
PESTICIDE RESIDUES IN FOOD - 1982
Sponsored jointly by FAO and WHO
EVALUATIONS 1982
Data and recommendations of the joint meeting
of the FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide Residues
in Food and the Environment and the
WHO Expert Group on Pesticide Residues
Rome, 23 November - 2 December 1982
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Rome 1983
ENDOSULFAN
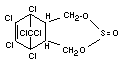 Explanation
Endosulfan was reviewed by the Joint Meetings of 1965, 1967 and
1968 (FAO/WHO 1965, 1968, 1969).1 An ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg bw was
recommended in 1968 based on additional data, e.g. a three-generation
reproduction study, reported by Industrial Bio-Test Laboratories (IBT)
in 1965.
The 1981 JMPR recommended that for compounds with no-effect
levels partly taken from IBT data, information should be used as a
partial basis for establishing no-effect levels, with the view to
recommending further action at future Joint Meetings. Replacement
study, independently obtained validation or additional data have not
been submitted to FAO/WHO. Accordingly the ADI for endosulfan was
re-evaluated.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE
COMMENTS
The 1967 JMPR was unable to set an ADI, pending evaluation of the
results on a reproduction study in rats. The reproduction study was
evaluated by the 1968 JMPR and an ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg body weight
was determined, based partly on the results of that study. However,
this study and a teratogenicity study were performed by IBT, and no
independently obtained validations, replacement studies or additional
data have been submitted to the JMPR. The long-term rat feeding study
and the one-year dog feeding study (Hazleton Laboratories 1959 a, b)
provide sufficient information on the chronic effects of endosulfan.
Endosulfan does not have cumulative properties, as determined
from biochemical evaluations in several species (FAO/WHO 1969). The
present ADI is therefore retained, but as a temporary ADI, pending
receipt of data validation and/or replacement studies for the non-
validated data.
1 See Annex 2 for WHO and FAO documentation.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing no Toxicological Effect
Rat : 30 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1.5 mg/kg bw
Dog : 0.75 mg/kg bw day
Estimate of Temporary Acceptable Daily Intake for Man
(Endosulfan A, endosulfan B and endosulfan sulphate)
0 - 0.008 mg/kg bw
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION
Required (by 1985)
1. A teratogenicity study in the rat.
2. A multi-generation reproduction study in the rat.
Desirable
Further information/observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Hazleton Laboratories. Report of 12 May 1959a submitted to the World
1959a Health Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
1959b Report of 22 May 1959b submitted to the World Health
Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
Explanation
Endosulfan was reviewed by the Joint Meetings of 1965, 1967 and
1968 (FAO/WHO 1965, 1968, 1969).1 An ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg bw was
recommended in 1968 based on additional data, e.g. a three-generation
reproduction study, reported by Industrial Bio-Test Laboratories (IBT)
in 1965.
The 1981 JMPR recommended that for compounds with no-effect
levels partly taken from IBT data, information should be used as a
partial basis for establishing no-effect levels, with the view to
recommending further action at future Joint Meetings. Replacement
study, independently obtained validation or additional data have not
been submitted to FAO/WHO. Accordingly the ADI for endosulfan was
re-evaluated.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE
COMMENTS
The 1967 JMPR was unable to set an ADI, pending evaluation of the
results on a reproduction study in rats. The reproduction study was
evaluated by the 1968 JMPR and an ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg body weight
was determined, based partly on the results of that study. However,
this study and a teratogenicity study were performed by IBT, and no
independently obtained validations, replacement studies or additional
data have been submitted to the JMPR. The long-term rat feeding study
and the one-year dog feeding study (Hazleton Laboratories 1959 a, b)
provide sufficient information on the chronic effects of endosulfan.
Endosulfan does not have cumulative properties, as determined
from biochemical evaluations in several species (FAO/WHO 1969). The
present ADI is therefore retained, but as a temporary ADI, pending
receipt of data validation and/or replacement studies for the non-
validated data.
1 See Annex 2 for WHO and FAO documentation.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing no Toxicological Effect
Rat : 30 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1.5 mg/kg bw
Dog : 0.75 mg/kg bw day
Estimate of Temporary Acceptable Daily Intake for Man
(Endosulfan A, endosulfan B and endosulfan sulphate)
0 - 0.008 mg/kg bw
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION
Required (by 1985)
1. A teratogenicity study in the rat.
2. A multi-generation reproduction study in the rat.
Desirable
Further information/observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Hazleton Laboratories. Report of 12 May 1959a submitted to the World
1959a Health Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
1959b Report of 22 May 1959b submitted to the World Health
Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
 Explanation
Endosulfan was reviewed by the Joint Meetings of 1965, 1967 and
1968 (FAO/WHO 1965, 1968, 1969).1 An ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg bw was
recommended in 1968 based on additional data, e.g. a three-generation
reproduction study, reported by Industrial Bio-Test Laboratories (IBT)
in 1965.
The 1981 JMPR recommended that for compounds with no-effect
levels partly taken from IBT data, information should be used as a
partial basis for establishing no-effect levels, with the view to
recommending further action at future Joint Meetings. Replacement
study, independently obtained validation or additional data have not
been submitted to FAO/WHO. Accordingly the ADI for endosulfan was
re-evaluated.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE
COMMENTS
The 1967 JMPR was unable to set an ADI, pending evaluation of the
results on a reproduction study in rats. The reproduction study was
evaluated by the 1968 JMPR and an ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg body weight
was determined, based partly on the results of that study. However,
this study and a teratogenicity study were performed by IBT, and no
independently obtained validations, replacement studies or additional
data have been submitted to the JMPR. The long-term rat feeding study
and the one-year dog feeding study (Hazleton Laboratories 1959 a, b)
provide sufficient information on the chronic effects of endosulfan.
Endosulfan does not have cumulative properties, as determined
from biochemical evaluations in several species (FAO/WHO 1969). The
present ADI is therefore retained, but as a temporary ADI, pending
receipt of data validation and/or replacement studies for the non-
validated data.
1 See Annex 2 for WHO and FAO documentation.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing no Toxicological Effect
Rat : 30 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1.5 mg/kg bw
Dog : 0.75 mg/kg bw day
Estimate of Temporary Acceptable Daily Intake for Man
(Endosulfan A, endosulfan B and endosulfan sulphate)
0 - 0.008 mg/kg bw
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION
Required (by 1985)
1. A teratogenicity study in the rat.
2. A multi-generation reproduction study in the rat.
Desirable
Further information/observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Hazleton Laboratories. Report of 12 May 1959a submitted to the World
1959a Health Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
1959b Report of 22 May 1959b submitted to the World Health
Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
Explanation
Endosulfan was reviewed by the Joint Meetings of 1965, 1967 and
1968 (FAO/WHO 1965, 1968, 1969).1 An ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg bw was
recommended in 1968 based on additional data, e.g. a three-generation
reproduction study, reported by Industrial Bio-Test Laboratories (IBT)
in 1965.
The 1981 JMPR recommended that for compounds with no-effect
levels partly taken from IBT data, information should be used as a
partial basis for establishing no-effect levels, with the view to
recommending further action at future Joint Meetings. Replacement
study, independently obtained validation or additional data have not
been submitted to FAO/WHO. Accordingly the ADI for endosulfan was
re-evaluated.
EVALUATION FOR ACCEPTABLE DAILY INTAKE
COMMENTS
The 1967 JMPR was unable to set an ADI, pending evaluation of the
results on a reproduction study in rats. The reproduction study was
evaluated by the 1968 JMPR and an ADI of 0-0.0075 mg/kg body weight
was determined, based partly on the results of that study. However,
this study and a teratogenicity study were performed by IBT, and no
independently obtained validations, replacement studies or additional
data have been submitted to the JMPR. The long-term rat feeding study
and the one-year dog feeding study (Hazleton Laboratories 1959 a, b)
provide sufficient information on the chronic effects of endosulfan.
Endosulfan does not have cumulative properties, as determined
from biochemical evaluations in several species (FAO/WHO 1969). The
present ADI is therefore retained, but as a temporary ADI, pending
receipt of data validation and/or replacement studies for the non-
validated data.
1 See Annex 2 for WHO and FAO documentation.
TOXICOLOGICAL EVALUATION
Level Causing no Toxicological Effect
Rat : 30 ppm in the diet, equivalent to 1.5 mg/kg bw
Dog : 0.75 mg/kg bw day
Estimate of Temporary Acceptable Daily Intake for Man
(Endosulfan A, endosulfan B and endosulfan sulphate)
0 - 0.008 mg/kg bw
FURTHER WORK OR INFORMATION
Required (by 1985)
1. A teratogenicity study in the rat.
2. A multi-generation reproduction study in the rat.
Desirable
Further information/observations in humans.
REFERENCES
Hazleton Laboratories. Report of 12 May 1959a submitted to the World
1959a Health Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
1959b Report of 22 May 1959b submitted to the World Health
Organization by Hazleton Laboratories. (Unpublished)
