n.d.
(1)
Groundnuts 0.375 kg/ha 56 n.d. India
(1)
n.d. = not detectable
"Thiometon residues" comprise thiometon, its sulfoxide and their
corresponding P=O analogues.
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The analytical method employed included a permangate oxidation
procedure which converts thiometon and thiometon sulfoxide to
thiometon sulfone along with P=O thiometon which is also measured as
the sulfone. It is probably the basic method evaluated by the 1976
Meeting (FAO/WHO, 1977) except for minor modifications, (e.g. in
certain trials acetone was identified as the extracting solvent rather
than acetonitrile). The limit of detection was 0.02 to 0.04 mg/kg for
each component depending on substrate. Residue values were reported
separately for thiometon sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone.
The residue components of thiometon are identical or similar to
several other pesticides including disulfoton, demeton-methyl, demeton
and phorate. These compounds would probably interfere with the
determination of thiometon. The method therefore has limited value as
a regulatory one.
APPRAISAL
A series of reports on additional supervised residue trials from five
countries tended to confirm previously recommended temporary MRLs for
twelve commodities, and permitted recommendation for three additional
MRLs.
RECOMMENDATIONS
An ADI having now been allocated, the temporary MRLs recommended by
the 1973 and 1976 Meetings can be converted to maximum residue limits.
The existing temporary MRL for chives was previously inserted by error
and should be deleted. In addition, maximum residue limits are
recommended for three new commodities listed below. The limits refer
to the sum of thiometon, thiometon sulfoxide, and thiometon sulfone
determined as thiometon sulfone and expressed as thiometon.
Commodity Maximum residue limit, mg/kg
Mustard seed 0.05*
Rape seed 0.05*
Eggplants 0.5
(* At or about limit of determination)
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION (in addition to items
previously listed)
Desirable
Further information on approved use patterns.
REFERENCES
Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - 3-Generation Study in Rats (including
Teratogenicity). (1978) Unpublished Data submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Hamburger, F., Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - Thiometon 2-year Feeding
Study in Dogs. (1978) Unpublished report submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Thiometon 2-year Feeding Study in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Tanner, P., Meier, J. and Schreier, E. - Thiometon. Pharmacokinetic
Studies with 14C-thiometon in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
 TOXICOLOGICAL STUDIES
Special Study on Reproduction
In a standard 3-generation, 2 litter/generation reproduction study,
groups of 30 female and 30 male animals were fed diets containing 0,
1, 2.5 and 6.25 ppm thiometon. From the F1b, F2b, and F3b
generations, five pregnant females per group were killed for
teratological investigation. From 10 animals per sex in each dosage
group of the F3b generation, about 30 organs or tissues were studied
histopathologically.
In the 6.25 ppm group, the lactation index was lower in the F1b, F3b
and F3c litters, the viability index in the F2b and F3b litters, and
pup weight in the F2a and P3b litters. The number of stillborns was
somewhat higher in the F3a. There was no influence on the fertility
or the gestation indices, and no histopathological or teratogenic
abnormalities were found. It was concluded that 6.25 ppm had a
marginal effect on reproduction (Carpy and Klotzsche, 1978).
Short-term studies
Dog
Groups of 4 male and 4 female animals were fed for two years on diets
containing 0, 6, 12 or 48 ppm thiometon. Treatment of the test
animals did not affect general condition, behaviour, mortality,
ophthalmoscopic findings and organ weights. Growth, food consumption,
hematology, clinical chemistry, and urinalysis showed occasionally
abnormal values, but there was no dose-response relationship. The
main effect was noted as cholinesterase inhibition. At 48 ppm, a
statistically significant cholinesterase inhibition in plasma and RBC
was found in males and females at all times (after 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 13,
20 and 26 weeks and thereafter each 3 months). At 12 ppm, only the
male animals showed a significant cholinesterase inhibition in RBC.
Plasma cholinesterase in the 12 ppm group was slightly inhibited in
males and females, especially toward the end of the experiment. Brain
cholinesterase activity was reduced slightly at 48 ppm.
Histopathologically no dose-related effects were found. The dosage
level of 6 ppm was considered to be the no-effect level (Hamburger,
et al., 1978).
Long-Term Studies
Rat
Groups of 50 male and 50 female animals were fed for two years on
diets containing 0, 1, 2.5, 6.25, or 300 ppm thiometon. During the
first six weeks of the study, the diets contained 0, 0.2, 1,2 or 20
ppm, respectively. After 60 weeks, five rats of each sex per dose
group (with the exception of the 300 ppm group) were sacrificed.
Soon after increasing the dosage level to 300 ppm, the animals lost
weight and showed signs of acute poisoning (11 males and 14 females
died). Thereafter, mortality did not differ from other dosage groups.
At 300 ppm, the body weight remained low during the study. In this
group, a decreased food consumption and water intake was observed and
a number of hematological and clinical chemical parameters were
affected. In females, hemoglobin, MCV, and MCH were generally lower
during the study. Glucose, protein, and cholesterol levels were also
decreased while urea in blood was increased. The activities of SGPT
and alkaline phosphatase were increased. Cholinesterase activity in
plasma, RBC, brain and liver was strongly inhibited with 300 ppm. At
6.5 ppm, lower values for cholinesterase in plasma and RBC were
observed on some occasions. In the brain, a slight inhibition of
cholinesterase was noted in females. At 2.5 ppm, RBC cholinesterase
activity was reduced in both sexes on most occasions. This reduction
was always less than 20% and of marginal significance. The urine had
a higher specific gravity at 300 ppm, but the volume produced in 24
hours was low. In the urine, red and white blood cells and amorphous
uric acid crystals were found more frequently in this group during the
last half year of the experiment. At the conclusion of the study, the
relative weight of spleen was decreased, while weights of adrenals,
lungs, brain pituitary and gonads were increased at 300 ppm in both
sexes. The relative weight of the liver was decreased in males only.
Histopathologically, the number of tumors at 300 ppm was decreased,
especially the mammary tumors. Thiometon was not carcinogenic and did
not induce any specific lesions in any organ at any dose level. A
no-effect level in this study is 2.5 ppm (Hamburger, et al., 1978).
COMMENTS
In 1973, a temporary acceptable daily intake of 0.005 mg/kg body
weight was established. The long-term study in rats, required by the
1977 Meeting and additional studies on metabolism in animals, a 2-year
study in dogs, and a 3-generation study in rats were reviewed.
Thiometon is almost completely absorbed in the rat and is excreted
rapidly, mainly in the urine.
In a 2-year dog study, a no-effect level was found to be 6 ppm in the
diet. In the long-term rat study, a no-effect level of 2.5 ppm was
observed. In both studies, the no-effect level was based on
cholinesterase inhibition. In a 3-generation reproduction study, it
was found that thiometon was not teratogenic and that 6.25 ppm in the
diet had a marginal effect on reproduction.
After evaluation of the available toxicological information, an ADI
was allocated.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing No Toxicological Effect
Rat: 2.5 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.12 mg/kg body weight
Dog: 6 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.15 mg/kg body weight
ESTIMATE OF ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE FOR MAN
0 - 0.003 mg/kg body weight
RESIDUES IN FOOD AND THEIR EVALUATION
USE PATTERNS
No additional information was received.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Reports of additional supervised trials on 19 crops in five countries
were available (Sandoz, 1979). Most of the residue trials were
carried out in India, while some other were carried out in Italy,
Australia, France and Switzerland. Of the crops studies the data
relative to 12 did not indicate a need for a change in any of the
previously recommended MRLs.
Of the remaining crops, the information supported additional MRLs for
mustard seed, rape seed and eggplant (See Recommendations). These
recommendations are based partly on similarities with other crops. No
information was available on "normal" or registered use patterns in
the countries where the trials were conducted. However, the
pre-harvest interval on these crops was not a factor in that residues
at no time exceeded the MRL level in the similar crops. On certain
other crops, substantial waiting periods would be required before
residues declined to MRL levels.
Table 1 contains a summary of the residues found in the supervised
trials for various crops. The residue values as reported by the
analyst are apparently the simple arithmetic sum of ppm thiometon
sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone which were determined separately.
In comparing these values to the recommended MRLs it should be noted
that the MRLs are based on measurement of the thiometon sulfone but
expressed as thiometon and excluding the P=O analogues.
Table 1. Thiometon residues in crops from supervised trials (formulated
product Ekatin 25 EC used in each trial)
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Cabbage 0.375 kg/ha 3 n.d. - 0.06 India
(1) 5 n.d
20 n.d.
Cauliflower 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.13-0.25 India
(1) 5 n.d - 0.03
10 n.d.
20 n.d.
Eggplant 0.375% 2 0.08 - 0.11 India
(1) 6 trace - 0.05
11 n.d.
20 n.d.
Okra 0.375% 3 trace - n.d. India
(1) 10 n.d. - 0.02
20 n.d.
0.375% 3 0.02 - 0.04 India
(1) 5 n.d.
20 n.d.
Tomatoes 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.08 India
(1) 10 n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.03 India
(1) 5 n.d.
Peach 0.03% 7 0.26 - 0.38 Italy
1 14 0.08 - 0.1
21 n.d. - 0.02
35 n.d.
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Grape 0.03% 13 0.8 Italy
(1) 28 0.2
40 0.11 - 0.16
63 0.08
Potatoes 0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
Sugarbeet 0.025% 0 Root: 0.22 - 0.12 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 4.95
28 Root: n.d.
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. - 0.05 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 0.23 - 0.7
28 Root. n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 1.4 - 2.6
28 Root: n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
Lucerne 98 g/ha 3 1.15 Australia
(1) 7 n.d.
14 n.d. - 0.02
24 n.d. - 0.02
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Lucerne 147 g/ha 7 trace - 0.02 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
220 g/ha 7 n.d. - 0.03 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
294 g/ha 7 0.09 Australia
(1) 14 0.03
24 0.09
Lupine 0.025% 7 0.24 Australia
(1) 28 0.03
0.05% 7 0.52 Australia
(1) 28 0.1
Rape 0.025% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
0.05% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
Wheat 243 g/ha 43 n.d. France
(1)
150 43 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 43 n.d.
(1)
240 66 n.d. France
(1)
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Wheat 150 66 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 66 n.d.
(1)
Rice 0.4375 kg/ha 41 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.4375 kg/ha 22 grain n.d.
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 43 grain n.d. India
(1) straw n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain (0.04 - 0.07)
(1) straw 0.02
Mustard 0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d.
(2)
Sorghum 0.375 kg/ha 31 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain n.d.
(1)
Groundnuts 0.375 kg/ha 56 n.d. India
(1)
n.d. = not detectable
"Thiometon residues" comprise thiometon, its sulfoxide and their
corresponding P=O analogues.
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The analytical method employed included a permangate oxidation
procedure which converts thiometon and thiometon sulfoxide to
thiometon sulfone along with P=O thiometon which is also measured as
the sulfone. It is probably the basic method evaluated by the 1976
Meeting (FAO/WHO, 1977) except for minor modifications, (e.g. in
certain trials acetone was identified as the extracting solvent rather
than acetonitrile). The limit of detection was 0.02 to 0.04 mg/kg for
each component depending on substrate. Residue values were reported
separately for thiometon sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone.
The residue components of thiometon are identical or similar to
several other pesticides including disulfoton, demeton-methyl, demeton
and phorate. These compounds would probably interfere with the
determination of thiometon. The method therefore has limited value as
a regulatory one.
APPRAISAL
A series of reports on additional supervised residue trials from five
countries tended to confirm previously recommended temporary MRLs for
twelve commodities, and permitted recommendation for three additional
MRLs.
RECOMMENDATIONS
An ADI having now been allocated, the temporary MRLs recommended by
the 1973 and 1976 Meetings can be converted to maximum residue limits.
The existing temporary MRL for chives was previously inserted by error
and should be deleted. In addition, maximum residue limits are
recommended for three new commodities listed below. The limits refer
to the sum of thiometon, thiometon sulfoxide, and thiometon sulfone
determined as thiometon sulfone and expressed as thiometon.
Commodity Maximum residue limit, mg/kg
Mustard seed 0.05*
Rape seed 0.05*
Eggplants 0.5
(* At or about limit of determination)
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION (in addition to items
previously listed)
Desirable
Further information on approved use patterns.
REFERENCES
Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - 3-Generation Study in Rats (including
Teratogenicity). (1978) Unpublished Data submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Hamburger, F., Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - Thiometon 2-year Feeding
Study in Dogs. (1978) Unpublished report submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Thiometon 2-year Feeding Study in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Tanner, P., Meier, J. and Schreier, E. - Thiometon. Pharmacokinetic
Studies with 14C-thiometon in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
TOXICOLOGICAL STUDIES
Special Study on Reproduction
In a standard 3-generation, 2 litter/generation reproduction study,
groups of 30 female and 30 male animals were fed diets containing 0,
1, 2.5 and 6.25 ppm thiometon. From the F1b, F2b, and F3b
generations, five pregnant females per group were killed for
teratological investigation. From 10 animals per sex in each dosage
group of the F3b generation, about 30 organs or tissues were studied
histopathologically.
In the 6.25 ppm group, the lactation index was lower in the F1b, F3b
and F3c litters, the viability index in the F2b and F3b litters, and
pup weight in the F2a and P3b litters. The number of stillborns was
somewhat higher in the F3a. There was no influence on the fertility
or the gestation indices, and no histopathological or teratogenic
abnormalities were found. It was concluded that 6.25 ppm had a
marginal effect on reproduction (Carpy and Klotzsche, 1978).
Short-term studies
Dog
Groups of 4 male and 4 female animals were fed for two years on diets
containing 0, 6, 12 or 48 ppm thiometon. Treatment of the test
animals did not affect general condition, behaviour, mortality,
ophthalmoscopic findings and organ weights. Growth, food consumption,
hematology, clinical chemistry, and urinalysis showed occasionally
abnormal values, but there was no dose-response relationship. The
main effect was noted as cholinesterase inhibition. At 48 ppm, a
statistically significant cholinesterase inhibition in plasma and RBC
was found in males and females at all times (after 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 13,
20 and 26 weeks and thereafter each 3 months). At 12 ppm, only the
male animals showed a significant cholinesterase inhibition in RBC.
Plasma cholinesterase in the 12 ppm group was slightly inhibited in
males and females, especially toward the end of the experiment. Brain
cholinesterase activity was reduced slightly at 48 ppm.
Histopathologically no dose-related effects were found. The dosage
level of 6 ppm was considered to be the no-effect level (Hamburger,
et al., 1978).
Long-Term Studies
Rat
Groups of 50 male and 50 female animals were fed for two years on
diets containing 0, 1, 2.5, 6.25, or 300 ppm thiometon. During the
first six weeks of the study, the diets contained 0, 0.2, 1,2 or 20
ppm, respectively. After 60 weeks, five rats of each sex per dose
group (with the exception of the 300 ppm group) were sacrificed.
Soon after increasing the dosage level to 300 ppm, the animals lost
weight and showed signs of acute poisoning (11 males and 14 females
died). Thereafter, mortality did not differ from other dosage groups.
At 300 ppm, the body weight remained low during the study. In this
group, a decreased food consumption and water intake was observed and
a number of hematological and clinical chemical parameters were
affected. In females, hemoglobin, MCV, and MCH were generally lower
during the study. Glucose, protein, and cholesterol levels were also
decreased while urea in blood was increased. The activities of SGPT
and alkaline phosphatase were increased. Cholinesterase activity in
plasma, RBC, brain and liver was strongly inhibited with 300 ppm. At
6.5 ppm, lower values for cholinesterase in plasma and RBC were
observed on some occasions. In the brain, a slight inhibition of
cholinesterase was noted in females. At 2.5 ppm, RBC cholinesterase
activity was reduced in both sexes on most occasions. This reduction
was always less than 20% and of marginal significance. The urine had
a higher specific gravity at 300 ppm, but the volume produced in 24
hours was low. In the urine, red and white blood cells and amorphous
uric acid crystals were found more frequently in this group during the
last half year of the experiment. At the conclusion of the study, the
relative weight of spleen was decreased, while weights of adrenals,
lungs, brain pituitary and gonads were increased at 300 ppm in both
sexes. The relative weight of the liver was decreased in males only.
Histopathologically, the number of tumors at 300 ppm was decreased,
especially the mammary tumors. Thiometon was not carcinogenic and did
not induce any specific lesions in any organ at any dose level. A
no-effect level in this study is 2.5 ppm (Hamburger, et al., 1978).
COMMENTS
In 1973, a temporary acceptable daily intake of 0.005 mg/kg body
weight was established. The long-term study in rats, required by the
1977 Meeting and additional studies on metabolism in animals, a 2-year
study in dogs, and a 3-generation study in rats were reviewed.
Thiometon is almost completely absorbed in the rat and is excreted
rapidly, mainly in the urine.
In a 2-year dog study, a no-effect level was found to be 6 ppm in the
diet. In the long-term rat study, a no-effect level of 2.5 ppm was
observed. In both studies, the no-effect level was based on
cholinesterase inhibition. In a 3-generation reproduction study, it
was found that thiometon was not teratogenic and that 6.25 ppm in the
diet had a marginal effect on reproduction.
After evaluation of the available toxicological information, an ADI
was allocated.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing No Toxicological Effect
Rat: 2.5 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.12 mg/kg body weight
Dog: 6 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 0.15 mg/kg body weight
ESTIMATE OF ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE FOR MAN
0 - 0.003 mg/kg body weight
RESIDUES IN FOOD AND THEIR EVALUATION
USE PATTERNS
No additional information was received.
RESIDUES RESULTING FROM SUPERVISED TRIALS
Reports of additional supervised trials on 19 crops in five countries
were available (Sandoz, 1979). Most of the residue trials were
carried out in India, while some other were carried out in Italy,
Australia, France and Switzerland. Of the crops studies the data
relative to 12 did not indicate a need for a change in any of the
previously recommended MRLs.
Of the remaining crops, the information supported additional MRLs for
mustard seed, rape seed and eggplant (See Recommendations). These
recommendations are based partly on similarities with other crops. No
information was available on "normal" or registered use patterns in
the countries where the trials were conducted. However, the
pre-harvest interval on these crops was not a factor in that residues
at no time exceeded the MRL level in the similar crops. On certain
other crops, substantial waiting periods would be required before
residues declined to MRL levels.
Table 1 contains a summary of the residues found in the supervised
trials for various crops. The residue values as reported by the
analyst are apparently the simple arithmetic sum of ppm thiometon
sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone which were determined separately.
In comparing these values to the recommended MRLs it should be noted
that the MRLs are based on measurement of the thiometon sulfone but
expressed as thiometon and excluding the P=O analogues.
Table 1. Thiometon residues in crops from supervised trials (formulated
product Ekatin 25 EC used in each trial)
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Cabbage 0.375 kg/ha 3 n.d. - 0.06 India
(1) 5 n.d
20 n.d.
Cauliflower 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.13-0.25 India
(1) 5 n.d - 0.03
10 n.d.
20 n.d.
Eggplant 0.375% 2 0.08 - 0.11 India
(1) 6 trace - 0.05
11 n.d.
20 n.d.
Okra 0.375% 3 trace - n.d. India
(1) 10 n.d. - 0.02
20 n.d.
0.375% 3 0.02 - 0.04 India
(1) 5 n.d.
20 n.d.
Tomatoes 0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.08 India
(1) 10 n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 3 0.02 - 0.03 India
(1) 5 n.d.
Peach 0.03% 7 0.26 - 0.38 Italy
1 14 0.08 - 0.1
21 n.d. - 0.02
35 n.d.
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Grape 0.03% 13 0.8 Italy
(1) 28 0.2
40 0.11 - 0.16
63 0.08
Potatoes 0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.25 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 22 n.d.
(2)
Sugarbeet 0.025% 0 Root: 0.22 - 0.12 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 4.95
28 Root: n.d.
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. - 0.05 Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 0.23 - 0.7
28 Root. n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
0.025% 0 Root: n.d. Switzerland
(1) Leaf: 1.4 - 2.6
28 Root: n.d. Switzerland
Leaf: n.d.
Lucerne 98 g/ha 3 1.15 Australia
(1) 7 n.d.
14 n.d. - 0.02
24 n.d. - 0.02
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Lucerne 147 g/ha 7 trace - 0.02 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
220 g/ha 7 n.d. - 0.03 Australia
(1) 14 n.d.
24 n.d.
294 g/ha 7 0.09 Australia
(1) 14 0.03
24 0.09
Lupine 0.025% 7 0.24 Australia
(1) 28 0.03
0.05% 7 0.52 Australia
(1) 28 0.1
Rape 0.025% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
0.05% 1 n.d. Australia
(1) 8 n.d.
15 n.d.
25 n.d.
Wheat 243 g/ha 43 n.d. France
(1)
150 43 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 43 n.d.
(1)
240 66 n.d. France
(1)
Table 1. Continued...
Rate
Crop (No. of Interval Residue Country
applications) (days)
Wheat 150 66 n.d. (grain)
(1)
100 66 n.d.
(1)
Rice 0.4375 kg/ha 41 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.4375 kg/ha 22 grain n.d.
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 43 grain n.d. India
(1) straw n.d.
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain (0.04 - 0.07)
(1) straw 0.02
Mustard 0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d. India
(2)
0.375 kg/ha 14 seed n.d.
(2)
Sorghum 0.375 kg/ha 31 grain n.d. India
(1)
0.375 kg/ha 26 grain n.d.
(1)
Groundnuts 0.375 kg/ha 56 n.d. India
(1)
n.d. = not detectable
"Thiometon residues" comprise thiometon, its sulfoxide and their
corresponding P=O analogues.
METHODS OF RESIDUE ANALYSIS
The analytical method employed included a permangate oxidation
procedure which converts thiometon and thiometon sulfoxide to
thiometon sulfone along with P=O thiometon which is also measured as
the sulfone. It is probably the basic method evaluated by the 1976
Meeting (FAO/WHO, 1977) except for minor modifications, (e.g. in
certain trials acetone was identified as the extracting solvent rather
than acetonitrile). The limit of detection was 0.02 to 0.04 mg/kg for
each component depending on substrate. Residue values were reported
separately for thiometon sulfone and P=O thiometon sulfone.
The residue components of thiometon are identical or similar to
several other pesticides including disulfoton, demeton-methyl, demeton
and phorate. These compounds would probably interfere with the
determination of thiometon. The method therefore has limited value as
a regulatory one.
APPRAISAL
A series of reports on additional supervised residue trials from five
countries tended to confirm previously recommended temporary MRLs for
twelve commodities, and permitted recommendation for three additional
MRLs.
RECOMMENDATIONS
An ADI having now been allocated, the temporary MRLs recommended by
the 1973 and 1976 Meetings can be converted to maximum residue limits.
The existing temporary MRL for chives was previously inserted by error
and should be deleted. In addition, maximum residue limits are
recommended for three new commodities listed below. The limits refer
to the sum of thiometon, thiometon sulfoxide, and thiometon sulfone
determined as thiometon sulfone and expressed as thiometon.
Commodity Maximum residue limit, mg/kg
Mustard seed 0.05*
Rape seed 0.05*
Eggplants 0.5
(* At or about limit of determination)
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION (in addition to items
previously listed)
Desirable
Further information on approved use patterns.
REFERENCES
Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - 3-Generation Study in Rats (including
Teratogenicity). (1978) Unpublished Data submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Hamburger, F., Carpy, S. and Klotzsche, C. - Thiometon 2-year Feeding
Study in Dogs. (1978) Unpublished report submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Thiometon 2-year Feeding Study in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
Tanner, P., Meier, J. and Schreier, E. - Thiometon. Pharmacokinetic
Studies with 14C-thiometon in Rats. (1978) Unpublished report
submitted by Sandoz Ltd.
