
FAO Meeting Report No. PL/1965/10/1
WHO/Food Add./27.65
EVALUATION OF THE TOXICITY OF PESTICIDE RESIDUES IN FOOD
The content of this document is the result of the deliberations of the
Joint Meeting of the FAO Committee on Pesticides in Agriculture and
the WHO Expert Committee on Pesticide Residues, which met in Rome,
15-22 March 19651
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
World Health Organization
1965
1 Report of the second joint meeting of the FAO Committee on
Pesticides in Agriculture and the WHO Expert Committee on Pesticide
Residues, FAO Meeting Report No. PL/1965/10; WHO/Food Add./26.65
PHOSPHAMIDON
Chemical name
2-chloro-2-(diethyl-carbamoyl)-1-methyl-vinyl-dimethylphosphate;
dimethyl (1-methyl-2-chloro-2-miethylcarbamoyl-vinyl) phosphate;
dimethyl diethylamido-1-chlorocrotonyl (2) phosphate.
Empirical formula
C10H19O5NCIP
Structural formula
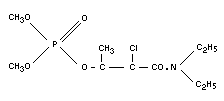 BIOLOGICAL DATA
In plants the metabolites of phosphamidon are
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl-dimethylphosphate,
alpha-chloroacetoacetic acid diethylamide, and alpha-chloroacetoacetic
acid monoethylamide. The first compound is of equal toxicity to
phosphamidon but the latter two compounds are less toxic after acute
oral administration (Anliker et al., 1961; Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Oral administration of 14C-labelled phosphamidon (3 mg/kg
body-weight) to 3 rats resulted within 24 hours in the excretion of
90%, and in 72 hours of 95%, of the administered radioactivity in the
urine, faeces and expired air. The excreted radioactive material
consisted neither of phosphamidon, des-ethylphosphamidon nor the
chloroacetoacetamides (Ciba).
Four rats were fed for 5 days on a diet containing 10 ppm of
14C-labelled phosphamidon and 2 oxen for 5 days on a diet containing
20 ppm. Neither phosphamidon nor any of its known metabolites could be
detected in tissue samples (Ciba). Mammary excretion of
cholinesterase-inhibitory substances was not found after the feeding
of 2 cows with grass which had been sprayed with phosphamidon (Ciba).
In vitro the I50 in 60 minutes for rat brain cholinesterase was
observed at concentrations 7 × 10-5 g/ml and for horse serum
cholinesterase at 5.8 × 10-7 g/ml phosphamidon (Jaques Bein, 1960).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 17-20 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Klotzsche, 1958
Subcutaneous 26 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Mouse Oral 13 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Intravenous 6 Jaques & Bein, 1960
The LD50 of the metabolite
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-dimethyl-phosphate after oral
administration in the mouse was 15 mg/kg body-weight, and in the rat
25 mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Short-term studies
Rat. Three groups each of 5 male rats were given a daily oral
dose of phosphamidon (83%) in an unnamed emulsifier by stomach-tube.
All animals survived a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg body-weight for 10 weeks.
At doses of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight all the rats died after 1-33
days. Oral administration of 20% phosphamidon in isopropanol killed
one of 5 rats during the 10-week period at a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. At dosages of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight, all rats died
within 41 days. Haematological examination showed a reduction of
lymphocytes and eosinophils, while the number of neutrophils was
increased (Klotzsche, 1958).
Four groups of 5 rats each were given 0.3 and 3.0 mg/kg
body-weight phosphamidon daily by stomach-tube in propylene glycol.
Rats in the groups receiving 0.3 mg/kg body-weight were killed after
1, 7, 14 and 21 days for determination of cholinesterase activity in
serum and brain. No significant inhibition of the serum and brain
cholinesterase activity was observed. A daily dose of 3 mg/kg
body-weight did result in 14% reduction of serum cholinesterase
activity and 12.5% of brain cholinesterase activity after one dose,
while treatment for 7 days lowered the serum cholinesterase activity
to 42.5% and the brain cholinesterase activity to 55%. After 14 days'
treatment, the inhibition was 37% in serum and 67.5% in the brain. One
group of 5 rats treated for 14 days was left undosed for an additional
7 days. In this group serum cholinesterase activity was only slightly
inhibited while the brain cholinesterase activity was still 47.5%
lower than control values (Jaques & Bein, 1960). Subcutaneous daily
injections at a dose of 4 mg/kg body-weight were tolerated by 5 rats
for 21 days. Subcutaneous injections of 10 mg/kg body-weight killed
all rats within 4 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
The metabolite 2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-
dimethylphosphate given orally daily to groups of 6 rats in a dose of
3 mg/kg body-weight killed one rat on the eighth day; a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight killed all rats within 9 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Rabbit. In a 21-day experiment 2 of 3 rabbits survived a daily
oral dose of 3.5 mg/kg body-weight; 7 mg/kg killed 2 of 3 animals
within 8 days, and 15 mg/kg body-weight all 5 within 7 days.
Intravenous injections daily for 14 days were survived by 3 rabbits at
a dose of 3 mg/kg body-weight, while 2 out of 3 died at a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Long-term studies
No data available.
Comments on the experimental studies reported
The studies reported have been carried out exclusively on
rodents, are of very short duration and comprise small numbers of
animals.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are considered to be insufficient to
enable an acceptable daily intake for man to be evaluated.
Further work required
Chemical composition and toxicity of the residues. Observations
on the effect in man. Reproduction studies in the rat.
REFERENCES
Anliker, R., Beriger, E., Geiger, M., & Schmid, K. (1961) Helv.
chim. Acta, 44, 162
CIBA Ltd., Basel. Investigation on the excretion of phosphamidon by
rats and cattle given single doses or diets containing
14C-labelled phosphamidon. Unpublished report
Jaques, R. & Bein, H. J. (1960) Arch. Toxicol., 18, 316
Klotzsche, C. (1958) Nachr. Deutsch. Pflanzenschutzd., 10, 60
BIOLOGICAL DATA
In plants the metabolites of phosphamidon are
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl-dimethylphosphate,
alpha-chloroacetoacetic acid diethylamide, and alpha-chloroacetoacetic
acid monoethylamide. The first compound is of equal toxicity to
phosphamidon but the latter two compounds are less toxic after acute
oral administration (Anliker et al., 1961; Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Oral administration of 14C-labelled phosphamidon (3 mg/kg
body-weight) to 3 rats resulted within 24 hours in the excretion of
90%, and in 72 hours of 95%, of the administered radioactivity in the
urine, faeces and expired air. The excreted radioactive material
consisted neither of phosphamidon, des-ethylphosphamidon nor the
chloroacetoacetamides (Ciba).
Four rats were fed for 5 days on a diet containing 10 ppm of
14C-labelled phosphamidon and 2 oxen for 5 days on a diet containing
20 ppm. Neither phosphamidon nor any of its known metabolites could be
detected in tissue samples (Ciba). Mammary excretion of
cholinesterase-inhibitory substances was not found after the feeding
of 2 cows with grass which had been sprayed with phosphamidon (Ciba).
In vitro the I50 in 60 minutes for rat brain cholinesterase was
observed at concentrations 7 × 10-5 g/ml and for horse serum
cholinesterase at 5.8 × 10-7 g/ml phosphamidon (Jaques Bein, 1960).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 17-20 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Klotzsche, 1958
Subcutaneous 26 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Mouse Oral 13 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Intravenous 6 Jaques & Bein, 1960
The LD50 of the metabolite
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-dimethyl-phosphate after oral
administration in the mouse was 15 mg/kg body-weight, and in the rat
25 mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Short-term studies
Rat. Three groups each of 5 male rats were given a daily oral
dose of phosphamidon (83%) in an unnamed emulsifier by stomach-tube.
All animals survived a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg body-weight for 10 weeks.
At doses of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight all the rats died after 1-33
days. Oral administration of 20% phosphamidon in isopropanol killed
one of 5 rats during the 10-week period at a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. At dosages of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight, all rats died
within 41 days. Haematological examination showed a reduction of
lymphocytes and eosinophils, while the number of neutrophils was
increased (Klotzsche, 1958).
Four groups of 5 rats each were given 0.3 and 3.0 mg/kg
body-weight phosphamidon daily by stomach-tube in propylene glycol.
Rats in the groups receiving 0.3 mg/kg body-weight were killed after
1, 7, 14 and 21 days for determination of cholinesterase activity in
serum and brain. No significant inhibition of the serum and brain
cholinesterase activity was observed. A daily dose of 3 mg/kg
body-weight did result in 14% reduction of serum cholinesterase
activity and 12.5% of brain cholinesterase activity after one dose,
while treatment for 7 days lowered the serum cholinesterase activity
to 42.5% and the brain cholinesterase activity to 55%. After 14 days'
treatment, the inhibition was 37% in serum and 67.5% in the brain. One
group of 5 rats treated for 14 days was left undosed for an additional
7 days. In this group serum cholinesterase activity was only slightly
inhibited while the brain cholinesterase activity was still 47.5%
lower than control values (Jaques & Bein, 1960). Subcutaneous daily
injections at a dose of 4 mg/kg body-weight were tolerated by 5 rats
for 21 days. Subcutaneous injections of 10 mg/kg body-weight killed
all rats within 4 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
The metabolite 2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-
dimethylphosphate given orally daily to groups of 6 rats in a dose of
3 mg/kg body-weight killed one rat on the eighth day; a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight killed all rats within 9 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Rabbit. In a 21-day experiment 2 of 3 rabbits survived a daily
oral dose of 3.5 mg/kg body-weight; 7 mg/kg killed 2 of 3 animals
within 8 days, and 15 mg/kg body-weight all 5 within 7 days.
Intravenous injections daily for 14 days were survived by 3 rabbits at
a dose of 3 mg/kg body-weight, while 2 out of 3 died at a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Long-term studies
No data available.
Comments on the experimental studies reported
The studies reported have been carried out exclusively on
rodents, are of very short duration and comprise small numbers of
animals.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are considered to be insufficient to
enable an acceptable daily intake for man to be evaluated.
Further work required
Chemical composition and toxicity of the residues. Observations
on the effect in man. Reproduction studies in the rat.
REFERENCES
Anliker, R., Beriger, E., Geiger, M., & Schmid, K. (1961) Helv.
chim. Acta, 44, 162
CIBA Ltd., Basel. Investigation on the excretion of phosphamidon by
rats and cattle given single doses or diets containing
14C-labelled phosphamidon. Unpublished report
Jaques, R. & Bein, H. J. (1960) Arch. Toxicol., 18, 316
Klotzsche, C. (1958) Nachr. Deutsch. Pflanzenschutzd., 10, 60
 BIOLOGICAL DATA
In plants the metabolites of phosphamidon are
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl-dimethylphosphate,
alpha-chloroacetoacetic acid diethylamide, and alpha-chloroacetoacetic
acid monoethylamide. The first compound is of equal toxicity to
phosphamidon but the latter two compounds are less toxic after acute
oral administration (Anliker et al., 1961; Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Oral administration of 14C-labelled phosphamidon (3 mg/kg
body-weight) to 3 rats resulted within 24 hours in the excretion of
90%, and in 72 hours of 95%, of the administered radioactivity in the
urine, faeces and expired air. The excreted radioactive material
consisted neither of phosphamidon, des-ethylphosphamidon nor the
chloroacetoacetamides (Ciba).
Four rats were fed for 5 days on a diet containing 10 ppm of
14C-labelled phosphamidon and 2 oxen for 5 days on a diet containing
20 ppm. Neither phosphamidon nor any of its known metabolites could be
detected in tissue samples (Ciba). Mammary excretion of
cholinesterase-inhibitory substances was not found after the feeding
of 2 cows with grass which had been sprayed with phosphamidon (Ciba).
In vitro the I50 in 60 minutes for rat brain cholinesterase was
observed at concentrations 7 × 10-5 g/ml and for horse serum
cholinesterase at 5.8 × 10-7 g/ml phosphamidon (Jaques Bein, 1960).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 17-20 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Klotzsche, 1958
Subcutaneous 26 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Mouse Oral 13 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Intravenous 6 Jaques & Bein, 1960
The LD50 of the metabolite
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-dimethyl-phosphate after oral
administration in the mouse was 15 mg/kg body-weight, and in the rat
25 mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Short-term studies
Rat. Three groups each of 5 male rats were given a daily oral
dose of phosphamidon (83%) in an unnamed emulsifier by stomach-tube.
All animals survived a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg body-weight for 10 weeks.
At doses of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight all the rats died after 1-33
days. Oral administration of 20% phosphamidon in isopropanol killed
one of 5 rats during the 10-week period at a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. At dosages of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight, all rats died
within 41 days. Haematological examination showed a reduction of
lymphocytes and eosinophils, while the number of neutrophils was
increased (Klotzsche, 1958).
Four groups of 5 rats each were given 0.3 and 3.0 mg/kg
body-weight phosphamidon daily by stomach-tube in propylene glycol.
Rats in the groups receiving 0.3 mg/kg body-weight were killed after
1, 7, 14 and 21 days for determination of cholinesterase activity in
serum and brain. No significant inhibition of the serum and brain
cholinesterase activity was observed. A daily dose of 3 mg/kg
body-weight did result in 14% reduction of serum cholinesterase
activity and 12.5% of brain cholinesterase activity after one dose,
while treatment for 7 days lowered the serum cholinesterase activity
to 42.5% and the brain cholinesterase activity to 55%. After 14 days'
treatment, the inhibition was 37% in serum and 67.5% in the brain. One
group of 5 rats treated for 14 days was left undosed for an additional
7 days. In this group serum cholinesterase activity was only slightly
inhibited while the brain cholinesterase activity was still 47.5%
lower than control values (Jaques & Bein, 1960). Subcutaneous daily
injections at a dose of 4 mg/kg body-weight were tolerated by 5 rats
for 21 days. Subcutaneous injections of 10 mg/kg body-weight killed
all rats within 4 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
The metabolite 2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-
dimethylphosphate given orally daily to groups of 6 rats in a dose of
3 mg/kg body-weight killed one rat on the eighth day; a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight killed all rats within 9 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Rabbit. In a 21-day experiment 2 of 3 rabbits survived a daily
oral dose of 3.5 mg/kg body-weight; 7 mg/kg killed 2 of 3 animals
within 8 days, and 15 mg/kg body-weight all 5 within 7 days.
Intravenous injections daily for 14 days were survived by 3 rabbits at
a dose of 3 mg/kg body-weight, while 2 out of 3 died at a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Long-term studies
No data available.
Comments on the experimental studies reported
The studies reported have been carried out exclusively on
rodents, are of very short duration and comprise small numbers of
animals.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are considered to be insufficient to
enable an acceptable daily intake for man to be evaluated.
Further work required
Chemical composition and toxicity of the residues. Observations
on the effect in man. Reproduction studies in the rat.
REFERENCES
Anliker, R., Beriger, E., Geiger, M., & Schmid, K. (1961) Helv.
chim. Acta, 44, 162
CIBA Ltd., Basel. Investigation on the excretion of phosphamidon by
rats and cattle given single doses or diets containing
14C-labelled phosphamidon. Unpublished report
Jaques, R. & Bein, H. J. (1960) Arch. Toxicol., 18, 316
Klotzsche, C. (1958) Nachr. Deutsch. Pflanzenschutzd., 10, 60
BIOLOGICAL DATA
In plants the metabolites of phosphamidon are
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methylvinyl-dimethylphosphate,
alpha-chloroacetoacetic acid diethylamide, and alpha-chloroacetoacetic
acid monoethylamide. The first compound is of equal toxicity to
phosphamidon but the latter two compounds are less toxic after acute
oral administration (Anliker et al., 1961; Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Oral administration of 14C-labelled phosphamidon (3 mg/kg
body-weight) to 3 rats resulted within 24 hours in the excretion of
90%, and in 72 hours of 95%, of the administered radioactivity in the
urine, faeces and expired air. The excreted radioactive material
consisted neither of phosphamidon, des-ethylphosphamidon nor the
chloroacetoacetamides (Ciba).
Four rats were fed for 5 days on a diet containing 10 ppm of
14C-labelled phosphamidon and 2 oxen for 5 days on a diet containing
20 ppm. Neither phosphamidon nor any of its known metabolites could be
detected in tissue samples (Ciba). Mammary excretion of
cholinesterase-inhibitory substances was not found after the feeding
of 2 cows with grass which had been sprayed with phosphamidon (Ciba).
In vitro the I50 in 60 minutes for rat brain cholinesterase was
observed at concentrations 7 × 10-5 g/ml and for horse serum
cholinesterase at 5.8 × 10-7 g/ml phosphamidon (Jaques Bein, 1960).
Acute toxicity
Animal Route LD50 mg/kg References
body-weight
Rat Oral 17-20 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Klotzsche, 1958
Subcutaneous 26 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Mouse Oral 13 Jaques & Bein, 1960
Intravenous 6 Jaques & Bein, 1960
The LD50 of the metabolite
2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-dimethyl-phosphate after oral
administration in the mouse was 15 mg/kg body-weight, and in the rat
25 mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Short-term studies
Rat. Three groups each of 5 male rats were given a daily oral
dose of phosphamidon (83%) in an unnamed emulsifier by stomach-tube.
All animals survived a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg body-weight for 10 weeks.
At doses of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight all the rats died after 1-33
days. Oral administration of 20% phosphamidon in isopropanol killed
one of 5 rats during the 10-week period at a dosage of 2.5 mg/kg
body-weight. At dosages of 5.0 and 10 mg/kg body-weight, all rats died
within 41 days. Haematological examination showed a reduction of
lymphocytes and eosinophils, while the number of neutrophils was
increased (Klotzsche, 1958).
Four groups of 5 rats each were given 0.3 and 3.0 mg/kg
body-weight phosphamidon daily by stomach-tube in propylene glycol.
Rats in the groups receiving 0.3 mg/kg body-weight were killed after
1, 7, 14 and 21 days for determination of cholinesterase activity in
serum and brain. No significant inhibition of the serum and brain
cholinesterase activity was observed. A daily dose of 3 mg/kg
body-weight did result in 14% reduction of serum cholinesterase
activity and 12.5% of brain cholinesterase activity after one dose,
while treatment for 7 days lowered the serum cholinesterase activity
to 42.5% and the brain cholinesterase activity to 55%. After 14 days'
treatment, the inhibition was 37% in serum and 67.5% in the brain. One
group of 5 rats treated for 14 days was left undosed for an additional
7 days. In this group serum cholinesterase activity was only slightly
inhibited while the brain cholinesterase activity was still 47.5%
lower than control values (Jaques & Bein, 1960). Subcutaneous daily
injections at a dose of 4 mg/kg body-weight were tolerated by 5 rats
for 21 days. Subcutaneous injections of 10 mg/kg body-weight killed
all rats within 4 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
The metabolite 2-chloro-2-ethylcarbamoyl-1-methyl-vinyl-
dimethylphosphate given orally daily to groups of 6 rats in a dose of
3 mg/kg body-weight killed one rat on the eighth day; a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight killed all rats within 9 days (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Rabbit. In a 21-day experiment 2 of 3 rabbits survived a daily
oral dose of 3.5 mg/kg body-weight; 7 mg/kg killed 2 of 3 animals
within 8 days, and 15 mg/kg body-weight all 5 within 7 days.
Intravenous injections daily for 14 days were survived by 3 rabbits at
a dose of 3 mg/kg body-weight, while 2 out of 3 died at a dose of 7.5
mg/kg body-weight (Jaques & Bein, 1960).
Long-term studies
No data available.
Comments on the experimental studies reported
The studies reported have been carried out exclusively on
rodents, are of very short duration and comprise small numbers of
animals.
EVALUATION
The toxicological data are considered to be insufficient to
enable an acceptable daily intake for man to be evaluated.
Further work required
Chemical composition and toxicity of the residues. Observations
on the effect in man. Reproduction studies in the rat.
REFERENCES
Anliker, R., Beriger, E., Geiger, M., & Schmid, K. (1961) Helv.
chim. Acta, 44, 162
CIBA Ltd., Basel. Investigation on the excretion of phosphamidon by
rats and cattle given single doses or diets containing
14C-labelled phosphamidon. Unpublished report
Jaques, R. & Bein, H. J. (1960) Arch. Toxicol., 18, 316
Klotzsche, C. (1958) Nachr. Deutsch. Pflanzenschutzd., 10, 60
