
FAO Meeting Report No. PL/1965/10/1
WHO/Food Add./27.65
EVALUATION OF THE TOXICITY OF PESTICIDE RESIDUES IN FOOD
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint Meeting of the FAO Committee on Pesticides in Agriculture and
the WHO Expert Committee on Pesticide Residues, which met in Rome,
15-22 March 19651
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1965
1 Report of the second joint meeting of the FAO Committee on
Pesticides in Agriculture and the WHO Expert Committee on Pesticide
Residues, FAO Meeting Report No. PL/1965/10; WHO/Food Add./26.65
ENDOSULFAN
Chemical name
6,7,8,9,10,10-hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-6,9-methano-
2,4,3- benzo(e) dioxathiepin-3-oxide, or 1,2,3,4,7,7,-
hexachlorobicyclo-(2,2,1)hepten-5,6-bisoxymethylene sulfite
chlorthiepin.
Synonym
Thiodan
Empirical formula
C9H6O3Cl6S
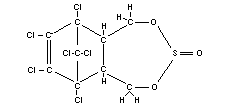
Structural formula
 BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
Endosulfan is rapidly absorbed from the intestinal tract and
about 30% of a lethal dose is eliminated during 24 hours in the rat
(Czech, 1958).
Acute toxicity (technical grade)
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 40-50 and 110* Hazleton Laboratories, 1957
Rat Intraperitoneal 8 Czech, 1958
* Dependent on the vehicle used.
Short-term studies
Rat. Rats tolerated daily 1.6-3.2 mg/kg body-weight orally for
12 weeks without any influence on growth-rate (Czech, 1958).
Dog. Endosulfan technical grade was administered daily in
gelatin capsules to 4 dogs for 5 days in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. Vomiting was observed in one dog and vomiting, tremors,
convulsions, rapid respiration, and mydriasis in 3 dogs (Hazleton
Laboratories, 1959a).
Three groups of dogs each consisting of 2 males and 2 females
were given endosulfan orally in gelatin capsules 6 days a week for one
year in doses corresponding to 0.075, 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg body-weight.
No signs of toxicity were observed. At autopsy gross and microscopic
examination of the tissues showed no difference between treated and
control animals (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959a).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 male and 25 female rats received 10, 30 and
100 ppm of endosulfan technical grade in the diet for 104 weeks.
Survival of the female rats in the 10- and 30-ppm group, was lower
than that of the female control group during the second year. In the
100-ppm female group, survival was significantly lower after 26 weeks
and abnormalities were observed in weight gain and on haematological
examinations. At autopsy the relative weight of the testes in the
10-ppm male group was significantly lower than in the control group.
Consistent histopathological findings were apparent only in the
100-ppm male group. In these the kidneys were enlarged and there were
signs of renal tubular damage with interstitial nephritis. Hydropic
cells were seen in the liver. The tumour incidence was within normal
range in all test groups (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959b).
Comments on experimental studies reported
The animal and biochemical studies are insufficient.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are inadequate to estimate an acceptable
intake for man.
Further work required
Investigation on the chemical nature and toxicity of the residue
occurring in the plant. Further long-term studies in rats and other
species, including reproduction studies. Determination of a no-effect
level in two species.
REFERENCES
Czech, M. (1958) Medizin u. Chemie., 6, 574
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 11 January 1957
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 12 May 1959a
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 22 May 1959b
BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
Endosulfan is rapidly absorbed from the intestinal tract and
about 30% of a lethal dose is eliminated during 24 hours in the rat
(Czech, 1958).
Acute toxicity (technical grade)
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 40-50 and 110* Hazleton Laboratories, 1957
Rat Intraperitoneal 8 Czech, 1958
* Dependent on the vehicle used.
Short-term studies
Rat. Rats tolerated daily 1.6-3.2 mg/kg body-weight orally for
12 weeks without any influence on growth-rate (Czech, 1958).
Dog. Endosulfan technical grade was administered daily in
gelatin capsules to 4 dogs for 5 days in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. Vomiting was observed in one dog and vomiting, tremors,
convulsions, rapid respiration, and mydriasis in 3 dogs (Hazleton
Laboratories, 1959a).
Three groups of dogs each consisting of 2 males and 2 females
were given endosulfan orally in gelatin capsules 6 days a week for one
year in doses corresponding to 0.075, 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg body-weight.
No signs of toxicity were observed. At autopsy gross and microscopic
examination of the tissues showed no difference between treated and
control animals (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959a).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 male and 25 female rats received 10, 30 and
100 ppm of endosulfan technical grade in the diet for 104 weeks.
Survival of the female rats in the 10- and 30-ppm group, was lower
than that of the female control group during the second year. In the
100-ppm female group, survival was significantly lower after 26 weeks
and abnormalities were observed in weight gain and on haematological
examinations. At autopsy the relative weight of the testes in the
10-ppm male group was significantly lower than in the control group.
Consistent histopathological findings were apparent only in the
100-ppm male group. In these the kidneys were enlarged and there were
signs of renal tubular damage with interstitial nephritis. Hydropic
cells were seen in the liver. The tumour incidence was within normal
range in all test groups (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959b).
Comments on experimental studies reported
The animal and biochemical studies are insufficient.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are inadequate to estimate an acceptable
intake for man.
Further work required
Investigation on the chemical nature and toxicity of the residue
occurring in the plant. Further long-term studies in rats and other
species, including reproduction studies. Determination of a no-effect
level in two species.
REFERENCES
Czech, M. (1958) Medizin u. Chemie., 6, 574
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 11 January 1957
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 12 May 1959a
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 22 May 1959b
 BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
Endosulfan is rapidly absorbed from the intestinal tract and
about 30% of a lethal dose is eliminated during 24 hours in the rat
(Czech, 1958).
Acute toxicity (technical grade)
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 40-50 and 110* Hazleton Laboratories, 1957
Rat Intraperitoneal 8 Czech, 1958
* Dependent on the vehicle used.
Short-term studies
Rat. Rats tolerated daily 1.6-3.2 mg/kg body-weight orally for
12 weeks without any influence on growth-rate (Czech, 1958).
Dog. Endosulfan technical grade was administered daily in
gelatin capsules to 4 dogs for 5 days in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. Vomiting was observed in one dog and vomiting, tremors,
convulsions, rapid respiration, and mydriasis in 3 dogs (Hazleton
Laboratories, 1959a).
Three groups of dogs each consisting of 2 males and 2 females
were given endosulfan orally in gelatin capsules 6 days a week for one
year in doses corresponding to 0.075, 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg body-weight.
No signs of toxicity were observed. At autopsy gross and microscopic
examination of the tissues showed no difference between treated and
control animals (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959a).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 male and 25 female rats received 10, 30 and
100 ppm of endosulfan technical grade in the diet for 104 weeks.
Survival of the female rats in the 10- and 30-ppm group, was lower
than that of the female control group during the second year. In the
100-ppm female group, survival was significantly lower after 26 weeks
and abnormalities were observed in weight gain and on haematological
examinations. At autopsy the relative weight of the testes in the
10-ppm male group was significantly lower than in the control group.
Consistent histopathological findings were apparent only in the
100-ppm male group. In these the kidneys were enlarged and there were
signs of renal tubular damage with interstitial nephritis. Hydropic
cells were seen in the liver. The tumour incidence was within normal
range in all test groups (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959b).
Comments on experimental studies reported
The animal and biochemical studies are insufficient.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are inadequate to estimate an acceptable
intake for man.
Further work required
Investigation on the chemical nature and toxicity of the residue
occurring in the plant. Further long-term studies in rats and other
species, including reproduction studies. Determination of a no-effect
level in two species.
REFERENCES
Czech, M. (1958) Medizin u. Chemie., 6, 574
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 11 January 1957
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 12 May 1959a
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 22 May 1959b
BIOLOGICAL DATA
Biochemical aspects
Endosulfan is rapidly absorbed from the intestinal tract and
about 30% of a lethal dose is eliminated during 24 hours in the rat
(Czech, 1958).
Acute toxicity (technical grade)
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 40-50 and 110* Hazleton Laboratories, 1957
Rat Intraperitoneal 8 Czech, 1958
* Dependent on the vehicle used.
Short-term studies
Rat. Rats tolerated daily 1.6-3.2 mg/kg body-weight orally for
12 weeks without any influence on growth-rate (Czech, 1958).
Dog. Endosulfan technical grade was administered daily in
gelatin capsules to 4 dogs for 5 days in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. Vomiting was observed in one dog and vomiting, tremors,
convulsions, rapid respiration, and mydriasis in 3 dogs (Hazleton
Laboratories, 1959a).
Three groups of dogs each consisting of 2 males and 2 females
were given endosulfan orally in gelatin capsules 6 days a week for one
year in doses corresponding to 0.075, 0.25 and 0.75 mg/kg body-weight.
No signs of toxicity were observed. At autopsy gross and microscopic
examination of the tissues showed no difference between treated and
control animals (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959a).
Long-term studies
Rat. Groups of 25 male and 25 female rats received 10, 30 and
100 ppm of endosulfan technical grade in the diet for 104 weeks.
Survival of the female rats in the 10- and 30-ppm group, was lower
than that of the female control group during the second year. In the
100-ppm female group, survival was significantly lower after 26 weeks
and abnormalities were observed in weight gain and on haematological
examinations. At autopsy the relative weight of the testes in the
10-ppm male group was significantly lower than in the control group.
Consistent histopathological findings were apparent only in the
100-ppm male group. In these the kidneys were enlarged and there were
signs of renal tubular damage with interstitial nephritis. Hydropic
cells were seen in the liver. The tumour incidence was within normal
range in all test groups (Hazleton Laboratories, 1959b).
Comments on experimental studies reported
The animal and biochemical studies are insufficient.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are inadequate to estimate an acceptable
intake for man.
Further work required
Investigation on the chemical nature and toxicity of the residue
occurring in the plant. Further long-term studies in rats and other
species, including reproduction studies. Determination of a no-effect
level in two species.
REFERENCES
Czech, M. (1958) Medizin u. Chemie., 6, 574
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 11 January 1957
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 12 May 1959a
Hazleton Laboratories, Falls Church, Virginia, United States of
America. Unpublished report of 22 May 1959b
